Abstract
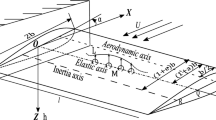
As the span length of suspension bridges increases, the diameter of cables and thus the wind load acting on them, the nonlinear wind-structure interaction and the wind speed spatial non-uniformity all increase consequently, which may have unnegligible influence on the aerostatic behavior of long-span suspension bridges. In this work, a method of advanced aerostatic analysis is presented firstly by considering the geometric nonlinearity, the nonlinear wind-structures and wind speed spatial non-uniformity. By taking the Runyang Bridge over the Yangtze River as example, effects of the nonlinear wind-structure interaction, wind speed spatial non-uniformity, and the cable’s wind load on the aerostatic behavior of the bridge are investigated analytically. The results showed that these factors all have important influence on the aerostatic behavior, and should be considered in the aerostatic analysis of long and particularly super long-span suspension bridges.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astiz, M.A., 1998. Flutter stability of very long suspension bridges. Journal of Bridge Engineering, ASCE, 3(3):132–139. [doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(1998)3:3(132)]
Boonyapinyo, V., Yamada, H., Miyata, T., 1994. Wind-induced nonlinear lateral-torsional buckling of cable-stayed bridges. J. Struct. Engrg., ASCE, 120(2):486–506.
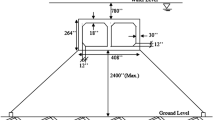
Chen, A.R., Song, J.Z., 2000. Research on the wind resistance of Runyang Bridge over the Yangtze River. The Key Laboratory for Disaster Reduction in Civil Engineering, Tongji University (in Chinese).
Cheng, J., Jiang, J.J., Xiao, R.C., Xiang, H.F., 2002. Nonlinear aerostatic stability analysis of Jiang Yin suspension bridge. Engineering Structures, 24(6):773–781. [doi: 10.1016/S0141-0296(02)00006-8]
Xiang, H.F., Chen, A.R., 1998. 21st Century Long-span Bridges in China. In: Larsen, A., Esdah, S. (Eds.), Bridge Aerodymics. Balkema, Rotterdam.
Xiang, H.F., Lin, Z.X., Bao, W.G., Chen, A.R., Gu, M. (Eds.), 1996. Wind-resistant Design Guidebook for Highway Bridges. People’s Communication Press, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
Xiao, R.C., Chen, J., 2004. Advanced aerostatic stability analysis of suspension bridges. Wind and Structures, 7(1):55–70.
Xie, Q.M., Xiang, H.F., 1985. Three flutter analysis for bridges by state-space approach. Journal of Tongji University, 3:1–13.
Zhang, X.J., Sun, B.N., Xiang, H.F., 2002. Nonlinear aerostatic and aerodynamic analysis of long-span suspension bridges considering wind-structure interactions. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 90(9):1065–1080. [doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(02)00251-9]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project (No. 502118) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Xj. Advanced aerostatic analysis of long-span suspension bridges. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. A 7, 424–429 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.A0424
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.A0424