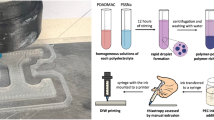
Abstract
Strong polyelectrolytes, poly(styrene sulfonate) (PSS), and poly(diallyldimethylammonium) (PDADMAC) dissolved in aqueous KBr can be 3D printed for the first time in the air via direct ink writing (DIW). Viscous polyelectrolyte complex (PEC) solutions were deposited layer-by-layer and quenched with deionized water to produce mechanically viable, viscoelastic hydrogel objects. Optimal inks were confirmed by rheology and thermogravimetric measurements to map flow behavior with material composition. Post-print handling and storage protocols were developed to produce printed resolutions more consistent with conventional DIW.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data for the work is either included in this manuscript or is part of the Electronic Supplementary Information file.
References
E. Josef, H. Bianco-Peled, Conformation of a natural polyelectrolyte in semidilute solutions with no added salt. Soft Matter 8(35), 9156 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2sm25733e
A. Reisch, E. Roger, T. Phoeung, C. Antheaume, C. Orthlieb, F. Boulmedais, P. Lavalle, J.B. Schlenoff, B. Frisch, P. Schaaf, On the benefits of rubbing salt in the cut: Self-healing of saloplastic PAA/PAH compact polyelectrolyte complexes. Adv. Mater. 26(16), 2547–2551 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201304991
T.M. Fulghum, N.C. Estillore, C.-D. Vo, S.P. Armes, R.C. Advincula, Stimuli-responsive polymer ultrathin films with a binary architecture: Combined layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte and surface-initiated polymerization approach. Macromolecules 41(2), 429–435 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/ma0717136
V.S. Meka, M.K.G. Sing, M.R. Pichika, S.R. Nali, V.R.M. Kolapalli, P. Kesharwani, A comprehensive review on polyelectrolyte complexes. Drug Discov. Today 22(11), 1697–1706 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2017.06.008
J.W. Park, K.H. Park, S. Seo, Natural polyelectrolyte complex-based PH-dependent delivery carriers using alginate and chitosan. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 136(43), 48143 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.48143
D. Mecerreyes, Polymeric ionic liquids: Broadening the properties and applications of polyelectrolytes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 36(12), 1629–1648 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.05.007
E.M. Wilts, J. Herzberger, T.E. Long, Addressing water scarcity: Cationic polyelectrolytes in water treatment and purification: Addressing water scarcity. Polym. Int. 67(7), 799–814 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.5569
R.C. Advincula, J.R.C. Dizon, E.B. Caldona, R.A. Viers, F.D.C. Siacor, R.D. Maalihan, A.H. Espera, On the progress of 3D-printed hydrogels for tissue engineering. MRS Commun. 11(5), 539–553 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43579-021-00069-1
K. Akkaoui, M. Yang, Z.A. Digby, J.B. Schlenoff, Ultraviscosity in entangled polyelectrolyte complexes and coacervates. Macromolecules 53(11), 4234–4246 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.0c00133
R.F. Shamoun, H.H. Hariri, R.A. Ghostine, J.B. Schlenoff, Thermal transformations in extruded saloplastic polyelectrolyte complexes. Macromolecules 45(24), 9759–9767 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ma302075p
A.S. Michaels, R.G. Miekka, Polycation-polyanion complexes: Preparation and properties of poly-(vinylbenzyltrimethylammonium) poly(styrene sulfonate). J. Phys. Chem. 65(10), 1765–1773 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1021/j100827a020
Q. Wang, J.B. Schlenoff, The polyelectrolyte complex/coacervate continuum. Macromolecules 47(9), 3108–3116 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ma500500q
Y. Chen, M. Yang, S.A. Shaheen, J.B. Schlenoff, Influence of nonstoichiometry on the viscoelastic properties of a polyelectrolyte complex. Macromolecules 54(17), 7890–7899 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.1c01154
P. Schaaf, J.B. Schlenoff, Saloplastics: Processing compact polyelectrolyte complexes. Adv. Mater. 27(15), 2420–2432 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201500176
G. Decher, J. Schmitt, Fine-tuning of the film thickness of ultrathin multilayer films composed of consecutively alternating layers of anionic and cationic polyelectrolytes. In Trends in Colloid and Interface Science VI; Helm, C., Lösche, M., Möhwald, H., Eds.; Progress in Colloid & Polymer Science; Steinkopff: Darmstadt, 1992; Vol. 89, pp 160–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0116302.
