Abstract
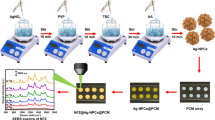
Biomass-derived porous carbon (PC) loaded with precious metals have a synergistic enhancement effect on surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). In this paper, PC containing various functional groups and large specific surface area, good stability and certain biocompatibility were prepared using tomato skins and introduced into the preparation of Ag nanoflowers (NFs) SERS substrates. Rhodamine 6G (R6G) was used as the Raman probe molecule to evaluate the sensing performance of Ag NFs@PC. The results showed that the stable dispersion and protective effect of PC on Ag NPs significantly improved the sensitivity and long-term stability of traditional Ag NFs. In practical application, Ag NFs@PC was further used to successfully achieve the quantitative analysis of trace methylene blue (10 ppt) and malachite green (10 ppt) in a lake water system. Therefore, SERS sensor Ag NFs@PC is expected to become a promising candidate sensor for detecting in the field of environment and food monitoring.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
X. Dong, H. Gu, J. Kang, X. Yuan, J. Wu, Effects of the surface modification of silver nanoparticles on the surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of methylene blue for borohydride-reduced silver colloid. J. Mol. Struct. 984, 396 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2010.10.014
G. Yang, X. Fang, Q. Jia, H. Gu, Y. Li, C. Han, L. Qu, Fabrication of paper-based SERS substrates by spraying silver and gold nanoparticles for SERS determination of malachite green, methylene blue, and crystal violet in fish. Mikrochim Acta (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04262-2
A. Otto, The ‘chemical’ (electronic) contribution to surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Raman Spectrosc. 36, 497 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.1355
K. Katrin, Y. Wang, K. Harald, L.T. Perelman, I. Irving, R.D. Ramachandra, S.F. Michael, Single molecule detection using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1667 (1997)
J. Zeng, Y. Zhang, T. Zeng, R. Aleisa, Z. Qiu, Y. Chen, J. Huang, D. Wang, Z. Yan, Y. Yin, Anisotropic plasmonic nanostructures for colorimetric sensing. Nano Today (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2020.100855
A.I. Perez-Jimenez, D. Lyu, Z. Lu, G. Liu, B. Ren, Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: benefits, trade-offs and future developments. Chem Sci 11(18), 4563–4577 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0sc00809e
J. Zhang, Y. Wang, X. Zhang, W. Xie, J. Li, Z. Wang, Study of the fabrication of gold nanoparticle-graphene-arrayed micro/nanocavities as SERS substrates compared to two different angles of triangular pyramid tips. Langmuir 38, 4894 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.2c00187
C. Caro, P. Quaresma, E. Pereira, J. Franco, L.M. Pernia, M.L. Garcia-Martin, J.L. Royo, J.M. Oliva-Montero, P.J. Merkling, A.P. Zaderenko, D. Pozo, R. Franco, Synthesis and characterization of elongated-shaped silver nanoparticles as a biocompatible anisotropic SERS probe for intracellular imaging: theoretical modeling and experimental verification. Nanomaterials (Basel) (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020256
S. Rodal-Cedeira, A. Vazquez-Arias, G. Bodelon, A. Skorikov, S. Nunez-Sanchez, A. Laporta, L. Polavarapu, S. Bals, L.M. Liz-Marzan, J. Perez-Juste, I. Pastoriza-Santos, An expanded surface-enhanced Raman scattering tags library by combinatorial encapsulation of reporter molecules in metal nanoshells. ACS Nano 14, 14655 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c04368
R. John, R.L.B. Lombardi, A unified view of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Acc. Chem. Res. 42, 734 (2008)
P.D. Nallathamby, T. Huang, X.H. Xu, Design and characterization of optical nanorulers of single nanoparticles using optical microscopy and spectroscopy. Nanoscale 2, 1715 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0nr00303d
S.Y. Ding, E.M. You, Z.Q. Tian, M. Moskovits, Electromagnetic theories of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46, 4042 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00238f
