Abstract
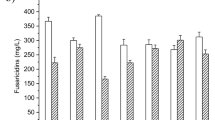
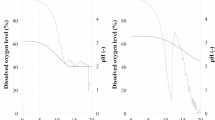
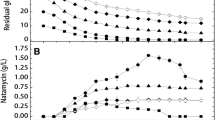
Study of the effect of dissolved oxygen and shear stress on rifamycin B fermentation with A. mediterranei XC 9–25 showed that rifamycin B fermentation with Amycolatoposis mediterranei XC 9–25 needs high dissolved oxygen and is not very sensitive to shearing stress. The scale-up of rifamycin B fermentation with A. mediterranei XC 9–25 from a shaking flask to a 15 L fermentor was realized by controlling the dissolved oxygen to above 25% of saturation in the fermentation process, and the potency of rifamycin B fermentation in the 15 L fermentor reached 10 g/L after 6-day batch fermentation. By continuously feeding glucose and ammonia in the fermentation process, the potency of rifamycin B fermentation in the 15 L fermentor reached 18.67 g/L, which was 86.65% higher than that of batch fermentation. Based on the scale-up principle of constantly aerated agitation power per unit volume, the scale-up of rifamycin B fed-batch fermentation with continuous feed from a 15 L fermentor to a 7 m3 fermentor and further to a 60 m3 fermentor was realized successfully. The potency of rifamycin B fermentation in the 7 m3 fermentor and in the 60 m3 fermentor reached 17.25 g/L and 19.11 g/L, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bader, F.G., 1986. Modeling mass transfer and agitator per-formance in multiturbine fermentor. Biotechnol Bioeng, 30:37–51.
Chen, J.M., Xu, L.T., 1991. Analysis of Antibiotic Industry. Chinese Press of Pharmaceutical Science, Beijing, p.109–111 (in Chinese).
Gao, K.N., 1989. Fermentation Engineering and Equipment. Press of Light Industry, Beijing, p.188–222 (in Chinese).
Ghisalba, O., Nüesch, J., 1981. A genetic approach to the biosynthesis of the rifamycin-chromophore in Nocardia mediterranei. IV Identification of 3-amino-hydroxybenzoic acid as a direct precursor of the seven-carbon amino starter-unit. J Antibiot, 34:67–71.
Jin, Z.H., Lin, J.P., Xu, Z.N., Cen, P.L., 2002. Improvement of industry-applied rifamycin B producing strain, Amycolatopsis mediterranei, by rational screening. J Gen Appl Microbiol, 48:329–334.
Kibby, J.J., McDonald, I.A., Richards, W.R., 1980. 3-Amino-5-hydroxybenzoic acid as a key intermediate in asamycin and maytansinoid biosynthesis. J Chem Soc Chem Commun, 1980:768–769.
Lancini, G., Carvelieri, B., 1997. Rifamycins. In: Strohl, W. R. (Ed.), Biotechnology of Antibiotics, vol. 2. Dekker, New York, p.521–549.
Leblihi, A., Germain, P., Lefebvre, G., 1987. Phosphate repression of cephamycin and clavulanic acid production by Streptomyces clavuligerus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 28:44–51.
Oosterhuis, N.M.G., Kossen, N.W.F., 1983. Dissolved oxygen concentration profiles in a production-scale bioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng, 26:546–550.
Oppolzer, W., Prelog, V., 1973. On the constitution and cofiguration of rifamycin B, O, S and SV. Helv Chim Acta, 56:2287–2314.
Rinehart, K.L.Jr., Shield, L.S., 1976. Chemistry of the ansamycin antibiotics. Fortschr Chem Org Naturst, 33:231–307.
Sensi, P., Thiemann, J.E., 1967. Production of rifamycins. Prog Ind Microbiol, 6: 21–59.
Sensi, P., Margalis, P., Timbal, M.T., 1959. Rifamycin, a new antibiotic: preliminary report. Farmaco Ed Sci, 14:146–147.
Sepkowitz, K.A., Rafalli, J., Riley, L., Kiehn, T.E., Armstrong, D., 1995. Tuberculosis in the AIDS era. Clin Microbiol Revs, 8:180–199.
Shuler, F.L., Kargi, F., 1992. Bioprocess Engineering: Basic Concepts. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Ziegler, H., Dunn, I.J., Bourine, J.R., 1980. Oxygen transfer and mycelial growth in a tubular loop fermentor. Biotechnol Bioeng, 22:1613–163.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Zh., Lin, Jp. & Cen, Pl. Scale-up of rifamycin B fermentation with Amycolatoposis mediterranei . J. Zheijang Univ.-Sci. 5, 1590–1596 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2004.1590
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2004.1590