Abstract
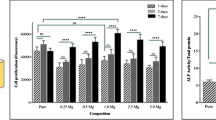
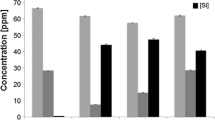
In this study, we introduced new magnetic nanoparticles based on iron oxide and Mg-phosphate ceramic (nMgP-Fe) for treatment of bone and pulp-dentin diseases. nMgP-Fe was characterized for the size, magnetism, and degradation properties, and its viability against human dental pulp-derived mesenchymal stem cells (DPSCs) was investigated as a first step to evaluate this material for dental pulp regeneration. The results showed that nMgP-Fe was characterized by its nanosize (10–40 nm), and the formed crystalline phases were farringonite and magnetite. Super-paramagnetic properties of nMgP-Fe were proved (coercivity and residual magnetization values were 20 Oe and 0.06 emu/g, respectively). The dissolution test demonstrated less release of iron ions than magnesium and phosphate ions. DPSCs incubated with nMgP-Fe particles showed a higher proliferation rate and increased osteogenic differentiation potentials compared to the control group. In conclusion, the new fabricated nanosized nMgP-Fe with its supramagnetic properties had biocompatible properties that make them a promising material for bone and pulp-dentin regeneration.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that have been used in this work are not available to be shared, as they are confidential data.
References
M. Pečová, L. Zajoncova, K. Polakova, J. Čuda, M. Šafaříková, M. Šebela, I. Šafařík, Biologically active compounds immobilized on magnetic carriers and their utilization in biochemistry and biotechnology. Chemické listy 105 (2011)
H. Vaghari, H. Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, M. Mohammadlou, A. Berenjian, N. Anarjan, N. Jafari, S. Nasiri, Application of magnetic nanoparticles in smart enzyme immobilization. Biotechnol. Lett. 38, 223–233 (2016)
A. Avasthi, C. Caro, E. Pozo-Torres, M.P. Leal, M.L. García-Martín, Magnetic nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents. Top. Curr. Chem. 378, 40 (2020)
S.-J. Lee, J.-R. Jeong, S.-C. Shin, J.-C. Kim, Y.-H. Chang, Y.-M. Chang, J.-D. Kim, Nanoparticles of magnetic ferric oxides encapsulated with poly(D, L latide-co-glycolide) and their applications to magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 272–276, 2432–2433 (2004)
A.J. Giustini, A.A. Petryk, S.M. Cassim, J.A. Tate, I. Baker, P.J. Hoopes, Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia in cancer treatment. Nano Life 1, 17–32 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793984410000067
M. Bañobre-López, A. Teijeiro, J. Rivas, Magnetic nanoparticle-based hyperthermia for cancer treatment. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 18, 397–400 (2013)
M. Kubovcikova, M. Koneracka, O. Strbak, M. Molcan, V. Zavisova, I. Antal, I. Khmara, D. Lucanska, L. Tomco, M. Barathova, M. Zatovicova, D. Dobrota, S. Pastorekova, P. Kopcansky, Poly-L-lysine designed magnetic nanoparticles for combined hyperthermia, magnetic resonance imaging and cancer cell detection. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 475, 316–326 (2019)
M. Ansari, A. Bigham, S.A. Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi, H. Abbastabar Ahangar, Synthesis and characterization of Cu0.3Zn0.5Mg0.2Fe2O4 nanoparticles as a magnetic drug delivery system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 439, 67–75 (2017)
J. Panda, B.S. Satapathy, S. Majumder, R. Sarkar, B. Mukherjee, B. Tudu, Engineered polymeric iron oxide nanoparticles as potential drug carrier for targeted delivery of docetaxel to breast cancer cells. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 485, 165–173 (2019)
Y. Ji, S.K. Choi, A.S. Sultan, K. Chuncai, X. Lin, E. Dashtimoghadam, M.A. Melo, M. Weir, H. Xu, L. Tayebi, Z. Nie, D.A. Depireux, R. Masri, Nanomagnetic-mediated drug delivery for the treatment of dental disease. Nanomedicine 14, 919–927 (2018)