J. Reguera, J. Langer, A.D. Jimenez, L.M. Liz-Marzan, Anisotropic metal nanoparticles for surface enhanced Raman scattering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46, 3866 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00158d
B.N. Khlebtsov, V.A. Khanadeev, A.M. Burov, R.E.C. Le, N.G. Khlebtsov, Reexamination of surface-enhanced Raman scattering from gold nanorods as a function of aspect ratio and shape. J. Phys. Chem. C 124, 10647 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c00991
P. Rodriguez-Zamora, C.A. Cordero-Silis, J. Fabila, J.C. Luque-Ceballos, F. Buendia, A. Heredia-Barbero, I.L. Garzon, Interaction mechanisms and interface configuration of cysteine adsorbed on gold, silver, and copper nanoparticles. Langmuir 38, 5418 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c03298
Q. Ding, J. Wang, X. Chen, H. Liu, Q. Li, Y. Wang, S. Yang, Quantitative and sensitive SERS platform with analyte enrichment and filtration function. Nano Lett. 20, 7304 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c02683
L. Dykman, N. Khlebtsov, Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 2256 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cs15166e
X. Bo, K. Xiang, Y. Zhang, Y. Shen, S. Chen, Y. Wang, M. Xie, X. Guo, Microwave-assisted conversion of biomass wastes to pseudocapacitive mesoporous carbon for high-performance supercapacitor. J. Energy Chem. 39, 1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2019.01.006
Y. Jiang, J.L. Yue, Q. Guo, Q. Xia, C. Zhou, T. Feng, J. Xu, H. Xia, Highly porous Mn3O4 micro/nanocuboids with in situ coated carbon as advanced anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Small 14, e1704296 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201704296
B. Ashourirad, M. Demir, R.A. Smith, R.B. Gupta, H.M. El-Kaderi, Rapid transformation of heterocyclic building blocks into nanoporous carbons for high-performance supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 8, 12300 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra00546j
C. Fang, P. Hu, S. Dong, Y. Cheng, D. Zhang, X. Zhang, Construction of carbon nanorods supported hydrothermal carbon and carbon fiber from waste biomass straw for high strength supercapacitor. J Colloid. Interface Sci. 582, 552 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.07.139
M. Zhu, M. Li, M. Su, J. Liu, B. Liu, Y. Ge, H. Liu, J. Hu, Can “hot spots” be stable enough for surface-enhanced Raman scattering? J. Phys. Chem. C 24, 125 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c03321
N.H. Kim, W. Hwang, K. Baek, M.R. Rohman, J. Kim, H.W. Kim, J. Mun, S.Y. Lee, G. Yun, J. Murray, J.W. Ha, J. Rho, M. Moskovits, K. Kim, Smart SERS hot spots: single molecules can be positioned in a plasmonic nanojunction using host-guest chemistry. J Am Chem. Soc. 13, 140 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b01501
C. Zhang, C. Li, J. Yu, S. Jiang, S. Xu, C. Yang, Y.J. Liu, X. Gao, A. Liu, B. Man, SERS activated platform with three-dimensional hot spots and tunable nanometer gap. Aensor Actuat. B. Chem. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.11.080
W. Zhang, L. Hao, Q. Lin, C. Lu, Z. Xu, X. Chen, Template-free fabrication and morphology regulation of Ag@carbon composite structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 190, 1 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2014.09.006
E. Lam, J.H.T. Luong, Carbon materials as catalyst supports and catalysts in the transformation of biomass to fuels and chemicals. ACS Catal. 4, 3393 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/cs5008393
J. Wang, Y. Zhao, H. Huang, T. Cong, H. Zhang, K. Liu, L. Pan, Facile synthesis of hybrid silver/porous carbon black substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Appl. Surf. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146948
X. Liu, Y. Fu, Q. Sheng, J. Zheng, Au nanoparticles attached Ag@C core-shell nanocomposites for highly selective electrochemical detection of dopamine. Microchem. 146, 509 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.01.023
