Abstract
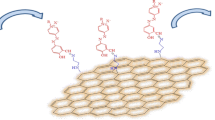
Herein, we have demonstrated and compared bimodal strategies towards augmenting the antimicrobial activity of graphene oxide (GO). Among the two modifications viz. through alteration of GO surface functionalities and secondly through surface modification of GO with an ampicillin-based antibacterial ionic liquid (IL), the IL modification was most effective in enhancing the bactericidal effect. pH and the zeta potential values of the nanodispersions support the alteration of surface functionalities of GO by variation in reaction conditions and SEM, XRD, Raman spectra establish the resulting sheet thickness, morphology, stacking and planarity. The surface modification of GO with trihexyltetradecyl phosphonium ampicillin ([TTP][Amp]) IL as indicated by FTIR, SEM, pH and zeta potential measurements imply in nearly five times lower MBC value compared to average MBC value of the four GO variants. Hence, judicious IL modification can be an effective approach towards augmenting antibacterial property of GO for enduring antifouling coatings and membranes.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated and/or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information file.
References
H. Chang, H. Wu, Graphene-based nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, and optical and optoelectronic applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 1984–1997 (2013)
C. Chung, Y.-K. Kim, D. Shin, S.-R. Ryoo, B.H. Hong, D.-H. Min, Biomedical applications of graphene and graphene oxide. Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 2211–2224 (2013)
S. Liu, T.H. Zeng, M. Hofmann, E. Burcombe, J. Wei, R. Jiang, J. Kong, Y. Chen, Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 5, 6971–6980 (2011)
J. Qiu, D. Wang, G. Hao, J. Guo, S. Qian, X. Liu, Adv. Mater. Interfaces 4, 1700228 (2017)
F. Perreault, A.F. de Faria, S. Nejati, M. Elimelech, Antimicrobial properties of graphene oxide nanosheets: why size matters. ACS Nano 9, 7226–7236 (2015)
V.T.H. Pham, V.K. Truong, M.D.J. Quinn, S.M. Notley, Y. Guo, V.A. Baulin, M. Al Kobaisi, R.J. Crawford, E.P. Ivanova, Graphene induces formation of pores that kill spherical and rod-shaped bacteria. ACS Nano 9, 8458–8467 (2015)
K. Krishnamoorthy, N. Umasuthan, R. Mohan, J. Lee, S.-J. Kim, Antibacterial activity of graphene oxide nanosheets. Sci. Adv. Mater. 4, 1111–1117 (2012)
S.S. Nanda, D.K. Yi, K. Kim, Study of antibacterial mechanism of graphene oxide using Raman spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 6, 28443 (2016)
J. Chen, G. Zhou, L. Chen, Y. Wang, X. Wang, S. Zeng, Interaction of graphene and its oxide with lipid membrane: a molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 6225–6231 (2016)
S. Prusty, K. Pal, D. Bera, A. Paul, M. Mukherjee, F. Khan, A. Dey, S. Das, Enhanced antibacterial activity of a novel biocompatible triarylmethane based ionic liquid-graphene oxide nanocomposite. Colloids Surf. B 203, 111729–111739 (2021)
X. Zou, L. Zhang, Z. Wang, Y. Luo, Mechanisms of the antimicrobial activities of graphene materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138(7), 2064–2077 (2016)
A.A. Menazea, M.K. Ahmed, Synthesis and antibacterial activity of graphene oxide decorated by silver and copper oxide nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 1218, 128536–128542 (2020)