Y. Li, X. Hu, Y. Xia, Y. Ji, J. Ruan, M.D. Weir, X. Lin, Z. Nie, N. Gu, R. Masri, X. Chang, H.H.K. Xu, Novel magnetic nanoparticle-containing adhesive with greater dentin bond strength and antibacterial and remineralizing capabilities. Dent. Mater. 34, 1310–1322 (2018)
D. Ramimoghadam, S. Bagheri, S.B.A. Hamid, Progress in electrochemical synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 368, 207–229 (2014)
H. Shokrollahi, A review of the magnetic properties, synthesis methods and applications of maghemite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 74–81 (2017)
M.B. Sathyanarayanan, R. Balachandranath, Y. Genji Srinivasulu, S.K. Kannaiyan, G. Subbiahdoss, The effect of gold and iron-oxide nanoparticles on biofilm-forming pathogens. Int. Scholarly Res. Not. (2013)
I.M. Garcia, A.A. Balhaddad, Y. Lan, A. Simionato, M.S. Ibrahim, M.D. Weir, R. Masri, H.H.K. Xu, F.M. Collares, M.A.S. Melo, Magnetic motion of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles- loaded dental adhesives: physicochemical/biological properties, and dentin bonding performance studied through the tooth pulpal pressure model. Acta Biomater. (2021)
Y. Li, X. Hu, Y. Xia, Y. Ji, J. Ruan, M.D. Weir, X. Lin, Z. Nie, N. Gu, R. Masri, Novel magnetic nanoparticle-containing adhesive with greater dentin bond strength and antibacterial and remineralizing capabilities. Dent. Mater. 34, 1310–1322 (2018)
R.A. Frimpong, J.Z. Hilt, Magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine: synthesis, functionalization and applications. Nanomedicine 5, 1401–1414 (2010)
Z. Mei, A. Dhanale, A. Gangaharan, D.K. Sardar, L. Tang, Water dispersion of magnetic nanoparticles with selective biofunctionality for enhanced plasmonic biosensing. Talanta 151, 23–29 (2016)
E.-J. Park, H. Kim, Y. Kim, J. Yi, K. Choi, K. Park, Inflammatory responses may be induced by a single intratracheal instillation of iron nanoparticles in mice. Toxicology 275, 65–71 (2010)
S.A.M. Abdel-Hameed, M.A. Marzouk, M.M. Farag, Effect of P2O5 and MnO2 on crystallization of magnetic glass ceramics. J. Adv. Res. 5, 543–550 (2014)
G. Da Li, D.L. Zhou, Y. Lin, T.H. Pan, G.S. Chen, Q.D. Yin, Synthesis and characterization of magnetic bioactive glass-ceramics containing Mg ferrite for hyperthermia. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 30, 148–153 (2010)
M.V. Velasco, M.T. Souza, M.C. Crovace, A.J.A. de Oliveira, E.D. Zanotto, Bioactive magnetic glass-ceramics for cancer treatment. Biomed. Glasses 5, 148–177 (2019)
J.A. Ramos-Guivar, A.C. Krohling, E.O. López, F. Jochen Litterst, E.C. Passamani, Superspinglass behavior of maghemite nanoparticles dispersed in mesoporous silica. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 485, 142–150 (2019)
H. Keshavarz, A. Khavandi, S. Alamolhoda, M.R. Naimi-Jamal, Magnetite mesoporous silica nanoparticles embedded in carboxybetaine methacrylate for application in hyperthermia and drug delivery. New J. Chem. 44, 8232–8240 (2020)
E. Cheraghipour, A.M. Tamaddon, S. Javadpour, I.J. Bruce, PEG conjugated citrate-capped magnetite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 328, 91–95 (2013)
C.L. Altan, B. Gurten, R. Sadza, E. Yenigul, N.A.J.M. Sommerdijk, S. Bucak, Poly(acrylic acid)-directed synthesis of colloidally stable single domain magnetite nanoparticles via partial oxidation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 416, 366–372 (2016)
E. Illés, M. Szekeres, I.Y. Tóth, Á. Szabó, B. Iván, R. Turcu, L. Vékás, I. Zupkó, G. Jaics, E. Tombácz, Multifunctional PEG-carboxylate copolymer coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical application. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 451, 710–720 (2018)
T. Iwasaki, R. Nakatsuka, K. Murase, H. Takata, H. Nakamura, S. Watano, Simple and rapid synthesis of magnetite/hydroxyapatite composites for hyperthermia treatments via a mechanochemical route. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14, 9365–9378 (2013)
