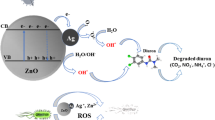
Abstract
ZnO is promising material for environmental remediation technology. To tune the material properties, Ag was added into the ZnO lattice. Herein, we report the hydrothermal synthesis of Ag-ZnO for its profound photocatalytic and antimicrobial action. The material was characterized with XRD, FESEM, EDX, and FTIR for the study of its crystal structure, morphology, elemental composition, and the availability of functional groups on the surface of the material, respectively. The optical characteristics of Ag-ZnO were investigated using UV–Visible spectroscopy and PL spectroscopy. Efficient photocatalytic degradation was performed by methylene blue. The photocatalytic MB removal was investigated over different pH values, followed by its cyclic stability. Further the material was tested for its antimicrobial activity. The antimicrobial activity was reported for methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), B. subtilis, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, E. coli, S. thyphi, A. flavus, and A. niger. The outcomes suggest that Ag-ZnO can be used for large-scale disinfecting purposes.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
X. Aihemaiti et al., Enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of S-scheme SnO2/Red phosphorus photocatalyst under visible light. Chemosphere 296, 134013 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134013
M. Kumar, P. Borah, and P. Devi: “Priority and emerging pollutants in water,” In: Inorganic Pollutants in Water, pp. 33–49 (2020). doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-818965-8.00003-2
M. D. Khan, M. ul H. Farooq, F. Iqra, A. Zulfiqar, and M. Rizwan: Designing of visible light active composites of CuS and ZnO for improved photocatalytic performance under solar light irradiation. Optik (Stuttg), vol. 271, p. 170147 (2022). doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.170147
M.A. Al-Nuaim, A.A. Alwasiti, Z.Y. Shnain, The photocatalytic process in the treatment of polluted water. Chem. Pap. 77(2), 677–701 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02468-7
I. Fareed, M. D. Khan, D. Rehman, M. ul Hassan Farooq, and F. K. Butt: 3D graphene for removal of inorganic pollutants (2023), pp. 169–187. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-36249-1_10
A.S. Alkorbi et al., Samarium vanadate affixed sulfur self doped g-C3N4 heterojunction; photocatalytic, photoelectrocatalytic hydrogen evolution and dye degradation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 47(26), 12988–13003 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.02.071
S. Dong et al., Recent developments in heterogeneous photocatalytic water treatment using visible light-responsive photocatalysts: a review. RSC Adv. 5(19), 14610–14630 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA13734E
Z. Guo et al., Heterojunction interface of zinc oxide and zinc sulfide promoting reactive molecules activation and carrier separation toward efficient photocatalysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 588, 826–837 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.11.118
I. Fareed et al., Comprehensive investigations into the synergy of S-scheme heterojunction between nitrogen-doped ZnO nano-rods and g-C3N4 nanosheets for improved photocatalytic degradation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 316, 129062 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2024.129062
M. Samadi, M. Zirak, A. Naseri, E. Khorashadizade, A.Z. Moshfegh, Recent progress on doped ZnO nanostructures for visible-light photocatalysis. Thin Solid Films 605, 2–19 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2015.12.064
S. Em et al., Uncovering the role of surface-attached Ag nanoparticles in photodegradation improvement of rhodamine B by ZnO-Ag nanorods. Nanomaterials 12(16), 2882 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/NANO12162882/S1
S. Shahid, S.A. Khan, W. Ahmad, U. Fatima, S. Knawal, Size-Dependent bacterial growth inhibition and antibacterial activity of ag-doped ZnO nanoparticles under different atmospheric conditions. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 80(1), 173–180 (2018). https://doi.org/10.4172/pharmaceutical-sciences.1000342
D. Ciumac, H. Gong, X. Hu, J.R. Lu, Membrane targeting cationic antimicrobial peptides. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 537, 163–185 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.10.103
