Abstract
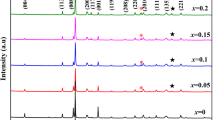
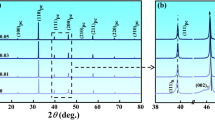
Piezoelectric Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 (BCZT) has been found to be a competitive lead‐free piezoceramic candidate and was prepared by a sol–gel technique due to its small particle size and homogeneous particle size distribution, but the sintering temperature is still quite high in the previous reports. In the present paper, lithium carbonate (Li2CO3) was used as a sintering aid and dopant for the sol–gel‐derived piezoceramic powder, to facilitate the sintering process and adjust the densification, the microstructures and functional properties. With the addition of 0.5 wt% Li2CO3 sintered at 1300 °C, a high relative density 96% with piezoelectric coefficient d33 ~447 pC/N, planar coupling coefficient kp ~0.51, and Curie point TC ~98.7 °C was obtained. The way to properly define the critical changing points on temperature‐dependent dielectric curves were further discussed. By altering sintering temperature and the amount of dopant, the mutual influence between the microstructures and the functional properties was explained, to further guide shaping BCZT in more complexed connectivities.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.R. Shrout and S.J. Zhang: Lead‐free piezoelectric ceramics: Alternatives for PZT? J. Electroceram. 19, 111 (2007).
W. Liu and X. Ren: Large piezoelectric effect in Pb‐free ceramics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 1 (2009).
K. Castkova, K. Maca, J. Cihlar, H. Hughes, A. Matousek, P. Tofel, Y. Bai, and T.W. Button: Chemical synthesis, sintering and piezoelectric properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15 Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 lead‐free ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98, 2373 (2015).
Y. Bai, A. Matousek, P. Tofel, V. Bijalwan, B. Nan, H. Hughes, and T.W. Button: (Ba,Ca)(Zr,Ti)O3 lead‐free piezoelectric ceramics – The critical role of processing on properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 3445 (2015).
C. Shu, D. Reed, and T.W. Button: A phase diagram of Ba1‐xCaxTiO3 (x=0‐0.30) piezoceramics by Raman spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101, 2589 (2018).
W. Li, Z. Xu, R. Chu, P. Fu, and G. Zang: High piezoelectric d33 coefficient in (Ba1‐xCa x)(Ti0.98Zr0.02)O3 lead‐free ceramics with relative high Curie temperature. Mater. Lett. 64, 2325 (2010).
X.G. Tang and H.L.W. Chan: Effect of grain size on the electrical properties of (Ba,Ca)(Zr,Ti)O3 relaxor ferroelectric ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 034109 (2005).
H.T. Martirena and J.C. Burfoot: Grain‐size effects on properties of some ferroelectric ceramics. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 7, 3182 (1974).
Z. Wang, J. Wang, X. Chao, L. Wei, B. Yang, D. Wang, and Z. Yang: Synthesis, structure, dielectric, piezoelectric, and energy storage performance of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3 ceramics prepared by different methods. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron 27, 5047 (2016).
S. Mahajan, O.P. Thakur, D.K. Bhattacharya, and K. Sreenivas: A comparative study of Ba0.95Ca0.05Zr0.25Ti0.75O3 relaxor ceramics prepared by conventional and microwave sintering techniques. Mater. Chem. Phys. 112, 858 (2008).
Y. Liu, Y. Pu, and Z. Sun: Enhanced relaxor ferroelectric behavior of BCZT lead‐free ceramics prepared by hydrothermal method. Mater. Lett. 137, 128 (2014).
S. Ye, J. Fuh, L. Lu, Y.L. Chang, and J.R. Yang: Structure and properties of hot‐pressed lead‐free (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O3 piezoelectric ceramics. RSC Adv. 3, 20693 (2013).
X. Yan and B. Peng: Microstructure and electrical properties of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.10Ti0.90)O3 lead‐free piezoelectric ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron 26, 9649 (2015).
