Abstract
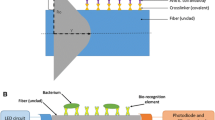
Luciferase from firefly lantern extract was immobilized on CNBr-activated Sepharose 4B. The kinetic properties of immobilized luciferase were extensively studied. TheK m′ for D-luciferin is 11.9 μmol/L, the optimum pH and temperature for Sepharose-bound enzyme were 7.8 and 25°C respectively. A luminescence fiber optic biosensor, making use of immobilized crude luciferase, was developed for assay of ATP. The peak light intensity was linear with respect to ATP concentration in range of 10−9–10−5 mol/L. A biological application was also demonstrated with the determination of serum ATP from rats bred in low versus normal oxygen environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blum, L. J., Gautier, S. M., Coulet, P. R., 1988. Luminescence fiber optic biosensor.Anal. Lett.,21: 717–726.
Lagido, C., Pettitt, J., Porter, A. J. R., Paton, G. I., Glover, L. A., 2001. Development and application of bioluminescentCaenorhabditis elegans as multicellular eukaryotic biosensors.FEBS Letters,493: 36–39.
Leach, F. R., 1981. ATP determination with direfly luciferase.J. Appl. Biochem.,3: 473–478.
Lee, Y., Jablonski, I., Deluca, M., 1981. Immobilization of firefly luciferase on glass rods: Properties of the immobilized enzyme.Anal. Biochem.,80: 496–500.
Ji, X. S., Li, H. X., Yuan, Z. Y., Liu S. H., 1984. Immobilization of NAD kinase. Enzyme Engineering 7.Anal. N. Y. Acad. Sci.,434: 264–266.
Maria, P. X., Begona, V., Maria, D. M., 2000. Fiber optic monitoring of carbamate pesticides using porous glass with covalently bound chlorophenol red.Biosensors & Bioelectronics,14: 895–905.
Michel, P. E., Gautier-Sauvigne, S. M., Blum, L. J., 1998. A transient enzymatic inhibition as an efficient tool for the discriminating bioluminescent analysis of three adenylic nucleotides with a fiberoptic sensor based on a compartmentalized tri-enzymatic sensing layer.Analytica Chimica Acta,360: 89–99.
Neuberg, C., 1944. Convenient method for deproteinization.Arch. Biochem. 4: 101–105.
Tservistas, M., Koneke, R., Comte, A., Scheper T., 2001. Oxygen monitoring in supercritical carbon dioxide using a fibre optic sensor.Enzyme and Microbial Technology,28: 637–634.
Vangelis, G. A., Yannis, D. C., 2002. A portable fiberoptic pesticide biosensor based on immobilized cholinesterase and sol-gel entrapped bromcresol purple for in-field use.Biosensor & Bioelectromics,17: 61–69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, C., Wen-fang, M. & Xin-song, J. Fiber optic biosensor of immobilized firefly luciferase. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 3, 563–566 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2002.0563
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2002.0563