W. Tong, Y. Xie, H. Luo, J. Niu, W. Ran, W. Hu, L. Wang, C. Yao, W. Liu, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, Phosphorus-rich microorganism-enabled synthesis of cobalt phosphide/carbon composite for bisphenol A degradation through activation of peroxymonosulfate. Chem. Eng. J. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122187
W. Zhong, W. Tu, Z. Wang, Z. Lin, A. Xu, X. Ye, D. Chen, B. Xiao, Ultralow-temperature assisted synthesis of single platinum atoms anchored on carbon nanotubes for efficiently electrocatalytic acidic hydrogen evolution. J Energy Chem. 51, 280 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2020.04.035
P.K. Midhun, S. Murugavelh, Experimental investigation and kinetics of tomato peel pyrolysis: performance, combustion and emission characteristics of bio-oil blends in diesel engine. J Clean. Prod. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120115
C. Rock, W. Yang, R.F.H. Goodrich-Schneider, Conventional and alternative methods for tomato peeling. Food Eng. Rev. 4, 1 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-011-9047-3
E. Elbadrawy, A. Sello, Evaluation of nutritional value and antioxidant activity of tomato peel extracts. Arab. J. Chem. 9, S1010 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2011.11.011
Z. Lu, J. Wang, R. Gao, F. Ye, G. Zhao, Sustainable valorisation of tomato pomace: Aa comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 86, 172 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.02.020
J. Zhu, L. Hu, P. Zhao, L.Y.S. Lee, K.Y. Wong, Recent advances in electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution using nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 120, 851 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00248
B.N. Riswana, T. Wang, Y. Chang, In-situ deposition of silver nanoparticles on silver nanoflowers for ultrasensitive and simultaneous SERS detection of organic pollutants. Microchem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.10552010
S. Zhang, X. Liu, N. Huang Q., Lu, M. Liu, H. Li, Y. Zhang, and S. Yao: Sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide and nitrite based on silver/carbon nanocomposite synthesized by carbon dots as reductant via one step method. Electrochimica Acta 211, (2016) . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.06.024
S.S. Mozhgan, K. Iraj, and N. Manijeh: Synthesis and characterization of Ag@Carbon core-shell spheres as a novel catalyst for room temperature N-arylation reaction. J. Catal. 361, (2018) . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2018.02.029
A. Kalam, A.G. Al-Sehemi, S. Alrumman, G. Du, M. Assiri, A.E. Hesham, Antibacterial studies of bio-functionalized carbon decorated silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). J. Indian Chem. Soc. 10, 98 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jics.2021.100155
A. Villalan, M. Mannacharaju, B. Ramasamy, K. Sekar, M.R. Regina, S. Ganesan, Functioned silver nanoparticle loaded activated carbon for the recovery of bioactive molecule from bacterial fermenter for its bactericidal activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.128
C.S. Barrera, K. Cornish, Novel mineral and organic materials from agro-industrial residues as fillers for natural rubber. J Polym. Environ. 4, 23 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-015-0737-4
S. Kamal, A. Chowdhury, T.C.K. Yang, Ultrasensitive SERS detection of Rhodamine 6G using a silver enriched MOF-derived CuFe2O4 microcubes substrate. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 270, 120826 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120826
N. Tanaka, H. Nishikiori, S. Kubota, M. Endo, T. Fujii, Photochemical deposition of Ag nanoparticles on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 47, 2752 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2009.05.030
M. Zhang, H. Sun, X. Chen, H. Zhou, L. Xiong, W. Chen, Z. Chen, Z. Bao, and Y. Wu: The influences of graphene oxide (GO) and plasmonic Ag nanoparticles modification on the SERS sensing performance of TiO2 nanosheet arrays. J. Alloys Compd., (2021) . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.158189
