Abstract
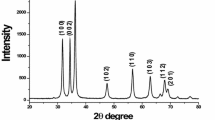
Present research paper focuses on the morphological changes that occur in zinc oxide NPs due to thermal treatment that are synthesized using green synthesis technique. The method selected for NPs synthesis incorporates the utilization of zinc nitrate salt and aloe vera extract. X-ray diffraction technique is utilized to confirm the chemical structure of the as-synthesized material. Size and morphology studies were carried out by changing reaction and calcination temperatures. Reaction temperatures were varied by 4° i.e., 64 °C, 68 °C and 72 °C, while calcination temperature variations were of hundred degrees, i.e., 470 °C, 570 °C and 670 °C. Scanning electron microscopy of samples at different reactions and calcination temperatures was also conducted. Particle size is determined using Debye Scherer formula. UV–Visible Spectroscopy was also opted to confirm zinc oxide at a wavelength of 368 nm. Results show that with increased calcination temperature there is a sharp morphological change from plates to hexagonal rods and from rods to spherical particles.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets of numerical results used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- SEM:
-
Scanning Electron Microscopy
References
O.H. Ahmed, M. Altarawneh, M. Al-Harahsheh, Z.-T. Jiang, B.Z. Dlugogorski, Recycling of zincite (ZnO) via uptake of hydrogen halides. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20(2), 1221–1230 (2018)
K. Harun, N.A. Salleh, B. Deghfel, M.K. Yaakob, A.A. Mohamad, DFT+ U calculations for electronic, structural, and optical properties of ZnO wurtzite structure: a review. Results Phys. 16, 102829 (2020)
F. Giovannelli, C. Chen, P. Díaz-Chao, E. Guilmeau, F. Delorme, Thermal conductivity and stability of Al-doped ZnO nanostructured ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(15), 5015–5020 (2018)
M.I. Din, R. Sehar, Z. Hussain, R. Khalid, A.T. Shah, Synthesis of biodegradable semolina starch plastic films reinforced with biogenically synthesized ZnO nanoparticles. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 51(7), 985–994 (2021)
Y. Li, H. Sun, Y. Zhang, M. Xu, S.Q. Shi, The three-dimensional heterostructure synthesis of ZnO/cellulosic fibers and its application for rubber composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 177, 10–17 (2019)
P. Sikora, A. Augustyniak, K. Cendrowski, P. Nawrotek, E. Mijowska, Antimicrobial activity of Al2O3, CuO, Fe3O4, and ZnO nanoparticles in scope of their further application in cement-based building materials. Nanomaterials 8(4), 212 (2018)
S.P.K. Malhotra, T. Mandal, Zinc oxide nanostructure and its application as agricultural and industrial material. Contamin. Agric. Environ. 1, 216 (2019)
H. Agarwal, S. Menon, S.V. Kumar, S. Rajeshkumar, Mechanistic study on antibacterial action of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using green route. Chem. Biol. Interact. 286, 60–70 (2018)
A. Saboor, S.M. Shah, H. Hussain, Band gap tuning and applications of ZnO nanorods in hybrid solar cell: Ag-doped verses Nd-doped ZnO nanorods. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 93, 215–225 (2019)
N. Ridhuan, K.A. Razak, Z. Lockman, A.A. Aziz, PLoS ONE 7(11), e50405 (2012)
J. Theerthagiri et al., A review on ZnO nanostructured materials: energy, environmental and biological applications. Nanotechnology 30(39), 392001 (2019)
C.P. Devatha, A.K. Thalla, Green synthesis of nanomaterials, in Synthesis of inorganic nanomaterials: (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2018), pp. 169–184
N. Singh, P. Jain, A. De, R. Tomar, Green synthesis and applications of nanomaterials. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 22(13), 1705–1747 (2021)
P. Luque et al., Green synthesis of tin dioxide nanoparticles using Camellia sinensis and its application in photocatalytic degradation of textile dyes. Optik 229, 166259 (2021)
M. Kokturk, et al., Perspective on green synthesis of RP-Pd/AC NPs: characterization, embryonic and neuronal toxicity assessment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1–12 (2022)
