Abstract
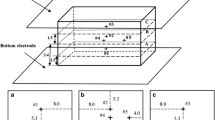
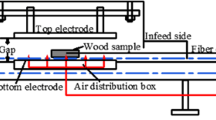
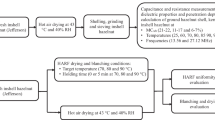
The multi-billion dollar US tree nut industries rely heavily on methyl bromide fumigation for postharvest insect control and are facing a major challenge with the mandated cessation by 2005 of its use for most applications. There is an urgent need to develop effective and economically viable alternative treatments to replace current phytosanitary and quarantine practives in order to maintain the competitiveness of US agriculture in domestic and international markets. With the reliable heating block system, the thermal death kinetics for fifth-instar codling moth, Indianmeal moth, and navel orangeworm were determined at a heating rate of 18°C/min. A practical process protocol was developed to control the most heat resistant insect pest, fifth-instar navel orangeworm, in in-shell walnuts using a 27 MHz pilot scale radio frequency (RF) system. RF heating to 55°C and holding in hot air for at least 5 min resulted in 100% mortality of the fifth-instar navel orangeworm. Rancidity, sensory qualities and shell characteristics were not affected by the treatments. If this method can be economically integrated into the handling process, it should have excellent potential as a disinfestation method for in-shell walnuts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gazit, Y., Rossler, Y., Wang, S., Tang, J., Lurie, S., 2004. Thermal death kinetics of egg and third-instar Mediterranean fruit fly Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Journal of Economic Entomology, in press.
Johnson, J.A., Wang, S., Tang, J., 2003. Thermal death kinetics of fifth-instar Plodia interpunctella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Journal of Economic Entomology, 96:519–524.
Lurie, S., 1998. Postharvest heat treatments Postharvest Biology and Technology, 14:257–269.
Nelson, S.O., 1996. Review and assessment of radio frequency and microwave energy for stored-grain insect control. Transactions of the ASAE, 39:1475–1484.
Tang, J., Ikediala, J.N., Wang, S., Hansen, J.D., Cavalieri, R.P., 2000. High-temperature-short-time thermal quarantine methods. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 21:129–145.
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency), 2001. Protection of Stratospheric Ozone: Process for exempting quarantine and preshipment applications of methyl bromide. Rules and Regulations, Federal Register, 66(139):37752–37769.
Wang, S., Tang, J., 2001. Radio frequency and microwave alternative treatments for nut insect control: a review. International Agricultural Engineering Journal, 10: 105–120.
Wang, S., Ikediala, J.N., Tang, J., Hansen, J.D., Mitcham, E., Mao, R., Swanson, B., 2001a. Radio frequency treatments to control codling moth in in-shell walnuts Postharvest Biology and Technology, 22:29–38.
Wang, S., Tang, J., Cavalieri, R.P., 2001b. Modeling fruit internal heating rates for hot air and hot water treatments. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 22:257–270.
Wang, S., Ikediala, J.N., Tang, J., Hansen, J.D., 2002a. Thermal death kinetics and heating rate effects for fifth-instar Cydia pomonella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Tortricicae). Journal of Stored Products Research, 38:441–453.
Wang, S., Tang, J., Johnson, J.A., Hansen, J.D., 2002b. Thermal death kinetics of fifth-instar Amyelois transitella (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) larvae. Journal of Stored Products Research, 38:427–440.
Wang, S., Tang, J., Johnson J.A., Mitcham, E., Hansen, J.D., Cavalieri, R.P., Bower, J., Biasi, B., 2002c. Process protocols based on radio frequency energy to control field and storage pests in in-shell walnuts. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 26:265–273.
Wang, S., Tang, J., Cavalieri, R.P., Davis, D., 2003a. Differential Heating of insects in dried nuts and fruits associated with radio frequency and microwave treatments. Transactions of the ASAE, 46:1175–1182.
Wang, S., Tang, J., Johnson, J.A., Mitcham, E., Hansen, J.D., Hallman, G., Drake, S.R., Wang, Y., 2003b. Dielectric properties of fruits and insect pests as related to radio frequency and microwave treatments. Biosystems Engineering, 85:201–212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Sj., Tang, Jm. Radio frequency heating: a potential method for post-harvest pest control in nuts and dry products. J. Zheijang Univ.-Sci. 5, 1169–1174 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2004.1169
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2004.1169