X. Zhang, L. Chen, X. Fang, Y. Shang, H. Gu, W. Jia, G. Yang, Y. Gu, L. Qu, Rapid and non-invasive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) detection of chlorpyrifos in fruits using disposable paper-based substrates charged with gold nanoparticle/halloysite nanotube composites. Mikrochim. Acta 189, 197 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05261-1
Z. Li, R. Hong, Q. Liu, Q. Wang, C. Tao, H. Lin, and D. Zhang: Laser patterning induced the tunability of nonlinear optical property in silver thin films. Chem. Phys. Lett. 751, (2020) . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2020.137535
S. Yin, D. Zhao, Q. Ji, Y. Xia, S. Xia, X. Wang, M. Wang, J. Ban, Y. Zhang, E. Metwalli, X. Wang, Y. Xiao, X. Zuo, S. Xie, K. Fang, S. Liang, L. Zheng, B. Qiu, Z. Yang, Y. Lin, L. Chen, C. Wang, Z. Liu, J. Zhu, P. Muller-Buschbaum, Y.J. Cheng, Si/Ag/C Nanohybrids with in Situ Incorporation of Super-Small Silver Nanoparticles: Tiny Amount. Huge Impact. ACS Nano 12, 861 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b08560
S. Kaja, A. Nag, Bimetallic Ag-Cu Alloy Microflowers as SERS Substrates with Single-Molecule Detection Limit. Langmuir 44, 37 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c02119
G.N. Xiao, S.Q. Man, Surface-enhanced Raman scattering of methylene blue adsorbed on cap-shaped silver nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 447, 305 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2007.09.045
M. Tiwari, A. Singh, S. Dureja, S. Basu, S.K. Pattanayek, Au nanoparticles decorated ZnO/ZnFe2O4 composite SERS-active substrate for melamine detection. Talanta 236, 122819 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122819
Z.H. Li, J.H. Bai, X. Zhang, J.M. Lv, C.S. Fan, Y.M. Zhao, Z.L. Wu, H.J. Xu, Facile synthesis of Au nanoparticle-coated Fe3O4 magnetic composite nanospheres and their application in SERS detection of malachite green. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 241, 118532 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118532
J. Li, Q. Wang, J. Wang, M. Li, X. Zhang, L. Luan, P. Li, W. Xu, Quantitative SERS sensor based on self-assembled Au@Ag heterogeneous nanocuboids monolayer with high enhancement factor for practical quantitative detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 413, 4207 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03366-9
J. He, G. Song, X. Wang, L. Zhou, J. Li: Multifunctional magnetic Fe3O4/GO/Ag composite microspheres for SERS detection and catalytic degradation of methylene blue and ciprofloxacin. J. Alloys Compd. 893, (2022) . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162226
V.N. Kuryakov, Phase behavior of n-octadecane in the form of water dispersion by the optical method. Mendeleev Commun. 3, 417 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mencom.2022.05.043
S. Naoki, M. Mitsuharu, F. Tomonori, Fukui Kunihiro, and Y. Hideto: Fine particle classification by a vertical type electrical water-sieve with various particle dispersion methods. Sep. Purif. Technol. 175, 107 (2017) . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.11.009
D. Zhang, P. Liang, J. Ye, J. Xia, Y. Zhou, J. Huang, D. Ni, L. Tang, S. Jin, Z. Yu, Detection of systemic pesticide residues in tea products at trace level based on SERS and verified by GC-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 27, 7187 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02103-7
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province (QKHJ[2020]1Y259); the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (2021D01C066); the United Foundation of Zunyi City and Zunyi Normal Collage (ZSKHHZ272); and the Education Department of Guizhou Provinceunder Grants (QJHKY[2019]115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have approved for the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Wang, Q., Yang, J. et al. Biomass-derived porous carbon-protected silver nanoflowers construction of long-term stable SERS substrate for ultrasensitive detection of organic pollution. Journal of Materials Research 38, 519–531 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00839-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00839-0