Abstract
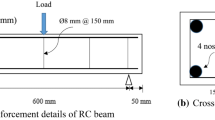
In China, fiber reinforced concrete (FRC) has been employed in practice for many years. In this paper, after a brief introduction to the current status of FRC applications in China, we will focus on recent research related to the use of pseudo-ductile cementitious composites (PDCC) to resist tensile splitting at the anchorage zone of post-tensioned concrete members. To simulate the situation at the anchorage zone, rectangular concrete columns were loaded under concentrated compression. Tests were performed on members made with (i) plain concrete, (ii) plain concrete and steel stirrups, as well as (iii) concrete with PDCC at the anchorage zone. According to the test results, PDCC is effective in improving the ultimate load under concentrated compression as long as failure is governed by tensile splitting. In some cases, it is found to be more effective than the steel stirrups. However, when the PDCC compressive strength is much lower than that of the concrete, compressive crushing failure may occur instead of tensile splitting, and the load capacity will then be decreased. For members that fail in splitting, a simple design method is proposed and the predicted failure load provides a close estimate of the experimental value. Based on the present study, the use of PDCC to replace all or part of the steel stirrups in the anchorage zone is proved to be feasible.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng QG, Gao LB, Xu WX, Wu SH (1999) Steel fiber reinforced concrete: theory and applications. Chinese Railway Publisher, Beijing (in Chinese)
Technical Specification for Fiber Reinforced Concrete Structures (2004) China Association for Engineering Construction Standardization (CECS) Publication no. 38 (in Chinese)
Leonhardt E (1964) Prestressed concrete design and construction. Wilhelm Ernst and Sohn, Berlin
Naaman AE (1982) Prestressed concrete analysis and design. McGraw Hill, New York
Libby JR (1990) Modern prestressed concrete: design principles and construction methods. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Li VC, Leung CKY (1992) Steady state and multiple cracking of short random fiber composites. ASCE J Eng Mech 118:2246–2264
Li VC (1993) From micromechanics to structural engineering—the design of cementitious composites for civil engineering applications. JSCE J Struct Mech Earth Eng 10:37–48
Leung CKY (1996) Design criteria for pseudo-ductile fiber composites. ASCE J Eng Mech 122:10–18
Kanda T, Li VC (1999) A new micromechanics design theory for pseudo strain hardening cementitious composite. ASCE J Eng Mech 125:373–381
Ramaswamy GS (1976) Modern prestressed concrete design. Pitman Publishing Ltd., London
Acknowledgements
Financial support of the present work by the Hong Kong Research Grant Council, under CERG UST6290/03E, is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leung, C.K.Y., Zhang, X. & Xia, Q. The application of pseudo-ductile cementitious composites in the anchorage zone of post-tensioned concrete members. Mater Struct 42, 1221–1231 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-009-9539-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-009-9539-2