Abstract
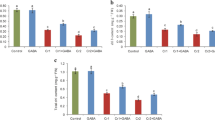
A solution with different Cu supply levels was cultured to investigate gama-aminobutyric acid (GABA) accumulation in Elsholtzia splendens, a native Chinese Cu-tolerant and accumulating plant species. Increasing Cu from 0.25 to 500 μmol/L significantly enhanced levels of GABA and histidine (His), but considerably decreased levels of aspartate (Asp) and glutamate (Glu) in the leaves. The leaf Asp level negatively correlated with leaf Cu level, while leaf GABA level positively correlated with leaf Cu level. The leaf Glu level negatively correlated with leaf GABA level in Elsholtzia splendens. The depletion of leaf Glu may be related to the enhanced synthesis of leaf GABA under Cu stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, A.J.M., Proctor, J., 1990. The influence of cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc on the distribution and evolution of metallophytes in British Isles.Plant Systematics and Evolution,173:91–108.
Beuve, N., Rispail, N., Laine, P., Cliquet, J.B., Ourry, A., Deunff, E.L., 2004. Putative role of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) as a long-distance signal in up-regulation of nitrate uptake inBrassica napus L.Plant Cell and Environment,27:1035–1046.
Jiang, L.Y., Shi, W.Y., Yang, X.E., Fu, C.X., Chen, W.G., 2002. Cu hyperaccumulators in mining area.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,13(7):906–908 (in Chinese).
Kinnersley, A.M., Fang, L., 2000. Receptor modifiers indicate that 4-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a potential modulator of ion transport in plants.Plant Growth Regulation,32:65–76.
Krämer, U., Cotter-Howells, J.D., Charnock, J.M., Baker, A.J.M., Smith, J.A.C., 1996. Free histidine as a metal chelator in plants that accumulate nickel.Nature,379:635–638.
Krämer, U., Smith, R.D., Wenzel, W.W., Raskin, I., Salt, D.E., 1997. The role of metal transport and tolerance in nickel hyperaccumulation byThlaspi goesingense Halacsy.Physiologia Plantarum,115:1641–1650.
Satyanarayan, V., Nair, P.M., 1990. Metabolism, enzymology and possible roles of 4-aminobutyrate in higher plants.Phytochemistry,29:367–375.
Schaeffer, G.W., Sharpe, F.T., 1997. Free and bound amino acids and proteins in developing grains of rice with enhanced lysine/proteins.Theoretical and Applied Genetics,94:878–881.
Scott-Taggart, C.P., Cauwenberghe, V.O.R., McLean, M.D., Shelp, B.J., 1999. Regulation of gama-aminobutyric acid synthesis in situ by glutamate availability.Physiologia Plantarum,106:363–369.
Shelp, B.J., Bown, A.W., McLean, M.D., 1999. Metabolism and functions of gama-aminobutyric acid.Trends in Plant Science,4(11):446–452.
Snedden, W.A., Chung, I., Pauls, R.H., Bown, A.W., 1992. Proton/L-glutamate symport and the regulation of intracellular pH isolated mesophyll cells.Plant Physiology,99:665–671.
Van Assche, F., Clijsters, H., 1990. Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants.Plant Cell and Environmental,13:195–206.
Verkleij, J.A.C., Schat, H., 1990. Mechanisms of Metal Tolerance in Higher Plants.In: Shaw, A.J. (Ed.), Heavy Metal Tolerance in Plants: Evolutionary Aspects. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, p.179–193.
Yang, X.E., Shi, W.Y., Fu, C.X., Yang, M.J., 1998. Copper Hyperaccumulators of Chinese Native Plants: Characteristics and Possible Use for Phytoremediation.In: Bassam, N.E.L. (Ed.), Sustainable Agriculture for Food, Energy and Industry. James & James, Science Publishers Ltd., London, p.484–489.
Yang, M.J., Yang, X.E., Roemheld, V., 2002. Growth and nutrient composition ofElsholtzia splendens nakai under copper toxicity.Journal of Plant Nutrition,25(7):1359–1375.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Projects supported by the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (No. 2002CB410804) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 29977017)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Xe., Peng, Hy. & Tian, Sk. Gama-aminobutyric acid accumulation in Elsholtzia splendens in response to copper toxicity. J Zheijang Univ Sci B 6, 96–99 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B0096
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B0096