Abstract
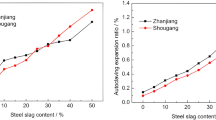
Steel slag used as binding materials often shows volumetric instability because of the existence of f-CaO (free calcium oxide). According to the composition analysis of steel slag, the tri-component f-CaO (CaO·aFeO1.5·bMnO2) was synthesized. The single phase CaO and some solid solution phases were detected in the tri-component f-CaO by XRD. The single phase CaO was found to be completely hydrated at room temperature after 18 h. The solid solution phase could not be hydrated at room temperature, while it could be hydrated partly via a boiling treatment. The hydration activity of CaO in the solid solution phase was lower than that of the single phase CaO. The f-CaO was mixed into Portland cement to study the expansibility by autoclave test. The single phase CaO had no contribution to the expansion when the content was not more than 1%. The solid solution phase in f-CaO was the main cause of the expansion. The relationship between the autoclave expansion rate and the f-CaO content conformed to the exponential equation. For the tri-component f-CaO, the smaller the molar ratio of Ca to Mn and Fe was, the more solid solution phase was present and the greater was the expansibility.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han F, Zhang Z, Wang D, Yan P (2015) Hydration heat evolution and kinetics of blended cement containing steel slag at different temperatures. Thermochim Acta 605:43–51
Yi H, Xu G, Cheng H, Wang J, Wan Y, Chen H (2012) An overview of utilization of steel slag. Proc Environ Sci 16:791–801
World Steel Association (2018) https://www.worldsteel.org/media-centre/press-releases/2018/World-crude-steel-output-increases-by-5.3–in-2017.html. Accessed 24 Jan 2018
Wang Q, Yang J, Yan P (2012) Influence of initial alkalinity on the hydration of steel slag. Sci China Technol Sci 55:3378–3387
Wang Q, Yan P (2010) Hydration properties of basic oxygen furnace steel slag. Constr Build Mater 24:1134–1140
Motz H, Geiseler J (2001) Products of steel slag an opportunity to save nature resources. Waste Manag 21:285–293
Tsakridis PE, Papadimitriou GD, Tsivilis S, Koroneos C (2008) Utilization of steel slag for Portland cement clinker production. J Hazard Mater 152:805–811
Belhadj E, Diliberto C, Lecomte A (2012) Characterization and activation of basic oxygen furnace slag. Cem Concr Compos 34:34–40
Xiang X, Xi J, Li C, Jiang X (2016) Preparation and application of the cement-free steel slag cementitious material. Constr Build Mater 114:874–879
San-José JT, Vegas I, Arribas I, Marcos I (2014) The performance of steel-making slag concretes in the hardened state. Mater Des 60:612–619
Wang Q, Yan P, Yang J, Bo Zhang (2013) Influence of steel slag on mechanical properties and durability of concrete. Constr Build Mater 47:1414–1420
Siddique R (2009) Utilization of waste materials and by-products in producing controlled low-strength materials. Resour Conserv Recycl 54:1–8
Xue Y, Wu S, Hou H, Zha J (2006) Experimental investigation of basic oxygen furnace slag used as aggregate in asphalt mixture. J Hazard Mater 138:261–268
Zhang H, Ogura H, Umezu M, Imai T, Ishii M (2017) Hydration reaction characteristics of CaO from various local limestone samples as chemical heat pump/storage materials. J Mater Sci 52(19):11360–11369
Wang G, Wang Y, Gao Z (2010) Use of steel slag as a granular material: volume expansion prediction and usability criteria. J Hazard Mater 184:555–560
Wang G (2010) Determination of the expansion force of coarse steel slag aggregate. Constr Build Mater 24:961–1966
Hou G, Li W, Guo W, Chen J, Luo J, Wang J (2008) Microstructure and mineral phase of converter slag. J Chin Ceram Soc 36(4):436–443
Nishinohara I, Kase N, Maruoka H, Hirai S, Eba H (2015) Powder X-ray diffraction analysis of lime-phase solid solution in converter slag. ISIJ Int 55(3):616–622
Jia R, Liu J (2016) Simulated experiment study of factors influences the hydration activity of f-CaO in basic oxygen furnace slag. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2016:1–15
Jia R, Liu J (2017) A study of factors that influence the hydration activity of mono-component CaO and bi-component CaO/Ca2Fe2O5 systems. Cem Concr Res 91:123–132
GB/T 1346-2001. Test method for water requirement of normal consistency, setting time and soundness of the Portland cements, China
Richardson IG, Groves GW (1992) Microstructure of hardened cement pastes involving ground blast furnace slag. J Mater Sci 27(22):6204–6212
Shi HS (1993) Study on microstructure of f-CaO and its effect on mechanical property of harden cement paste. PhD Dissertation, Tong Ji University
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Collaborative Innovation Center for Ecological Building Materials and Environmental Protection Equipment (Grant No. YCXT201613).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, J., Lv, Y., Liu, J. et al. Expansibility of cement paste with tri-component f-CaO in steel slag. Mater Struct 51, 113 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-018-1240-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-018-1240-x