Abstract
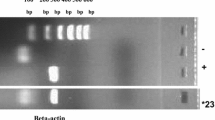
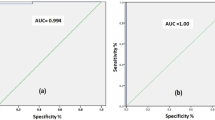
Objective: To evaluate the diagnostic significance of detecting cytokeratin 19 (CK19) mRNA by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in benign and malignant pleural effusions. Methods: CK19 mRNA was examined by quantitative RT-PCR and CK19 was detected by Enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay (ELISA) in 32 patients with malignant pleural effusions and 35 patients with benign pleural effusion. Results: On the threshold of 200 copies/μl, the positive rate of CK19 mRNA in patients with malignant pleural effusions was 62.5%. The positive rates of CK19 mRNA and CK19 in the malignant pleural effusions were significantly higher than those in the benign group (P<0.01). Furthermore, the positive rate of CK19 mRNA was higher than that of CK19 in the malignant group (P<0.05). Conclusion: Detection of CK19 mRNA can be a promising diagnostic marker in differential diagnosis of benign and malignant pleural effusions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kao, R.H., Huang, L.C., 2002. High false-positive rate of cytokeratin-19 in detecting circulating tumor cells for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chang Gung Med J, 25(4): 238–44.
Lockett, M.A., Baron, P.L., O’Brien, P.H., Elliott, B.M., Robison, J.G., Maitre, N., Metcalf, J.S., Cole, D.J., 1998. Detection of occult breast cancer micrometastases in axillary lymph nodes using a multimarker reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction panel. J Am Coll Surg, 187(1):9–16.
Mori, M., Mimori, K., Ueo, H., Karimine, N., Barnard, G.F., Sugimachi, K., 1996. Molecular detection of circulating solid carcinoma cells in the peripheral blood: the concept of early systemic disease. Int J cancer, 68(5): 739–743.
Noguchi, S., Aihara T., Motomura, K., Inaji, H., Imaoka, S., Koyama, H., 1996. Histologic characteristics of breast cancer with occult lymph node metastases detected by cytokeratin 19 mRNA reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Cancer, 78(5):1235–1240.
Wong, L.S., Cantrill, J.E., Odogwu, S., Morris, A.G., Fraser, I.A., 1997. Detection of circulating tumor cells and nodal metastasis by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction technique. Br J Surg, 84(6):834–839.
Wong, I.H., Yeo, W., Chan, A.T., Johnson, P.J., 2001. Quantitative relationship of the circulating tumor burden assessed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction for cytokeratin 19 mRNA in peripheral blood of colorectal cancer patients with Dukes’ stage, serum carcinoembryonic antigen leveland tumor progression. Cancer Letters, 162(1):65–73.
Xu, F., Zhang, X.H., Chen, J., Xia, J.Y., Zhang, X., Shen, H.H., 2003. Detection of cytokeratin 19 mRNA by quantitative RT-PCR for differentiating the characteristic of pleural effusions. Chinese Journal of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases, 26(8):501–502. (in Chinese).
Yuan, C.C., Wang, P.H., Ng, H.T., Li, Y.F., Huang, T.S., Chen, C.Y., Tsai, L.C., 2002. Detecting cytokeratin 19 mRNA in the peripheral blood cells of cervical cancer patients and its clinical-pathological correlation. Gynecol Oncol, 85(1):148–153.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Chen, J., Shen, Hh. et al. The diagnostic significance of the detection of cytokeratin 19 mRNA by quantitative RT-PCR in benign and malignant pleural effusions. J. Zheijang Univ.-Sci. 5, 1286–1289 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2004.1286
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2004.1286