Abstract
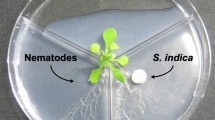
Four rhizobacteria selected out of over 500 isolates from rhizosphere of the vegetables in China were further studied for suppression of the root-knot nematode and soil-borne fungal pathogens in laboratory and greenhouse in Belgium. They were identified as Brevibacillus brevis or Bacillus subtilis by Biolog test and partial 16s rDNA sequence comparison. They not only inhibited the radial growth of the root-infecting fungi Rhizoctonia solani SX-6, Pythium aphanidermatum ZJP-1 and Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cucumerinum ZJF-2 in vitro, but also exhibited strong nematicidal activity by killing the second stage larvae of Meloidogyne javanica to varying degrees in the greenhouse. The toxic principles of bacterium B7 that showed the highest juvenile mortality were partially characterized. The active factors were heat stability and resistance to extreme pH values. B7 used either as seed dressing or soil drench significantly reduced the nematode populations in the rhizosphere and enhanced the growth of mungbean plants over the controls in the presence or absence of R. solani.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, N.I., Siddiqui, I.A., Shaukat, S.S., Zaki, M.J., 2002. Nematicidal activity of some strains ofPseudomonas spp.Soil Biology & Biochemistry,34:1051–1058.
Ausubel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., Struhl, K., 1992. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley Interscience, New York.
Davies, P.J., 1987. The Plant Hormones: Their Nature, Occurrence, and Functions.In: Davies, P.J. (Ed.), Plant Hormones and Their Role in Plant Growth and Development. Martinus-Nijhoff Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, p. 1–11.
De Weert, S., Vermeiren, H., Mulders, I.H.M., Kuiper, I., Hendrickx, N., Bloemberg, G.V., Vanderleyden, J., De Mot, R., Lugtenberg, B.J.J., 2002. Flagella-driven chemotaxis towards exudates components is an important trait for tomato root colonization byPseudomonas fluorescens.Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions,15(11):1173–1180.
Han, R.Y., Min, H., Cheng, Z.Q., Liu, L.H., 2002. Phenotypic characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of crude oil degrading bacteria.Biodiversity Science,10(2):202–207 (in Chinese).
Johnsson, L., Hökeberg, M., Gerhardson, B., 1998. Performance of thePseudomonas chlororaphis biocontrol agent MA 342 against seed-borne diseases in field experiments.European Journal of Plant Pathology,104:701–711.
Kassab, A.S., Ali, M.K., 1996. Interaction amongMeloidogyne incognita, Rotylenchulus reniformis, Rhizoctonia solani, andRhizobium on cowpea.Annals of Agricultural Sciences (Cairo),41:521–531.
Mew, T.W., Misra, J.K., 1994. A Manual of Rice Seed Health Testing. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, p. 109–110.
Shawadfy, M.M., Mousa, E.M., 1997. Biological Management of Soil-Borne Pathogens and Root-Knot Nematode Complexes on Soybean. Proceedings of the First International Workshop of Afro-Asian Nematologists. Menoufiya University, Shebin El-Kom, Egypt, p. 7–27.
Siddiqui, I.A., Ehteshamul-Haque, S., Shaukat, S.S., 2001. Use of rhizobacteria in the control of root rot-root knot disease complex of mungbean.Journal of Phytopathology,149:337–346.
Soad, A.A., Xie, G.L., Li, B., Coosemans, J., 2004. Comparative performance ofBacillus spp. in growth promotion and suppression of tomato bacterial wilts caused byRalstonia solanacearum.Journal of Zhejiang University (Agric. & Life Sci.),30(6):603–610 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Flemish Governments of Belgium
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Xie, Gl., Soad, A. et al. Suppression ofMeloidogyne javanica by antagonistic and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. J Zheijang Univ Sci B 6, 496–501 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B0496
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B0496