Abstract
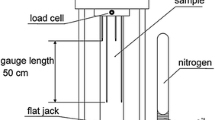
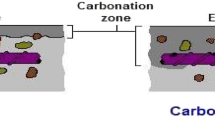
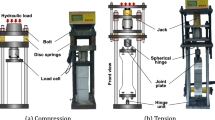
At present several methods are available to predict the durability of reinforced concrete structures. In most cases, one dominant deterioration process such as carbonation or chloride penetration is taken into consideration. Experimental results as well as observations in practice show that this is not a realistic and certainly not a conservative approach. In order to test more realistically, RILEM TC 246-TDC, founded in 2011, has developed a method to determine the durability of concrete exposed to the combined action of chloride penetration and mechanical load. In this report, a test method is presented which allows determination of realistic diffusion coefficients for chloride ions in concrete under compressive or tensile stress. Comparative test results from five different laboratories showed that the combination of mechanical and environmental loads may be much more severe than a single environmental load without mechanical loading. Modelling and probabilistic analysis also showed that the obvious synergetic effects cannot be neglected in realistic service life prediction.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eurocode 2 (2004) Design of concrete structures, Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings, EN 1992-1-1
ACI 318-14 (2014) Building code requirements for structural concrete and commentary
JSCE Guidelines for Concrete No. 15 (2007) Standard specifications for concrete structures—design
GB 50010 Chinese National Standard (2010) Code for design of concrete structures
Schießl P, Bamforth P, Baroghel-Bouny V, Corley G, Faber M, Forbes J, Gehlen C et al (2006) Model code for service life design. fib bulletin 34
ASCE (2013) 2013 Report card for America’s Infrastructure
Wittmann FH, Zhao T, Jiang F, Wan X (2012) Influence of combined actions on durability and service life of reinforced concrete structures exposed to aggressive environment. Restor Build Monum 18:105–112
Wan X, Wittmann FH, Zhao T (2011) Influence of mechanical load on service life of reinforced concrete structures under dominant influence of carbonation. Restor Build Monum 17:103–110
Yao Y, Wang L, Wittmann FH (eds) (2013) Publications on durability of reinforced concrete structures under combined mechanical loads and environmental actions. An Annotated Bibliography, RILEM TC 246-TDC
GB 175 Chinese National Standard (2007) Common Portland Cement
BS EN 197-1 Cement (2011) Composition, specifications and conformity criteria for common cements-part 1: cement
RILEM TC 107-CSP Recommendation (1998) Measurement of time-dependent strains of concrete. Mater Struct 31:507–512
Recommendation of RILEM TC 246-TDC: Influence of applied stress on chloride diffusion. Submitted to Materials and Structures
EN 14629 (2007) Products and systems for the protection and repair of concrete structures—test methods—determination of chloride content in hardened concrete
EN 12390-11 (2015) Determination of the chloride resistance of concrete, unidirectional diffusion
Gehlen C, Bartholemew M, Edvardsen C, Ferreira MV, Greve-Dierfeld S, Gulikers J, Helland S, Markeset G, McKenna P, Papworth F, Pielstick B, Rahimi A (2015) Benchmarking of deemed-to-satisfy provisions in standards, fib bulletin 76: ISBN: 978-88394-116-8, May 2015
Setzer MJ, Heine P, Kasparek S, Palecki S, Auberg R, Feldrappe V, Siebel E (2004) Internal damage of concrete due to frost action. Mater Struct 31:743–753
RILEM TC 117-FDC Recommendation (1996) CDF test—test method for the freeze thaw and deicing resistance of concrete—tests with sodium chloride (CDF). Mater Struct 29:523–528
ISO 5725-1 (1994) Accuracy (trueness and precision) of measurement methods and results
Setzer MJ, Development of the Micro-Ice-Lens Model, Setzer MJ, Auberg R, Keck H-J (2002) Frost resistance of concrete. In: Proceedings of Intern. RILEM Workshop, Essen 2002. RILEM Proceedings of 24. RILEM Publ. S.A.R.L., Cachan-Cedex, France, pp 133–146
Acknowledgements
The financial support from the following four organizations is gratefully acknowledged: (1) National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51320105016), (2) the Ecuadorian National Secretary for Science and Technology “SENESCYT”, (3) ESPOL University (Ecuador) and Magnel Laboratory for Concrete Research of Ghent University (Belgium), (4) Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (MOHE) and Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This final report was reviewed and approved by all members of the RILEM TC 246-TDC. TC Membership: TC Chairlady—Yan Yao, China; TC Secretary—Ling Wang, China. Members: Folker H.Wittmann, Germany; Nele De Belie, Belgium; Erik Schlangen, The Netherlands; Christoph Gehlen, Germany; Hugo Eguez Alava, Ecuador; Max Setzer, Germany; Carmen Andrade, Spain; Rui Miguel Ferreira, Finland; Erika Elaine Holt, Finland; Gideon Van Zijl, South Africa; Feng Xing, China; Tiejun Zhao, China; Michal A. Glinicki, Poland; Xiaomei Wan, China; R. G .Pillai, India; Klaas Van Breugel, The Netherlands.
Zhendi Wang, Yin Cao, Balqis Md Yunus and Juan Li are Ph.D. students who have contributed substantially to the TC.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Y., Wang, L., Wittmann, F.H. et al. Test methods to determine durability of concrete under combined environmental actions and mechanical load: final report of RILEM TC 246-TDC. Mater Struct 50, 123 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-016-0983-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-016-0983-5