Abstract
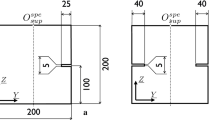
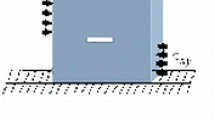
In real concrete structures cracks often open in mixed mode after their initiation. To capture the direct material behavior of a mixed mode crack opening a stiff biaxial testing machine, capable of imposing both normal and shear loads on a given crack area, has been applied. The opening and sliding components of the mixed mode displacement are measured using a custom made orthogonal gauge, and the measurements are used directly as the closed loop control signals. A double notch, concrete specimen is used for the crack investigation. The tests are divided into two steps, a pure Mode I opening step, where a macro crack is initiated in the specimen followed by the mixed mode opening step. The high stiffness of the set-up together with the closed control loop ensures a stable crack initiation followed by a controllable mixed mode opening. The deep notches result in a plane crack, only influenced by material aspects such as the aggregate size and concrete strength. Despite the occurrence of a few, local, secondary cracks during the mixed mode crack opening, the results can be treated as the mixed mode material point behavior of a crack in concrete. Results are reported for a range of mixed mode angles and for varying initial Mode I openings of the crack.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carol I, Prat PC, López CM (1997) Normal/shear cracking model: application to discrete crack analysis. J Eng Mech 123(8):765–773
Carpinteri A, Brighenti R (2010) Fracture behaviour of plain and fiber-reinforced concrete with different water content under mixed mode loading. Mater Des 31(4):2032–2042 Design of nanomaterials and nanostructures
Gettu R, Mobasher B, Carmona S, Jansen DC (1996) Testing of concrete under closed-loop control. Adv Cem Based Mater 3(2):54–71
GOM (2005) Aramis user manual (4M) v5.4.1. GOM mbH, Germany
Hassanzadeh M (1992) Behaviour of fracture process zones in concrete influenced by simultaneously applied normal and shear displacements. Report TVBM-1010. PhD thesis, Lund Institute of Technology
Hillerborg A (1989) Stability problems in fracture mechanics testing. In Shah SP et al (eds) Fracture of concrete and rock—recent developments. Elsevier, London, pp 369–378
Hillerborg A, Modéer M, Petersson P-E (1976) Analysis of crack formation and crack growth in concrete by means of fracture mechanics and finite elements. Cem Concr Res 6(6):773–781
Madsen A (2009) Cracks in concrete under repetitive load; experiments and modeling. Master’s thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, Technical University of Denmark
Nielsen LO, Mougaard JF, Jacobsen JS, Poulsen PN (2010) A mixed mode model for fracture in concrete. In: Oh BH et al (ed) Fracture mechanics of concrete and concrete structures—recent advances in fracture mechanics of concrete. Korea Concrete Institute, Seoul
Nooru-Muhamed MB (1992) Mixed mode fracture of concrete: an experimental approach. PhD thesis, Delft University
Petersen RB (2008) Fracture mechanical analysis of reinforced concrete. Master’s thesis, Department of Civil Engineering. Technical University of Denmark, Project no. 07-062
Reinhardt HW, Ozbolt J, Xu S, Dinku A (1997) Shear of structural concrete members and pure Mode II testing. Adv Cem Based Mater 5(3–4):75–85
Reinhardt HW, Xu S (2000) A practical testing approach to determine Mode II fracture energy G IIf for concrete. Int J Fract 105(2):107–125
Østergaard L, Olesen JF, Poulsen PN (2007) Biaxial testing machine for mixed mode cracking of concrete. In: Fracture mechanics of concrete and concrete structures: new trends in fracture mechanics of concretes
THK (2008) THK General catalog, catalog no. 400-1e edition
Walter R, Olesen JF (2008) Cohesive mixed mode fracture modelling and experiments. Eng Fract Mech 75(18):5163–5176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacobsen, J.S., Poulsen, P.N. & Olesen, J.F. Characterization of mixed mode crack opening in concrete. Mater Struct 45, 107–122 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-011-9754-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-011-9754-5