G. Bharath, K. Rambabu, A. Hai, S. Anwer, F. Banat, N. Ponpandian, Synthesis of one-dimensional magnetite hydroxyapatite nanorods on reduced graphene oxide sheets for selective separation and controlled delivery of hemoglobin. Appl. Surf. Sci. 501, 144215 (2020)
H. Kawahara, Bioceramics for hard tissue replacements. Clin. Mater. 2, 181–206 (1987)
X. Pan, J. Huang, K. Zhang, Z. Pei, Z. Ding, Y. Liang, Z. Gu, G. Li, H. Xie, Iron-doped brushite bone cement scaffold with enhanced osteoconductivity and antimicrobial properties for jaw regeneration. Ceram. Int. 47, 25810–25820 (2021)
E.I. Ruskin, P.P. Coomar, P. Sikder, S.B. Bhaduri, Magnetic calcium phosphate cement for hyperthermia treatment of bone tumors. Materials 13, 3501 (2020)
S. Sakka, J. Bouaziz, F.B. Ayed, Advances in biomaterials science and biomedical applications, Chapter Book: Mechanical Properties of Biomaterials Based on Calcium Phosphates and Bioinert Oxides for Applications in Biomedicine, InTech Croatia (2013), pp. 23–50
A.K. Sarkar, Phosphate cement-based fast-setting binders. Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 69, 234–238 (1990)
S. Xing, C. Wu, Preparation of Magnesium Phosphate Cement and Application in Concrete Repair, MATEC Web of Conferences, EDP Sciences (2018) ,p. 02007.
A.S. Wagh, C. Primus, Method and product for phosphosilicate slurry for use in dentistry and related bone cements, Google Patents (2006).
S. Meininger, C. Blum, M. Schamel, J.E. Barralet, A. Ignatius, U. Gbureck, Phytic acid as alternative setting retarder enhanced biological performance of dicalcium phosphate cement in vitro. Sci. Rep. 7, 558 (2017)
C. Moseke, V. Saratsis, U. Gbureck, Injectability and mechanical properties of magnesium phosphate cements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 22, 2591–2598 (2011)
F. Tamimi, D. Le Nihouannen, D.C. Bassett, S. Ibasco, U. Gbureck, J. Knowles, A. Wright, A. Flynn, S.V. Komarova, J.E. Barralet, Biocompatibility of magnesium phosphate minerals and their stability under physiological conditions. Acta Biomater. 7, 2678–2685 (2011)
Y. Yu, J. Wang, C. Liu, B. Zhang, H. Chen, H. Guo, G. Zhong, W. Qu, S. Jiang, H. Huang, Evaluation of inherent toxicology and biocompatibility of magnesium phosphate bone cement. Colloids Surf. B 76, 496–504 (2010)
J. Lee, M.M. Farag, E.K. Park, J. Lim, H.-S. Yun, A simultaneous process of 3D magnesium phosphate scaffold fabrication and bioactive substance loading for hard tissue regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 36, 252–260 (2014)
M.M. Farag, M.M. Ahmed, N.M. Abdallah, W. Swieszkowski, A.M. Shehabeldine, The combined antibacterial and anticancer properties of nano Ce-containing Mg-phosphate ceramic. Life Sci. 257, 117999 (2020)
M. Waselau, V.F. Samii, S.E. Weisbrode, A.S. Litsky, A.L. Bertone, Effects of a magnesium adhesive cement on bone stability and healing following a metatarsal osteotomy in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 68, 370–378 (2007)
F. Wu, J. Wei, H. Guo, F. Chen, H. Hong, C. Liu, Self-setting bioactive calcium–magnesium phosphate cement with high strength and degradability for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 4, 1873–1884 (2008)
B.-M. Seo, M. Miura, S. Gronthos, P.M. Bartold, S. Batouli, J. Brahim, M. Young, P.G. Robey, C.Y. Wang, S. Shi, Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. The Lancet 364, 149–155 (2004)
A. Pisciotta, M. Riccio, G. Carnevale, F. Beretti, L. Gibellini, T. Maraldi, G.M. Cavallini, A. Ferrari, G. Bruzzesi, A. De Pol, Human serum promotes osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 7, e50542 (2012)
