Abstract
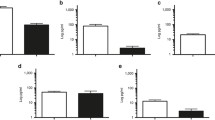
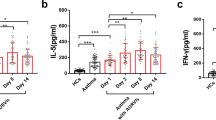
Objective: To investigate the cytokine response pattern (IL-4/IFN-γ) in infants with RSV infections and bronchiolitis during the acute phase. Methods: Four-color flow cytometry was used to measure intracellular IL-4 and IFN-γ expressions in peripheral blood CD3+ and CD8+ lymphocytes from RSV-infected and bronchiolitis infants. Serum IL-4 and IFN-γ levels were also determined. Results: RSV-infected and bronchiolitis infants showed no statistical differences from not-RSV-infected or pneumonia infants and control in the frequency of IL-4 and IFN-γ expressions in CD3+CD8-lymphocytes, showed no obvious Th1/Th2 imbalance, while IFN-γ was expressed much more frequently in CD3+CD8+ lymphocytes. Systematically, RSV-infected and bronchiolitis infants showed much lower levels of serum IL-4 and IL-4/IFN-γ ratios and much higher serum IFN-γ levels than control. Howevr, there were no statistical differences in the above three indices between RSV-infected and not-RSV infected infants or between bronchiolitis and pneumonia infants, except that bronchiolitis infants had a higher level of serum IFN-γ than pneumonia infants statistically. Conclusions: There is not type-2 cytokine response predominance in the acute phase of RSV infection and bronchiolitis. IL-4 production is suppressed and IFN-γ production upregulated, the latter being most prominent inbronchiolitis infants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendelja, K., Gagro, A., Bace, A., Lokar-Kolbas, R., Krsulovic-Hresic, V., Drazenovic, V., Mlinaric-Galinovic, G., Rabatic, S., 2000. Predominant type-2 response in infants with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection demonstrated by cytokine flow cytometry.Clin Exp Immunol.,121(2): 332–338.
Bont, L., Heijnen, C. J., Kavelaars, A., van Aalderen, W. M., Brus, F., Draaisma, J. T., Geelen, S. M., Kimpen, J. L., 2000, Monocyte IL-10 production during respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis is associated with recurrent wheezing in a one-year follow-up study.Am J Respir Crit Care Med,161(5): 1518–1523.
Brandenburg, A. H., Kleinjan, A., van HetLand, B., Moll, H. A., Timmerman, H. H., de-Swart, R. L., Neijens, H. J., Fokkens, W., Osterhaus, A. D., 2000. Type 1-like immune response is found in children with respiratory syncytial virus infection regardless of clinical severity.J Med Virol,62(2): 267–277.
Hussell, T., Georgiou, A., Sparer, T. E., Matthews, S., Pala, P., Openshaw, P. J., 1998. Host genetic determinants of vaccine-induced eosinophilia during respiratory syncytial virus infection.J Immunol,161 (11): 6215–6222.
Kneyber, M. C. J., Steyerberg, E. W., de Groot, R., Moll, H. A., 2000. Long-term effects of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) bronchiolitis in infants and young children: a quantitative review.Acta Paediatr,89(6): 654–660.
Roman, M., Calhoun, W. J., Hinton, K. L., Avendano, L. F., Simon, V., Escobar, A. M., Gaggero, A., Diaz, P. V., 1997. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants is associated with predominant Th-2-like response.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 156(1): 190–195.
Rudwaleit, M., Yin, Z., Siegert, S., Grolms, M., Radbruch, A., Braun, J., Sieper, J., 2000. Response to methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis is associated with a decrease of T cell derived tumour necrosis factor α, increase of interleukin 10, and predicted by the initial concentration of interleukin 4.J Ann Rheum Dis,59 (4): 311–314.
Sewell, W. A., North, M. E., Webster, A. D. B., Farrant, J., 1997. Determination of intracellular cytokines by flow-cytometry following whole-blood culture.J Immunol Methods,209(1): 67–74.
Sigurs, N., Biarnason, R., Sigurbergsson, F., Kjellman, B., 2000. Respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in infancy is an important risk factor for asthma and allergy at age 7.Am J Respir Crit Care Med,161(5): 1501–1507.
van Schaik, S. M., Tristram, D. A., Nagpal, I. S., Hintz, K. M., Welliver, R. C., Welliver, R. C. 1999. Increased production of IFN-γ and cysteinyl leukotrienes in virus-induced wheezing.J Allergy Clin Immunol,103(4): 630–636.
van Schaik, S. M., Obot, N., Enhorning, G., Hintz, K., Gross, K., Hancock, G. E., Stack, A. M., Welliver, R. C., 2000. Role of interferon gamma in the pathogenesis of primary respiratory syncytial virus infection in BALB/Cc mice.J Med Virol,62(2): 257–266.
Waris, M. E., Tsou, C., Erdman, D. D., Zaki, S. R., Anderson, L. J., 1996. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in BALB/c mice previously immunized with formalin-inactivated virus induces enhanced pulmonary inflammatory response with a predominant Th2-like cytokine pattern.J. Virol,70(5): 2852–2860.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi-min, C., Li-zhong, D., Jian-hua, M. et al. Use of flow cytometry to investigate the cytokine response pattern in infants with respiratory syncytial virus infection and bronchiolitis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 3, 622–626 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2002.0622
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2002.0622