Abstract
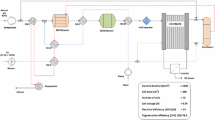
The electrical and thermal performances of a simulated 60 kW Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) cogeneration system are first analyzed and then strategies to make the system operation stable and efficient are developed. The system configuration is described first, and then the power response and coordination strategy are presented on the basis of the electricity model. Two different thermal models are used to estimate the thermal performance of this cogeneration system, and heat management is discussed. Based on these system designs, the 60 kW PEMFC cogeneration system is analyzed in detail. The analysis results will be useful for further study and development of the system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amphlett, J.C., Baumert, R.M., Harris, T.J., Mann, R.F., Reppley, B.A., Roberge, P.R., 1995a. Performance modeling of the Ballard Mark IV solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell I. Mechanistic model development. J. Electrochem. Soc., 142(1):1–8.
Amphlett, J.C., Baumert, R.M., Harris, T.J., Mann, R.F., Peppley, B.A., Roberge, P.R., 1995b. Performance modeling of the Ballard Mark IV solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell II. Empirical model development. J. Electrochem. Soc., 142(1):9–15.
DOE NETL (US Department of Energy, National Energy Technology Laboratory), 2002. Grid-independent, Residential Fuel-cell Conceptual Design and Cost Estimate. Final Report for DOE NETL in Subcontract to Parsons Infrastructure & Technology Group, Inc.
Dutta, S., Shimpalee, S., van Zee, J.W., 2001. Numerical prediction of mass-exchange between cathode and anode channels in a PEM fuel cell. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 44(11):2029–2042. [doi:10.1016/S0017-9310(00)00257-X]
Ferguson, A., Ugursal, V.I., 2004. Fuel cell modeling for building cogeneration applications. Journal of Power Sources, 137(1):30–42.
Ferguson, A., Beausoleil-Morrison, I., Ugursal, V.I., 2003. A Comparative Assessment of Fuel Cell Cogeneration Heat Recovery Models. Proceedings of Building Simulation 2003, The Eighth International IBPSA Conference.
Gunes, M.B., 2001. Investigation of a Fuel Cell Based Total Energy System for Residential Applications. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University.
Hawkes, A., Leach, M., 2005. Impacts of temporal precision in optimisation modelling of micro-combined heat and power. Energy, 30(10):1759–1779. [doi:10.1016/j.energy.2004.11.012].
Kim, J., Lee, S., Srinivasan, S., Chamberlin, C.E., 1995. Modeling of proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance with an empirical equation. J. Elelctrochem. Soc., 142(8):2670–2674.
Pukrushpan, J.T., Peng, H., Stefanopoulou, A.G., 2004. Control-oriented modeling and analysis for automotive fuel cell systems. Journal of Dynamic Systems Measurement, and Control, 126(1):14–25. [doi:10.1115/1.1648308]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project (No. 2002AA517020) supported by the Hi-Tech Research and Development Program (863) of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Yy., Yu, Qc., Cao, Gy. et al. Research on a simulated 60 kW PEMFC cogeneration system for domestic application. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. A 7, 450–457 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.A0450
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.A0450