H.H. Kong, Skin microbiome: genomics-based insights into the diversity and role of skin microbes. Trends Mol. Med. 17(6), 320–328 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2011.01.013
S. Sasi et al., Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. J. Alloys Compd. 924, 166431 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166431
M. Vaseem, A. Umar, and Y. Hahn, ZnO nanoparticles: growth, properties, and applications, vol. 5. 2010. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/225076578_ZnO_Nanoparticles_Growth_Properties_and_Applications/file/79e414fd3251942ea8.pdf
Y. Rilda et al., Biosynthesis of Ag-doped ZnO nanorods using template Bacillus sp. and polyethylene glycol via sol-gel-hydrothermal methods for antifungal application. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 47, 91–97 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SAJCE.2023.10.013
Ö.A. Yildirim, H.E. Unalan, C. Durucan, Highly efficient room temperature synthesis of silver-doped zinc oxide (ZnO: Ag) nanoparticles: Structural, optical, and photocatalytic properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96(3), 766–773 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.12218
T.N. Ravishankar et al., Comparison of the photocatalytic degradation of trypan blue by undoped and silver-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 26(1), 7–17 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2014.03.027
A. Roy, O. Bulut, S. Some, A.K. Mandal, M.D. Yilmaz, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: biomolecule-nanoparticle organizations targeting antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv. 9(5), 2673–2702 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra08982e
D. Shen et al., Synthesized Z-scheme photocatalyst ZnO/g-C3N4for enhanced photocatalytic reduction of CO2. New J. Chem. 44(38), 16390–16399 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nj02270e
Q.T.H. Ta, G. Namgung, J.-S. Noh, Facile synthesis of porous metal-doped ZnO/g-C3N4 composites for highly efficient photocatalysts. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 368, 110–119 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.09.049
M. Danish, M. Muneer, Facile synthesis of highly efficient Co@ZnSQDs/g-C3N4/MWCNT nanocomposites and their photocatalytic potential for the degradation of RhB dye: efficiency, degradation kinetics, and mechanism pathway. Ceram. Int. 47(9), 13043–13056 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.01.168
N.T.T. Truc et al., The advanced photocatalytic degradation of atrazine by direct Z-scheme Cu doped ZnO/g-C3N4. Appl. Surf. Sci. 489, 875–882 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.360
S. Kumar, A. Baruah, S. Tonda, B. Kumar, V. Shanker, B. Sreedhar, Cost-effective and eco-friendly synthesis of novel and stable N-doped ZnO/g-C3N4 core-shell nanoplates with excellent visible-light responsive photocatalysis. Nanoscale 6(9), 4830–4842 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr05271k
P. Dhiman, G. Rana, A. Kumar, G. Sharma, D.V.N. Vo, M. Naushad, ZnO-based heterostructures as photocatalysts for hydrogen generation and depollution: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 20(2), 1047–1081 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01361-1
K. Sowri Babu, A. Ramachandra Reddy, C. Sujatha, K. Venugopal Reddy, A.N. Mallika, Synthesis and optical characterization of porous ZnO. J. Adv. Ceram. 2(3), 260–265 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-013-0069-6
S. Gea et al., Facile synthesis of ZnO–Ag nanocomposite supported by graphene oxide with stabilised band-gap and wider visible-light region for photocatalyst application. J. Market. Res. 19, 2730–2741 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.05.184
J. Swain et al., Photocatalytic dye degradation by BaTiO3/zeolitic imidazolate framework composite. J. Alloys Compd. 965, 171438 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.171438
Funding
We are thankful to Higher Education Commission (HEC), Pakistan for providing financial support for this research work under National Research Project for Universities No. 8421/Punjab/NRPU/R&D/HEC/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies involving human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, Z., Fatima, Z., Fareed, I. et al. Investigations of Ag-ZnO nanosheets for improved photocatalytic performance and antimicrobial activity. MRS Advances (2024). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-024-00869-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-024-00869-2