A. Giuliani, A. Manescu, M. Langer, F. Rustichelli, V. Desiderio, F. Paino, A. De Rosa, L. Laino, R. d’Aquino, V. Tirino, Three years after transplants in human mandibles, histological and in-line holotomography revealed that stem cells regenerated a compact rather than a spongy bone: biological and clinical implications. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2, 316–324 (2013)
O. Veiseh, J.W. Gunn, M. Zhang, Design and fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 62, 284–304 (2010)
H. Zhou, T.J. Luchini, S.B. Bhaduri, Microwave assisted synthesis of amorphous magnesium phosphate nanospheres. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 23, 2831–2837 (2012)
A. Sinha, S. Nayar, A. Agrawal, D. Bhattacharyya, P. Ramachandrarao, Synthesis of nanosized and microporous precipitated hydroxyapatite in synthetic polymers and biopolymers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 86, 357–359 (2003)
M. Ishii, M. Nakahira, T. Yamanaka, Infrared absorption spectra and cation distributions in (Mn, Fe)3O4. Solid State Commun. 11, 209–212 (1972)
H. Namduri, S. Nasrazadani, Quantitative analysis of iron oxides using Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometry. Corros. Sci. 50, 2493–2497 (2008)
G. Perumal, P.M. Sivakumar, A.M. Nandkumar, M. Doble, Synthesis of magnesium phosphate nanoflakes and its PCL composite electrospun nanofiber scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 109, 110527 (2020)
Y.-W. Jun, Y.-M. Huh, J.-S. Choi, J.-H. Lee, H.-T. Song, S. Kim, S. Kim, S. Yoon, K.-S. Kim, J.-S. Shin, Nanoscale size effect of magnetic nanocrystals and their utilization for cancer diagnosis via magnetic resonance imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 5732–5733 (2005)
D.L. Huber, Synthesis, properties, and applications of iron nanoparticles. Small 1, 482–501 (2005)
F. Ozel, H. Kockar, Growth and characterizations of magnetic nanoparticles under hydrothermal conditions: reaction time and temperature. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 373, 213–216 (2015)
R.M. Cornell, U. Schwertmann, The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses (Wiley, New York, 2003)
M. Fang, V. Ström, R.T. Olsson, L. Belova, K.V. Rao, Particle size and magnetic properties dependence on growth temperature for rapid mixed co-precipitated magnetite nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 23, 145601 (2012)
G. Racz, R. Soper, Solubility of dimagnesium phosphate trihydrate and trimagnesium phosphate. Can. J. Soil Sci. 48, 265–269 (1968)
J. Anastassopoulou, T. Theophanides, The Role of Metal Ions in Biological Systems and Medicine, Bioinorganic Chemistry (Springer, New York, 1995), pp. 209–218
T. Michigami, M. Kawai, M. Yamazaki, K. Ozono, Phosphate as a signaling molecule and its sensing mechanism. Physiol. Rev. 98, 2317–2348 (2018)
E.M. Múzquiz-Ramos, D. Cortés-Hernández, J. Escobedo-Bocardo, A. Zugasti-Cruz, X. Ramírez-Gómez, J. Osuna-Alarcón, In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of apatite-coated magnetite nanoparticles for cancer therapy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 24, 1035–1041 (2013)
M.S. Laranjeira, A. Moço, J. Ferreira, S. Coimbra, E. Costa, A. Santos-Silva, P.J. Ferreira, F.J. Monteiro, Different hydroxyapatite magnetic nanoparticles for medical imaging: Its effects on hemostatic, hemolytic activity and cellular cytotoxicity. Colloids Surf. B 146, 363–374 (2016)
X. Guo, Y. Long, W. Li, H. Dai, Osteogenic effects of magnesium substitution in nano-structured β-tricalcium phosphate produced by microwave synthesis. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 11197–11212 (2019)
C. Liu, X. Fu, H. Pan, P. Wan, L. Wang, L. Tan, K. Wang, Y. Zhao, K. Yang, P.K. Chu, Biodegradable Mg-Cu alloys with enhanced osteogenesis, angiogenesis, and long-lasting antibacterial effects. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–17 (2016)
