Abstract
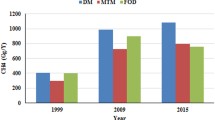
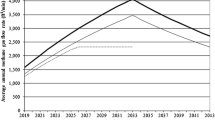
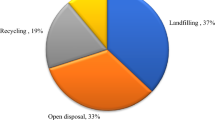
Methane (CH4) is an important greenhouse gas and a major environmental pollutant, second only to carbon dioxide (CO2) in its contribution to potential global warming. In many cases, methane emission from landfills otherwise emitted to the atmosphere can be removed and utilized, or significantly reduced in quantity by using cost-effective management methods. The gas can also be used as a residential, commercial, or industrial fuel. Therefore, emission reduction strategies have the potential to become low cost, or even profitable. The annual growth rate of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) output in China is 6.24%, with the highest levels found in South China, Southwest China and East China. Cities and towns are developing quickly in these regions. MSW output was only 76.36 Mt in 1991 and increased to 109.82 Mt in 1997, registering an average increase of 43.8%. In China, methane emission from landfills also increased from 5.88 Mt in 1991 to 8.46 Mt in 1997; so the recovery of methane from landfills is a profitable project.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aviel, V., 1996. An introduction to CHP issues.International Journal of Global Energy Issues,8(4): 301–318.
El-Fadel, M., Findikakis, A. N. and Leckie, I. O., 1996. Estimating and enhancing methane yield from municipal solid waste.Hazardous Waste and Hazardous Materials,13: 309–331.
Gradner, N. and Probert, S. D., 1993. Forecasting Landfill — Gas Yields.Applied Energy,44: 131–163.
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), 1992. Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Printed in Frances.
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), 1995. Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Printed in Frances.
Lovely, D. R., Dwyer, D. F. and Klug, M. J., 1982. Kinetic analysis od competition of sulfate reducers and methnogens for hydrogen in sediments.Appl. Environ. Microbiol.,43: 1373–1379.
Lovely, D. R. and Klug, M. J., 1986. Model for the distribution of sulfate reduction and methanogenesis in fresh water sediments.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,50: 11–18.
Manley, B. and Pearson, J. M., 1993. Gas Emissions from landfills and Their Contributions to Global Warming.Applied Energy,44: 165–174.
National Statistical Bureau, 1999.Statistical Yearbook of China 1991–1998. China Statistical Press (in Chinese).
Peer, R. L., Darcy, D. L., Campbell, D. L. and Brook, P., 1992. Development of an empirical model of methane emissions from landfill. EPA/600/SR-92/037, U. S. A.
Sandeep, P. and Saburo, M., 1999. Mathematical Modeling and Simulation of Methane Gas Production in Simulated Landfill Column Reactors Under Sulfidogenic and Methanogenic Environments.Wat. Sci. Tech.,39 (7): 235–242.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Office of Air and Radiation (6202J) of U.S.A., 1999. Methane Emissions 1990–2020: Inventories, Projections, and Opportunities for Reduction. EPA 430-R-99-013, Washington, DC.
Xu, X. H., Wang, D. H., Jiang, H. and Shi, H. X., 1999. Study on Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Jiangsu Province.Water Air and Soil Pollution,109: 293–301.
Young, A., 1989. Mathematical modeling of landfill gas extraction.J. Environ. Eng. ASCE,115(6): 1073–1087.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Germany Technological Cooperation Co. (GTZ)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Xh., Yang, Yp. & Wang, Dh. CH4 emission and recovery from Municipal Solid Waste in China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 4, 352–357 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2003.0352
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2003.0352