Abstract
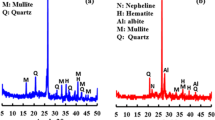
This paper presents the laboratory scale study on the preparation of ecocement clinkers, whose main mineral is alinite, from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. X-ray diffraction technique was used to monitor the phase formation during the burning of raw mixes. Effects of compositions, firing time and firing temperature on the properties of clinkers have been investigated. The hydration behaviour of the ecocement obtained from the optimized clinkers was also studied. From the results it is observed that the characteristics of the clinkers are strongly dependent on the raw mix compositions and firing temperature but not so much on firing time. The desirable clinkers can be obtained by firing the raw mix at 1,200°C for 1 h and controlling the compositional parameters KH (lime saturation moduli) around 1.02, a (silica-alumina ratio) around 4.50, Cl (Chlorides content) around 7.6% and m (MgO content) around 1.40%. Results also show that the ecocement exhibit a faster hydration kinetics than Ordinary Portland Cement.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shimoda T, Yokoyama S (1999) Ecocement-a new Portland cement to solve municipal and industrial waste problems. Proceedings of International Congress on Creating with Concrete, Dundee, pp 17–30
Ampadu KO, Torii K (2001) Characterization of ecocement pastes and mortars produced from incinerated ashes. Cem Concr Res 31(3):431–436
Aubert JE, Husson B, Sarramone N (2006) Utilization of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash in blended cement Part 1: processing and characterization of MSWI fly ash. J Hazard Mater 136(3):624–631
Bertolini L, Carsana M, Cassago D (2004) MSWI ashes as mineral additions in concrete. Cem Concr Res 34(10):1899–1906
Gao XB, Wang W, Ye TM, Wang F, Lan YX (2008) Utilization of washed MSWI fly ash as partial cement substitute with the addition of dithiocarbamic chelate. J Environ Manage 88(2):293–299
Lin KL, Wang KS, Tzeng BY, Wang NF, Lin CY (2005) Effects of Al2O3 on the hydration activity of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash slag. Cem Concr Res 34(4):587–592
Pan JR, Huang C, Kuo JJ, Lin SH (2008) Recycling MSWI bottom and fly ash as raw materials for Portland cement. Waste Manage 28(7):1113–1118
Singhal A, Tewari VK, Prakash S (2008) Utilization of treated spent liquor sludge with fly ash in cement and concrete. Build Environ 43(6):991–998
Vaidyanathan PD, Kapur PC, Singh BN (1990) Production and properties of alinite cements from steel plant wastes. Cem Concr Res 20(1):15–24
Kim YM, Lee JH, Hong SH (2003) Study of alinite cement hydration by impedance spectroscopy. Cem Concr Res 33(3):299–304
Ilyukin VV, Nevsky NN, Bikbaou MJ (1977) Crystal structure of alinite. Nature 269:397
Lampe V, Hilmer W, Jost KH, Reck G, Boikova AI (1986) Synthesis, structure and thermal decomposition of alinite. Cem Concr Res 16(4):505–510
Neubauer J, Pollmann H (1994) Alinite-chemical composition, solid solution and hydration behavior. Cem Concr Res 24(8):1413–1422
Noudelman BI, Bikbaou M, Sventsitski A, Ilukhine V (1980) Structure and properties of alinite and alinite cements. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Chemistry of Cements, Paris, vol 4, pp 702–706
Chang J, Cheng X, Lu LC, Liu FT (2005) Study on the composition and hydration of alinite and calcium chloroaluminate minerals. Cem Concr Res 35(2):248–255
Kim YM, Hong SH, Park HM (2003) Isomorphic substitution and the hydration behavior of alinite cement. J Eur Ceram Soc 23(12):2067–2073
Singh M, Kapur PC, Pradip (2008) Preparation of Alinite based cement from incinerator ash. Waste Manage 28 (8):1310–1316
Kostogloudis GC, Kalogridis D, Ftikos C et al (1998) Comparative investigation of corrosion resistance of steel reinforcement in alinite and Portland cement mortars. Cem Concr Res 28(7):995–1010
Massazza F, Gilioli C (1983) Contribution to the alinite knowledge II. Cemento 2:101–106
Ftikos CH, Philippou TH, Marinos J (1993) A study of the effect of some factors influencing alinite clinker formation. Cem Concr Res 23(6):1268–1272
Ftikos CH, Kiatos D (1994) The effect of chlorides on the formation of Belite and alinite. Cem Concr Res 24(1):49–54
Saikia N, Kato S, Kojima T (2007) Production of cement clinkers from municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash. Waste Manage 27(9):1178–1189
Wang L, Jin YY, Nie YF (2010) Investigation of accelerated and natural carbonation of MSWI fly ash with a high content of Ca. J Hazard Mater 174(1–3):334–343
Murat M, Sorrentino F (1996) Effect of large additions of Cd, Pb, Cr, Zn to cement raw meal on the composition and the properties of the clinker and the cement. Cem Concr Comp 26(3):377–385
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the National High-tech R&D Program (863 Program) (2006AA06Z363) of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51172164), and Special research funding for public benefit industries from National Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (201209026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, K., Shi, H., De Schutter, G. et al. Experimental study on alinite ecocement clinker preparation from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Mater Struct 45, 1145–1153 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-012-9822-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-012-9822-5