H. Windhagen, K. Radtke, A. Weizbauer, J. Diekmann, Y. Noll, U. Kreimeyer, R. Schavan, C. Stukenborg-Colsman, H. Waizy, Biodegradable magnesium-based screw clinically equivalent to titanium screw in hallux valgus surgery: short term results of the first prospective, randomized, controlled clinical pilot study. Biomed. Eng. 12, 1–10 (2013)
R. Zhang, Y. Lu, L. Ye, B. Yuan, S. Yu, C. Qin, Y. Xie, T. Gao, M.K. Drezner, L.F. Bonewald, Unique roles of phosphorus in endochondral bone formation and osteocyte maturation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 26, 1047–1056 (2011)
A. Angelucci, C. Festuccia, G.L. Gravina, P. Muzi, L. Bonghi, C. Vicentini, M. Bologna, Osteopontin enhances the cell proliferation induced by the epidermal growth factor in human prostate cancer cells. Prostate 59, 157–166 (2004)
Z. Wang, Y. Ma, J. Wei, X. Chen, L. Cao, W. Weng, Q. Li, H. Guo, J. Su, Effects of sintering temperature on surface morphology/microstructure, in vitro degradability, mineralization and osteoblast response to magnesium phosphate as biomedical material. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–11 (2017)
J.M. Díaz-Tocados, C. Herencia, J.M. Martínez-Moreno, A.M. de Oca, M.E. Rodríguez-Ortiz, N. Vergara, A. Blanco, S. Steppan, Y. Almadén, M. Rodríguez, Magnesium chloride promotes osteogenesis through notch signaling activation and expansion of mesenchymal stem cells. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–12 (2017)
A. Orimoto, S. Kyakumoto, T. Eitsuka, K. Nakagawa, T. Kiyono, T. Fukuda, Efficient immortalization of human dental pulp stem cells with expression of cell cycle regulators with the intact chromosomal condition. PLoS ONE 15, e0229996 (2020)
S. Naz, F.R. Khan, R.R. Zohra, S.S. Lakhundi, M.S. Khan, N. Mohammed, T. Ahmad, Isolation and culture of dental pulp stem cells from permanent and deciduous teeth. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 35, 997 (2019)
Y. Hadaegh, M. Niknam, A. Attar, M.K. Maharlooei, M.S. Tavangar, A.M. Aarabi, A. Monabati, Characterization of stem cells from the pulp of unerupted third molar tooth. Indian J. Dent. Res. 25, 14 (2014)
I. Kalaszczynska, S. Ruminski, A.E. Platek, I. Bissenik, P. Zakrzewski, M. Noszczyk, M. Lewandowska-Szumiel, Substantial differences between human and ovine mesenchymal stem cells in response to osteogenic media: how to explain and how to manage? BioRes. Open Access 2, 356–363 (2013)
S. Zhang, H. Geng, H. Xie, Q. Wu, X. Ma, J. Zhou, F. Chen, The heterogeneity of cell subtypes from a primary culture of human amniotic fluid. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 15, 424–439 (2010)
M. Zavatti, L. Bertoni, T. Maraldi, E. Resca, F. Beretti, M. Guida, G.B. La Sala, A. De Pol, Critical-size bone defect repair using amniotic fluid stem cell/collagen constructs: effect of oral ferutinin treatment in rats. Life Sci. 121, 174–183 (2015)
G. Fernandez de Grado, L. Keller, Y. Idoux-Gillet, Q. Wagner, A.-M. Musset, N. Benkirane-Jessel, F. Bornert, D. Offner, Bone substitutes: a review of their characteristics, clinical use, and perspectives for large bone defects management. J. Tissue Eng. 9, 2041731418776819 (2018)
H. Böttcher, K. Eisbrenner, S. Fritz, G. Kindermann, F. Kraxner, I. McCallum, M. Obersteiner, An assessment of monitoring requirements and costs of reduced emissions from deforestation and degradation. Carbon Balance Manag. 4, 1–14 (2009)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Research Centre, Egypt, and the Oral Biology Department, Faculty of Dentistry, Cairo University, Egypt for the use of their facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farag, M.M., Beherei, H., Al-Rashidy, Z.M. et al. Dental pulp stem cell viability and osteogenic potential assessment of new Mg-phosphate magnetic bioceramic nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Research 37, 595–607 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-021-00454-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-021-00454-5