T. Arun, S.K. Verma, P.K. Panda, R.J. Joseyphus, E. Jha, A. Akbari-Fakhrabadi, P. Sengupta, D.K. Ray, V.S. Benitha, K. Jeyasubramanyan, P.V. Satyam, Facile synthesized novel hybrid graphene oxide/cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles based surface coating material inhibit bacterial secretion pathway for antibacterial effect. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 104, 109932–109945 (2019)
L. Sun, T. Du, C. Hu, J. Chen, J. Lu, Z. Lu, H. Han, Antibacterial activity of graphene oxide/g-C3N4 composite through photocatalytic disinfection under visible light. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 5, 8693–8701 (2017)
K. Dutta, R.S. Saraffin, B. Dutta, A. Datta, A. Kapuria, S. Ghosh, F. Khan, S. Das, S.K. Saha, Room temperature synthesis of GO/Ag2O nanocomposite: broad spectral ranged solar photocatalyst and high efficacy antibiotic for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng 10, 107175 (2022)
M.L. Bhaisare, Wu. Bo-Sgum, Wu. Mon-Chun, M. Shahnawaz Khan, M.-H. Tseng, Wu. Hui-Fen, MALDI MS analysis, disk diffusion and optical density measurements for the antimicrobial effect of zinc oxide nanorods integrated in graphene oxide nanostructures. Biomater. Sci. 4, 183–194 (2016)
M.Y. Ashfaq, M.A. Al-Ghouti, N. Zouari, Investigating the effect of polymer-modified graphene oxide coating on RO membrane fouling. J. Water Process. Eng. 49, 103164 (2022)
Z. Fan, K.H. Po, K.K. Wong, S. Chen, S.P. Lau, Nano Mater. 1(4), 1811–1818 (2018)
Y. Yuan, G. Zhang, Y. Li, G. Zhang, F. Zhang, X. Fan, Poly(amidoamine) modified graphene oxide as an efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions. Polym. Chem. 4, 2164–2167 (2013)
N. Fatimaa, U. Qazib, A. Manshac, I. Bhattia, R. Javaidd, Q. Abbase, N. Nadeema, Z. Rehanf, S. Noreena, M. Zahid, Recent developments for antimicrobial applications of graphene-based polymeric composites: a review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 100, 40–58 (2021)
X. Zhou, Y. Zhang, Z. Huang, D. Lu, A. Zhu, G. Shi, Ionic liquids modified graphene oxide composites: a high efficient adsorbent for phthalates from aqueous solution. Sci. Rep. 6, 38417 (2016)
X. Xiong, J. Wang, H. Jia, E. Fang, L. Ding, Structure, thermal conductivity, and thermal stability of bromobutyl rubber nanocomposites with ionic liquid modified graphene oxide. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 98(11), 2208–2214 (2013)
S. Das, P.K.S. Magut, L. Zhao, F. Hasan, A.B. Karki, R. Jin, I.M. Warner, Multimodal theranostic nanomaterials derived from phthalocyanine-based organic salt. RSC Adv. 5, 30227–30233 (2015)
N. Nikfarjam, M. Ghomi, T. Agarwal, M. Hassanpour, E. Sharifi, D. Khorsandi, M. Ali, F. Rossi, A. Rossetti, E. Nazarzadeh, N. Rabiee, D. Afshar, M. Vosough, T. Kumar, V. Mattoli, E. Lichtfouse, F.R. Tay, P. Makvandi, Antimicrobial ionic liquid-based materials for biomedical applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2104148 (2021)
S. Das, A. Paul, D. Bera, A. Dey, A. Roy, A. Dutta, D. Ganguly, Design, development and mechanistic insights into the enhanced antibacterial activity of mono and bis-phosphonium fluoresceinate ionic liquids. Mater. Today Commun. 28, 102672–102687 (2021)
M. Markiewicz, J. Maszkowska, V.N. Rataj, S. Stolte, Readily biodegradable and low-toxic biocompatible ionic liquids for cellulose processing. RSC Adv. 6, 87325–87331 (2016)
J. Blando, R. Porcja, B. Turpin, Issues in the quantitation of functional groups by FTIR spectroscopic analysis of impactor-collected aerosol samples. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 35(5), 899–908 (2001)
J. Guerrero-Contreras, F. Caballero-Briones, Graphene oxide powders with different oxidation degree, prepared by synthesis variations of the Hummers method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 153, 209–220 (2015)
