Abstract
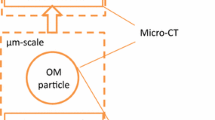
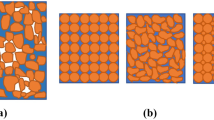
3D visualisations of the microstructure of flocculated particulates and sediments using optical confocal laser microscopy and high resolution X-ray microtomography (XMT) methods are described. Data obtained from in-situ measurements should enable direct computation of the properties of solids assembly (shape, size, contact area) and their permeability to fluids. A specific application relating to the formation of silica aggregates is described from which the behaviour of sediments containing these materials can be predicted on the basis of a bench-top test and the use of a Lattice Boltzman simulation. It is proposed that the method can potentially be used to predict trends such as the filtration behaviour of porous structures under different states of compression. This offers a significant benefit in assisting the formulation design of flocculated materials pertinent to a number of industrial sectors wishing to design optimal filtration or relevant operations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bushell, G.C., Yan, Y.D., Woodfield, D., Raper, J., Amal, R., 2002. On techniques for the measurement of the mass fractal dimensions of aggregates.Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,95:1–50.
Gregory, J., 1998. The role of floc density in solid-liquid separation.Filtration & Separation,35(4):367–371.
Hermawan, M., Bushell, G., Bickert, G., Amal, R., 2004. Characterisation of short-range structure of silica aggregates—implication to sediment compaction.International Journal of Mineral Processing,73:65–81.
Jia, X., Wedlock, D.J., Williams, R.A., 2000. Simulation of simultaneous aggregation and sedimentation.Minerals Engineering,13:1349–1360.
Leonard, A., Blacher, S., Marchot, P., Pirard, J.P., Crine, M., 2003. Moisture Profile Determination During Convective Drying Using X-ray Microtomography. Proc. Third World Congress in Industrial Process Tomography, p.730–735.
Lin, C.L., Miller, J.D., 2004. Pore structure analysis of particle beds for fluid transport simulation during filtration.International Journal of Mineral Processing,73(2–4): 281–294.
Qian, Y., D'Humieres, D., Lallemand, P., 1992. Lattice-BGK models for Navier-Stokes equations.Europhysics Letter,17(6):479–484.
Selomulya, C., Bushell, G., Amal, R., Waite, T.D., 2002. Aggregation mechanisms of latex of different particle sizes in a controlled shear environment.Langmuir,18(6):1974–1984.
Thill, A., Veerapaneni, S., Simon, B., Wiesner, M., Bottero, J.Y., Snidaro, D., 1998. Determination of structure of aggregates by confocal scanning laser microscopy.Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,204:357–362.
Wildenschild, D., Hopmans, J.W., Vaz, C.M.P., Rivers, M.L., Rikard, D., Christensen, B.S.B., 2002. Using X-ray computed tomography in hydrology: systems, resolutions, and limitations.Journal of Hydrology,267:285–297.
Williams, R.A., Jia, X., 2003. Tomographic imaging of particulate systems.Advanced Powder Technology,14(1): 1–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, R.A., Selomulya, C. & Jia, X. XMT enabled prediction of structure and permeability of flocculated structures and sediments. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 6, 1367–1373 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.A1367
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.A1367