K. Shubhashree et al., Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using aqueous extracts from Hyptis suaveolens (L.). Mater. Chem. Phys. 280, 125795 (2022)
E. Üstün, S.C. Önbaş, S.K. Çelik, M.Ç. Ayvaz, N. Şahin, Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by using Ficus carica leaf extract and its antioxidant activity. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021(12), 2108–2116 (2022)
L. Farhadi et al., Green synthesis of chitosan-coated silver nanoparticle, characterization, antimicrobial activities, and cytotoxicity analysis in cancerous and normal cell lines. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 1–13 (2022)
J.P.Z. Gonçalves, J. Seraglio, D.L.P. Macuvele, N. Padoin, C. Soares, H.G. Riella, Green synthesis of manganese based nanoparticles mediated by Eucalyptus robusta and Corymbia citriodora for agricultural applications. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 636, 128180 (2022)
M.S. Punnoose, B. Mathew, Microwave-assisted green synthesis of Cyanthillium cinereum mediated gold nanoparticles: evaluation of its antibacterial, anticancer and catalytic degradation efficacy. Res. Chem. Intermed. 1–20 (2022)
M.G. Kordy et al., Phyto-capped Ag nanoparticles: green synthesis, characterization, and catalytic and antioxidant activities. Nanomaterials 12(3), 373 (2022)
M.A.A. Al-Khafaji, R.A. Al-Refai’a, O.M.Y. Al-Zamely, Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using artemisia plant extract. Mater. Today 49, 2831–2835 (2022)
P. Pon Matheswari, G. Jenit Sharmila, C. Murugan, Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Delonix regia and Nerium oleander flower extract and evaluation of their antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 1–12 (2022)
S.T. Sahil et al., Cow milk lactose inspired fabrication of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanorods for bio-applications. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 1–9 (2022)
K. Ahmed, I. Tariq, S.U.S.M. Mudassir, 11. Green synthesis of cobalt nanoparticles by using methanol extract of plant leaf as reducing agent. Pure Appl. Biol. 5(3), 453–457 (2021)
R.D. Rivera-Rangel, M.P. González-Muñoz, M. Avila-Rodriguez, T.A. Razo-Lazcano, C. Solans, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles in oil-in-water microemulsion and nano-emulsion using geranium leaf aqueous extract as a reducing agent. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 536, 60–67 (2018)
S. Sadjadi, F. Koohestani, M. Atai, Echinops bannaticus plant and Zinnia grandiflora extract as char biosource and reducing agent for the biosynthesis of Ag on magnetic char-polymer: an efficient catalyst for water treatment. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 34(9), e5799 (2020)
T. Theivasanthi, M. Alagar, X-ray diffraction studies of copper nanopowder. arXiv preprint arXiv:1003.6068 (2010)
Z.A. Ali, M.A. Roslan, R. Yahya, W.Y.W. Sulaiman, R. Puteh, Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its larvicidal property against fourth instar larvae of Aedes aegypti. IET Nanobiotechnol. 11(2), 152–156 (2017)
I. Karmous, A. Pandey, K.B. Haj, A. Chaoui, Efficiency of the green synthesized nanoparticles as new tools in cancer therapy: insights on plant-based bioengineered nanoparticles, biophysical properties, and anticancer roles. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 196(1), 330–342 (2020)
Z. Sabouri et al., Plant-based synthesis of NiO nanoparticles using salvia macrosiphon Boiss extract and examination of their water treatment. Rare Met. 39(10), 1134–1144 (2020)
M.E. Taghavizadeh Yazdi et al., Eco-friendly and plant-based synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Allium giganteum and investigation of its bactericidal, cytotoxicity, and photocatalytic effects. Mater. Technol. 34(8), 490–497 (2019)
A.C. Paiva-Santos et al., Plant-mediated green synthesis of metal-based nanoparticles for dermopharmaceutical and cosmetic applications. Int. J. Pharm. 597, 120311 (2021)
