Abstract
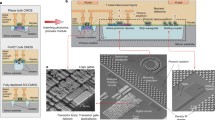
Optical computing, based on the photonic CMOS technology, may substantially improve the analog or digital processing capabilities, and expand silicon photonics markets. There are two types of optical computing: photon-assisted optoelectronic computing and quantum optical computing. The former requires no change in existing circuit designs. The latter may require new features in logic designs, so is suitable for newly developed sections that are connected and fully compatible with existing sub-5nm ULSI circuits. In this paper, we will discuss how to implement the coherent micro-holographic effects, generated by photonic CMOSFETs, for optical computers.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Tahara, Review of incoherent digital holography: applications to multidimensional incoherent digital holographic microscopy and palm-sized digital holographic recorder—holosensor. Front. Photonics (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphot.2021.829139
J. Liu, Incoherent digital holography: a review. Appl. Sci. 8, 143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/app8010143
Optipedia • SPIE Press Books—Phase-Shift Masks: Phase-Shift Masks (spie.org)
I. Prieto, Near Thresholdless Laser Operation at Room Temperature (Optical Society of America, Washington, 2015)
A.A. Vyshnevyy, Lasing threshold of thresholdless and nonthresholdless metal-semiconductor nanolasers. Opt. Express 26(25), 33474 (2018)
W. Shin, Novel micro-optical waveguide on microactuating platform for re-configurable wavelength selective optical switch. 2004 Optical Society of America, OCIS codes: (060.0060) Fiber Optics and Optical communications; (060.2310) Fiber Optics (2004)
F. Cairone, Micro-optical waveguides realization by low-cost technologies. Micro 2, 123–136 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/micro2010008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, J.N. Micro-holographic effects with sub-7nm photonic CMOS transistors for nonlinear optoelectronic processors and optical computers. MRS Communications 13, 608–611 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43579-023-00393-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43579-023-00393-8