K.A. Shiyanova, M.V. Gudkov, M.K. Rabchinskii, L.A. Sokura, D.Y. Stolyarova, M.V. Baidakova, D.P. Shashkin, A.D. Trofimuk, D.A. Smirnov, I.A. Komarov, V.A. Timofeeva, V.P. Melnikov, Graphene oxide chemistry management via the use of KMnO4/K2Cr2O7 oxidizing agents. Nanomaterials 11, 915 (2021)
K.-C. Hsu, D.-H. Chen, Microwave-assisted green synthesis of Ag/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite as a surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate with high uniformity. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9, 193–122 (2014)
A.C. Ferrari, Raman spectroscopy of graphene and graphite: disorder, electron–phonon coupling, doping and nonadiabatic effects. Solid State Commun. 143, 47–57 (2007)
F. Mouhat, F.-X. Coudert, M.-L. Bocquet, Structure and chemistry of graphene oxide in liquid water from first principles. Nat. Commun. 11, 1566–1575 (2020)
O. Akhavan, E. Ghaderi, Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. ACS Nano 4, 5731–5736 (2010)
R. Ferraz, L.C. Branco, I.M. Marrucho, J.M.M. Araújo, L.P.N. Rebelo, M.N. Ponte, C. Prudêncio, J.P. Noronha, Ž Petrovski, Development of novel ionic liquids based on ampicillin. Med. Chem. Commun. 3, 494–497 (2012)
A. Olborska, A. Janas-Naze, L. Kaczmarek, T. Warga, D. Halin, Antibacterial effect of graphene and graphene oxide as a potential material for fiber finishes. Autex Res. J. 20(4), 506–516 (2020)
S.B. Mohamed, T.A. Adlan, N.A. Khalafalla et al., Proteomics and docking study targeting penicillin-binding protein and penicillin-binding protein2a of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus strain SO-1977 isolated from Sudan. Evolut. Bioinform. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/1176934319864945
L.D. Mendelsohn, ChemDraw 8 ultra, windows and macintosh versions. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 44, 2225–2226 (2004)
M.J. Frisch, G.W. Trucks, H.B. Schlegel, G.E. Scuseria, M.A. Robb, J.R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, G.A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, M. Caricato, X. Li, H.P. Hratchian, A.F. Izmaylov, J. Bloino, G. Zheng, J.L. Sonnenberg, M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J. Hasegawa, M. Ishida, T. Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, T. Vreven, J.A. Montgomery Jr., J.E. Peralta, F. Ogliaro, M. Bearpark, J.J. Heyd, E. Brothers, K.N. Kudin, V.N. Staroverov, R. Kobayashi, J. Normand, K. Raghavachari, A. Rendell, J.C. Burant, S.S. Iyengar, J. Tomasi, M. Cossi, N. Rega, J.M. Millam, M. Klene, J.E. Knox, J.B. Cross, V. Bakken, C. Adamo, J. Jaramillo, R. Gomperts, R.E. Stratmann, O. Yazyev, A.J. Austin, R. Cammi, C. Pomelli, J.W. Ochterski, R.L. Martin, K. Morokuma, V.G. Zakrzewski, G.A. Voth, P. Salvador, J.J. Dannenberg, S. Dapprich, A.D. Daniels, O. Farkas, J.B. Foresman, J.V. Ortiz, J. Cioslowski, D.J. Fox, Gaussian 09, rev. A.02 (Gaussian Inc, Wallingford, 2009)
Acknowledgments
S. Das acknowledges Amity University Kolkata for infrastructural support. K Dutta acknowledges the financial support from the Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, through the TARE Scheme [No.TAR/2018/000420].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, F., Prusty, S., Saha, P. et al. Bimodal surface modification strategies towards improving the antibacterial activity of graphene oxide. Journal of Materials Research 38, 4247–4260 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01138-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01138-y