C.H. Porcel, J.B. Schlenoff, Compact polyelectrolyte complexes: “Saloplastic” candidates for biomaterials. Biomacromolecules 10(11), 2968–2975 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/bm900373c
R.L. Truby, J.A. Lewis, Printing soft matter in three dimensions. Nature 540(7633), 371–378 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21003
L. Li, Q. Lin, M. Tang, A.J.E. Duncan, C. Ke, Advanced polymer designs for direct-ink-write 3D printing. Chemistry 25(46), 10768–10781 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201900975
S. Lankalapalli, V.R.M. Kolapalli, Polyelectrolyte complexes: A review of their applicability in drug delivery technology. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 71(5), 481 (2009). https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474X.58165
H. Wang, X. Zhou, J. Wang, X. Zhang, M. Zhu, H. Wang, Fabrication of channeled scaffolds through polyelectrolyte complex (PEC) printed sacrificial templates for tissue formation. Bioact. Mater. 17, 261–275 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.01.030
R.A. Ghostine, R.F. Shamoun, J.B. Schlenoff, Doping and diffusion in an extruded saloplastic polyelectrolyte complex. Macromolecules 46(10), 4089–4094 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/ma4004083
F. Elahee, L. Rong, C. Breting, J. Bonilla-Cruz, T. Ceniceros, Z. Smith, J. Ge, X. Cheng, M. Xu, M. Yang, E. Ribeiro, E. Caldona, R. Advincula, Acrylic sealants as practicable direct ink writing (DIW) 3D-printable materials. MRS Commun. 13, 299–305 (2023)
A. Espera, J. Dizon, A. Valino, Q. Chen, I. Silva, S. Nguyen, L. Rong, R. Advincula, On the 3D printability of silicone-based adhesives via viscous paste extrusion. MRS Commun. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43579-022-00318-x
Q. Chen, J. Zhao, J. Ren, L. Rong, P.-F. Cao, R. Advincula, 3D printed multifunctional, hyperelastic silicone rubber foam. Adv. Func. Mater. 29(23), 1900469 (2019)
D. Gutierrez, E. Caldona, Z. Yang, X. Suo, X. Cheng, S. Dai, R. Espiritu, R. Advincula, 3D-printed PDMS-based membranes for CO2 separation applications. MRS Commun. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43579-022-00287-1
A. Stephen, S. Bhoyate, P. Cao, R. Advincula, N. Dahotre, Y. Jiang, W. Choi, 3D-printed flexible anode for high-performance zinc ion battery. MRS Commun. 12, 894–901 (2022)
W. Niu, Z. Zhang, Q. Chen, P.-F. Cao, R. Advincula, Highly recyclable, mechanically isotropic and healable 3D-printed elastomers via polyurea vitrimers. ACS Mater. Lett. 3(8), 1095–1103 (2021)
F. Siacor, Q. Chen, J. Zhao, L. Han, A. Valino, E. Taboada, E. Caldona, R. Advincula, On the additive manufacturing (3D printing) of viscoelastic materials and flow behavior: from composites to food manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 5(23), 102043 (2021)
W. Hua, K. Mitchell, L. Raymond, B. Godina, D. Zhao, W. Zhou, Y. Jin, Fluid bath-assisted 3D printing for biomedical applications: from pre- to postprinting stages. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 7(10), 4736–4756 (2021)
H. Honaryar, S. Amirfattahi, Z. Niroobakhsh, Associative liquid-in-liquid 3D printing techniques for freeform fabrication of soft matter. Small 19(16), 2206524 (2023)
H. Haoyu Wang, X. Xiaqing Zhou, J. Juan Wang, X. Xinping Zhang, M. Meifeng Zhu, H. Hongjun Wang, Fabrication of channeled scaffolds through polyelectrolyte complex (PEC) printed sacrificial templates for tissue formation. Bioact. Mater. 17, 261–275 (2022)
A. Singh, K. Pramanik, Fabrication and investigation of physicochemical and biological properties of 3D printed sodium alginate-chitosan blend polyelectrolyte complex scaffold for bone tissue engineering application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 140(12), 53642 (2023)
F. Zhu, L. Cheng, J. Yin, Z. Wu, J. Qian, J. Fu, Q. Zheng, 3D printing of ultratough polyion complex hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 31304–31310 (2016)
X. Meng, J. Schiffman, S. Perry, Cargo-containing polyelectrolyte complex fibers: Correlating molecular interactions to complex coacervate phase behavior and fiber formation. Macromolecules 51(21), 8821–8832 (2018)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge technical support from Frontier Laboratories and Quantum Analytics. This work (or part of this work) was conducted in Oak Ridge National Laboratory Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences by R. C. Advincula, a US Department of Energy Office of Science User Facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no known conflict of interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rigoberto Advincula was an editor of this journal during the review and decision stage. For the MRS Communications policy on review and publication of manuscripts authored by editors, please refer to http://www.mrs.org/editormanuscripts/.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MOV 81353 kb)
Supplementary file2 (MOV 13440 kb)
Supplementary file3 (MOV 4534 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jurago, A.A., Viers, R.A., Nguyen, A.T. et al. On the 3D printing of polyelectrolyte complexes: A novel approach to overcome rheology constraints. MRS Communications 13, 862–870 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43579-023-00415-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43579-023-00415-5