Abstract
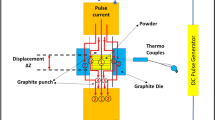
In present work, Ti-Al3Ti core–shell structured particle reinforced Al matrix composites were fabricated via powder metallurgy technique followed by annealing process. The results indicated that via adjusting annealing parameters, Ti-Al3Ti core–shell particles with 8:0, 2:1, 1:1, and 1:15 volume fraction ratio of Ti to Al3Ti, respectively, were in situ formed in the prepared composites. With the reduction of volume fraction ratio of Ti to Al3Ti, the compressive strength of the composite increases gradually. Besides, as the volume fraction ratio of Ti to Al3Ti reaches 1:1, the composite shows the best wear resistance among these studied specimens. Furthermore, the relationship between sliding time and wear mechanisms of the composite was investigated in detail via friction and wear tests. As the sliding time increased constantly, the main wear mechanism of the composite is changed from adhesion wear to a combination of fatigue, adhesion, oxidation, and abrasion wear.
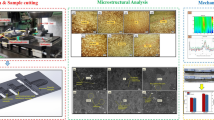
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time due to legal or ethical reasons.
References
K. Ma, E.J. Lavernia, J.M. Schoenung, Particulate reinforced aluminum alloy matrix composites-A review on the effect of microconstituents. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 48(2), 91–104 (2017)
J.M. Torralba, C. Costa, F. Velasco, P/M aluminum matrix composites: an overview. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 133(1–2), 203–206 (2003)
S.T. Mavhungu, E.T. Akinlabi, M.A. Onitiri et al., Aluminum matrix composites for industrial use: advances and Trends. Proc. Manuf. 7, 178–182 (2016)
R. Casati, M. Vedani, Metal matrix composites reinforced by nano-particles-a review. Metals-Open Access Metall. J. 4(1), 65–83 (2014)
X. Deng, N. Chawla, Modeling the effect of particle clustering on the mechanical behavior of SiC particle reinforced Al matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 41(17), 5731–5734 (2006)
C. Sun, R. Shen, M. Song et al., Mechanical behaviors of SiC particle reinforced Al matrix composites: a study based on finite element method. Adv. Mater. Res. 535–537, 3–7 (2012)
Y. Xiong, W. Wang, R. Jiang et al., Tool wear mechanisms for milling in situ TiB2 particle-reinforced Al matrix composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 86, 9–12 (2016)
Z. Ge, Z. Shi, T. Na et al., Effect of the heating rate on the microstructure of in situ Al2O3 particle-reinforced Al matrix composites prepared via displacement reactions in an Al/CuO system. Mater. Des. 66, 492–497 (2015)
X. Wang, A. Jha, R. Brydson, In situ fabrication of Al3Ti particle reinforced aluminium alloy metal-matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 364(1–2), 339–345 (2004)
F.M. Heim, Y. Zhang, X. Li, Uniting strength and toughness of Al matrix composites with coordinated Al3Ni and Al3Ti reinforcements. Adv. Eng. Mater. 20(1), 1700605 (2018)
X. Guo, Q. Guo, Z. Li et al., Interfacial strength and deformation mechanism of SiC-Al composite micro-pillars. Scripta Mater. 114, 56–59 (2016)
P. Liu, A. Wang, J. Xie et al., Characterization and evaluation of interface in SiCp/2024 Al composite. Trans. Nonferrous Metals Soc. China 25(5), 1410–1418 (2015)
S. Selvakumar, I. Dinaharan, R. Palanivel et al., Characterization of molybdenum particles reinforced Al6082 aluminum matrix composites with improved ductility produced using friction stir processing. Mater. Charact. 125, 13–22 (2017)
P. Krishnan, P. Lakshmanan, S. Palani et al., Analyzing the hardness and wear properties of SiC and hBN reinforced aluminum hybrid nanocomposites. Mater. Today 62(2), 566–571 (2022)
B. Guo, N. Song, R. Shen et al., Fabrication of Ti-Al3Ti core-shell structured particle reinforced Al based composite with promising mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 639, 269–273 (2015)
W. Wu, B. Guo, Y. Xue et al., Ni-AlxNiy core-shell structured particle reinforced Al-based composites fabricated by in-situ powder metallurgy technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 160, 352–358 (2015)
Y. Wang, M. Song, S. Ni et al., In situ formed core-shell structured particle reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Mater. Des. 56, 405–408 (2014)
Y. Xue, R. Shen, S. Ni et al., Fabrication, microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Fe intermetallic particle reinforced Al-based composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 618, 537–544 (2015)
M.T. Junqani, H. Hosseini, A. Azarniya, Comprehensive structural and mechanical characterization of in-situ Al-Al3Ti nanocomposite modified by heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 785, 139351 (2020)
B. Guo, M. Song, X. Zhang et al., Achieving high combination of strength and ductility of Al matrix composite via in-situ formed Ti-Al3Ti core-shell particle. Mater. Charact. 170, 110666 (2020)
S. Ma, X. Zhang, T. Chen et al., Microstructure-based numerical simulation of the mechanical properties and fracture of a Ti-Al3Ti core-shell structured particulate reinforced A356 composite. Mater. Des. 191, 108685 (2020)
L. Peng, H. Li, J. Wang, Processing and mechanical behavior of laminated titanium-titanium tri-aluminide (Ti-Al3Ti) composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 406(1–2), 309–318 (2005)
