Abstract
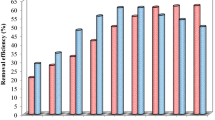
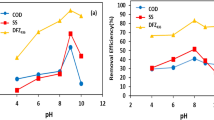
Chemical coagulation was used to remove the compounds present in wastewater from dye manufacturing industry. The character of wastewater was determined. Most compounds found in the wastewater are phenol derivatives, aniline derivatives, organic acid and benzene derivatives, output from dye manufacturing. Various polyferric chloride coagulants were investigated. Results showed that high extent of Fe(III) hydrolysis was not always suited for chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal in our wastewater, that electrostatic interaction between flocs and organic contaminants played an important role in removal of organic contaminants, that copolymers of Al(III), Si(IV) and Fe(III) were helpful for high flocculating effect, that COD removal efficiency of poly-silicate-aluminium-ferric chloride (PSAFC) and polyferric chloride (PFC) coagulant increased with increasing dose of coagulants, and that the performance of PSAFC and PFC coagulants was superior to PAC coagulant. This difference in efficiency may also be attributed to the copolymers of Si(IV), Al(III) and Fe(III). However, compared with PFC, PSAFC can easily reach high COD removal efficiency below coagulant dose 0.3 g/L. Thus, from the economic point of view, PSAFC is more suitable for treatment of wastewater effluent from dye manufacturing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Degs, Y., Khraishen, M.A.M., Allenand, S.J., Ahmad, M.N., 2000. Effect of carbon surface chemistry on the removal of reactive dyes from textile effluent. Wat. Res., 34(3):927–935.
APHA, 1980. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (16th Ed.). American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C.
Arslan, I., 2001. Treatability of a simulated disperse dye-bath by ferrous iron coagulation, ozonation, and ferrous iron-catalyzed ozonation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B85:229–241.
Cheng, W.P., 2001. Hydrolysis characteristic of polyferric sulphate coagulant and its optimal condition of preparation. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 182:57–63.
Cheng, W.P., Chi, F.H., 2002. A study of coagulation mechanisms of polyferric sulphate reacting with humic acid using a fluorescence-quenching method. Wat. Res., 36:4583–4591.
Huang, S., Liu, G., Li, H., Hu, Y., 2004. Study of coagulant interaction in treatment of pulping waste water by using PAC and PFS together. J. Huanzhong Univ. of Sci. & Tech. (Nature Science Edition), 32(3):51–53.
Jiang, J., Graham, N.J.D., 1998. Preliminary evaluation of the performance of new pre-polymerised inorganic coagulants for lowland surface water treatment. Wat. Res., 37(2):121–128.
Kim, T.K., Park, C., Shin, E., Kim, S., 2004. Decolorization of disperse and reactive dye solutions using ferric chloride. Desalination, 161:49–58.
Liu, Y.J., Jiang, X.Z., 2005. Phenol degradation by a nonpulsed diaphragm glow discharge in an aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Technol., 39(21):8512–8517.
Sarasa, J., Roche, M.P., Ormad, M.P., Gimeno, E., Puig, A., Ovelleiro, J.L., 1998. Treatment of a wastewater resulting from dyes manufacturing with ozone and chemical coagulation. Wat. Res., 32(9):2721–2727.
Tang, H., 1990. Basic researches on inorganic polymer flocculant. Environmental Chemistry, 10:1–12.
Wang, D., Tang, H., 2001. Modified inorganic polymer flocculant-PFSi: its preparation, characterization and coagulation behavior. Wat. Res., 35(14):3418–3428.
Wang, H., Meng, J., Luan, Z., Liu, W., 2003. Study on the stability and species distribution of inorganic polymer flocculant-polyferric chloride by basification. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 30(4):449–452 (in Chinese).
Wen, Y.Z., Liu, W.Q., Fang, Z.H., Liu, W.P., 2005. Effect of adsorption interferents on removal of reactive red 195 dye in wastewater by chitosan. Journal of Environmental Science—China, 17(5):766–769.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Key Open-end Fund of Zheijiang University of Technology and State Key Laboratory Breeding Base of Green Chemistry-Synthesis Technology in Zhejiang University of Technology, Zhejiang Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Yl., Wen, Yz., Li, Xy. et al. Treatment of wastewater from dye manufacturing industry by coagulation. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. A 7 (Suppl 2), 340–344 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.AS0340
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.AS0340