S. Boulahlib, K. Dib, M. Özacar, Y. Bessekhouad, Optical, dielectric, and transport properties of Ag-doped ZnO prepared by Aloe Vera assisted method. Opt. Mater. 113, 110889 (2021)
S. Irshad et al., Green tea leaves mediated ZnO nanoparticles and its antimicrobial activity. Cogent Chem. 4(1), 1469207 (2018)
R. Amirante et al., Effects of ultrasound and green synthesis ZnO nanoparticles on biogas production from Olive Pomace. Energy Procedia 148, 940–947 (2018)
S. Senthilkumar, T. Sivakumar, Green tea (Camellia sinensis) mediated synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles and studies on their antimicrobial activities. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 6(6), 461–465 (2014)
N. Talebian, S.M. Amininezhad, M. Doudi, Controllable synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their morphology-dependent antibacterial and optical properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 120, 66–73 (2013)
H. Upadhyaya, S. Shome, R. Sarma, S. Tewari, M.K. Bhattacharya, S.K. Panda, Green synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles. Am. J. Plant Sci. 9(6), 1279–1291 (2018)
K. Ali et al., Aloe vera extract functionalized zinc oxide nanoparticles as nanoantibiotics against multi-drug resistant clinical bacterial isolates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 472, 145–156 (2016)
S. Bognár, P. Putnik, D. Šojić Merkulov, Sustainable green nanotechnologies for innovative purifications of water: synthesis of the nanoparticles from renewable sources. Nanomaterials 12(2), 263 (2022)
M. Rai, A.P. Ingle, I.R. Gupta, S.S. Birla, A.P. Yadav, K.A. Abd-Elsalam, Potential role of biological systems in formation of nanoparticles: mechanism of synthesis and biomedical applications. Curr. Nanosci. 9(6), 576–587 (2013)
S.K. Nath, P. Kalita, Temperature dependent structural, optical and electrical properties of CuS nanorods in aloe vera matrix. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 25, 100651 (2021)
P. Basnet, T.I. Chanu, D. Samanta, S. Chatterjee, A review on bio-synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant extracts as reductants and stabilizing agents. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 183, 201–221 (2018)
R.K. Sharma, R. Ghose, Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by homogeneous precipitation method and its application in antifungal activity against Candida albicans. Ceram. Int. 41(1), 967–975 (2015)
N.I. Rasli, H. Basri, Z. Harun, Zinc oxide from aloe vera extract: two-level factorial screening of biosynthesis parameters. Heliyon 6(1), e03156 (2020)
F.M. Mohammadi, N. Ghasemi, Influence of temperature and concentration on biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using cherry extract. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 8(1), 93–102 (2018)
S. Maensiri, P. Laokul, J. Klinkaewnarong, S. Phokha, V. Promarak, S. Seraphin, Indium oxide (In2O3) nanoparticles using Aloe vera plant extract: synthesis and optical properties. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 10(3), 161–165 (2008)
J.D.O. Primo et al., Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by ecofriendly routes: adsorbent for copper removal from wastewater. Front. Chem. 8, 1100 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express deep sense of gratitude and profound thanks to Department of Materials Engineering, NED University of Engineering & Technology, Karachi for supporting experimentation facility for this study.
Funding
This study received no funding from any resource.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SAAZ conceived of this study. DM and MNN carried out the experimental work, and data analysis. MA supported in compilation and collection of data. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majeed, D., Zaidi, A.A., Naseer, M.N. et al. Influence of thermal treatment on the morphology of zinc oxide NPs synthesized by green method. MRS Advances 7, 420–426 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-022-00279-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-022-00279-2