Y. Huashun, H. Chen, L. Sun et al., Preparation of Al-Al3Ti in situ composites by direct reaction method. Rare Met. 25(1), 32–36 (2006)
X. Cui, G. Fan, G. Lin et al., Growth kinetics of TiAl3 layer in multi-laminated Ti-(TiB2/Al) composite sheets during annealing treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 539, 337–343 (2012)
Y. Zhao, J. Li, R. Qiu et al., Growth characterization of intermetallic compound at the Ti/Al solid state interface. Materials 12(3), 472 (2019)
L. Xu, Y. Cui, Y. Hao et al., Growth behavior of intermetallic compound layer in multi-laminated Ti-Al diffusion couples. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 435–436, 638–647 (2006)
M. Yuan, L. Li, Z. Wang, Study of the microstructure modulation and phase formation of Ti Al3Ti laminated composites. Vacuum 157, 481–486 (2018)
M. Tavoosi, The Kirkendall void formation in Al/Ti interface during solid-state reactive diffusion between Al and Ti. Surf. Interfaces 9, 196–200 (2017)
N. Thiyaneshwaran, K. Sivaprasad, B. Ravisankar, Nucleation and growth of TiAl3 intermetallic phase in diffusion bonded Ti/Al metal intermetallic laminate. Sci. Rep. 8, 16797 (2018)
Y. He, Y. Jiang, N. Xu et al., Fabrication of Ti-Al micro/nanometer-sized porous alloys through the Kirkendall effect. Adv. Mater. 19(16), 2102–2106 (2007)
L. Peng, J. Wang, H. Li et al., Synthesis and microstructural characterization of Ti-Al3Ti metal-intermetallic laminate (MIL) composites. Scripta Mater. 52(3), 243–248 (2005)
C. Lin, F. Jiang, Y. Han et al., Microstructure evolution and fracture behavior of innovative Ti-(SiCf/Al3Ti) laminated composites. J. Alloy Compd. 743, 52–62 (2018)
Y. Han, C. Lin, X. Han et al., Fabrication, interfacial characterization and mechanical properties of continuous Al2O3 ceramic fiber reinforced Ti/Al3Ti metal-intermetallic laminated (CCFR-MIL) composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 688, 338–345 (2017)
M. Mirjalili, M. Soltanieh, K. Matsuura et al., On the kinetics of TiAl3 intermetallic layer formation in the titanium and aluminum diffusion couple. Intermetallics 32, 297–302 (2013)
C. Lin, Y. Han, C. Guo et al., Synthesis and mechanical properties of novel Ti-(SiCf/Al3Ti) ceramic-fiber-reinforced metal-intermetallic-laminated (CFR-MIL) composites. J. Alloy Compd. 722, 427–437 (2017)
S. Lu, L. Wang, J. Zhang et al., Microstructure and tribological properties of laser-cladded Co-Ti3SiC2 coating with Ni-based interlayer on copper alloy. Tribol. Int. 171, 107549 (2022)
X. Liu, J. Yang, J. Hao et al., A near-frictionless and extremely elastic hydrogenated amorphous carbon film with self-assembled dual nanostructure. Adv. Mater. 24(34), 4614–4617 (2012)
T. Weikert, S. Wartzack, M.V. Baloglu et al., Evaluation of the surface fatigue behavior of amorphous carbon coatings through cyclic. Surf. Coat. Technol. 407, 126769 (2021)
C.J. Hsu, C. Chang, P. Kao et al., Al-Al3Ti nanocomposites produced in situ by friction stir processing. Acta Mater. 54(19), 5241–5249 (2006)
Q. Zhang, B. Xiao, D. Wang et al., Formation mechanism of in situ Al3Ti in Al matrix during hot pressing and subsequent friction stir processing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 130(3), 1109–1117 (2011)
Y. Wang, C. Wu, L. Zhang et al., Thermal oxidation and its effect on the wear of Mg alloy AZ31B. Wear 476, 203673 (2021)
C. Liu, F. Su, J. Liang, Nanocrystalline Co-Ni alloy coating produced with supercritical carbon dioxide assisted electrodeposition with excellent wear and corrosion resistance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 292, 37–43 (2016)
J.K. Lancaster, The influence of temperature on metallic wear. Proc. Phys. Soc. 70(1), 112–118 (1957)
J. Zhou, D. Kong, Friction-wear performances and oxidation behaviors of Ti3AlC2 reinforced Co-based alloy coatings by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 408(25), 126816 (2021)
K. Zhang, J. Deng, R. Meng et al., Influence of laser substrate pretreatment on anti-adhesive wear properties of WC/Co-based TiAlN coatings against AISI 316 stainless steel. Int. J. Refract Metal Hard Mater. 57, 101–114 (2016)
S.C. Lim, J.H. Brunton, The unlubricated wear of sintered iron. Wear 113(3), 371–382 (1986)
I.A. Ditenberg, D.A. Osipov, M.A. Korchagin, et al. Influence of ball milling duration on the morphology, features of the structural-phase state and microhardness of 3Ni-Al powder mixture. Advanced Powder Technology (2021)
J. An, R.G. Li, Y. Lu et al., Dry sliding wear behavior of magnesium alloys. Wear 265, 97–104 (2008)
J. Su, J. Teng, Z. Xu et al., Corrosion-wear behavior of a biocompatible magnesium matrix composite in simulated body fluid. Friction 10(1), 31–43 (2022)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports of this study by the Natural Science foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20220690), Initial Scientific Research Fund in Changshu Institute of Technology (Grant Nos. KYZ2018044Q, KYZ2018043Q) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51901058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y., Liu, J., Wang, Q. et al. Effect of volume fraction ratio of Ti to Al3Ti on mechanical and tribological performances of the in situ Ti–Al3Ti core–shell structured particle reinforced Al matrix composite. Journal of Materials Research 37, 3695–3707 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00742-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00742-8