A. Frattini, A. Di Loreto, O. de Sanctis, and E. Benavidez: BCZT Ceramics prepared from activated powders. Procedia Mater. Sci. 1, 359 (2012).
T. Chen, T. Zhang, G. Wang, J. Zhou, J. Zhang, and Y. Liu: Effect of CuO on the microstructure and electrical properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.90Zr0.10O3 piezoceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 4612 (2012).
X. Liu, Z. Chen, D. Wu, B. Fang, J. Ding, X. Zhao, H. Xu, and H. Luo: Enhancing pyroelectric properties of Li‐doped (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O3 lead‐free ceramics by optimizing calcination temperature. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 54, 071501 (2015).
X. Wang, P. Liang, X. Chao, and Z. Yang: Dielectric properties and impedance spectroscopy of MnCO3‐modified (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O3 lead‐free ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98, 1506 (2015).
J. Wu, W. Wu, D. Xiao, J. Wang, Z. Yang, Z. Peng, Q. Chen, and J. Zhu: (Ba,Ca)(Ti,Zr)O3‐BiFeO3 lead‐free piezoelectric ceramics. Curr. Appl. Phys. Lett. 12, 534 (2012).
X. Chao, J. Wang, P. Liang, T. Zhang, L. Wei, and Z. Yang: Phase transition and improved electrical performance of Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3‐Ca0.28Ba0.72Nb2O6 ceramics with high Curie temperature. Mater. Des. 89, 465 (2016).
J. Wu, D. Xiao, W. Wu, Q. Chen, J. Zhu, Z. Yang, and J. Wang: Role of room‐temperature phase transition in the electrical properties of (Ba, Ca)(Ti, Zr)O3 ceramics. Scr. Mater. 65, 771 (2011).
M. Kakihana: Invited review “sol‐gel” preparation of high temperature superconducting oxides. J. Sol‐Gel Sci. Technol. 6, 7 (1996).
G.T. Park, J.J. Choi, C.S. Park, J.W. Lee, and H.E. Kim: Piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties of 1‐μm‐thick lead zirconate titanate film fabricated by a double‐spin‐coating process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 2322 (2004).
Y. Natsume and H. Sakata: Zinc oxide films prepared by sol‐gel spin‐coating. Thin Solid Films 372, 30 (2000).
E.B. Duoss, M. Twardowski, and J.A. Lewis: Sol‐gel inks for direct‐write assembly of functional oxides. Adv. Mater. 19, 3485 (2007).
J.F. Destino, N.A. Dudukovic, M.A. Johnson, D.T. Nguyen, T.D. Yee, G.C. Egan, A.M. Sawvel, W.A. Steele, T.F. Baumann, E.B. Duoss, T. Suratwala, and R. Dylla‐Spears: 3D Printed optical quality silica and silica–titania glasses from sol–gel feedstocks. Adv. Mater. Technol. 3, 1 (2018).
A. Stashans and J. Chimborazo: Effect of interstitial hydrogen on structural and electronic properties of BaTiO3. Philos. Mag. B Phys. Condens. Matter; Stat. Mech. Electron. Opt. Magn. Prop. 82, 1145 (2002).
T.U. Ito, A. Koda, K. Shimomura, W. Higemoto, T. Matsuzaki, Y. Kobayashi, and H. Kageyama: Excited configurations of hydrogen in the BaTiO3‐xHx perovskite lattice associated with hydrogen exchange and transport. Phys. Rev. B 95, 1 (2017).
I. Coondoo, N. Panwar, H. Amorín, V.E. Ramana, M. Algueró, and A. Kholkin: Enhanced piezoelectric properties of praseodymium‐modified lead‐free (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.90Zr0.10)O3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98, 3127 (2015).
C.K.I. Tan, K. Yao, and J. Ma: Effects of LiF on the structure and properties of Ba0.85Ca 0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 lead‐free piezoelectric ceramics. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 10, 701 (2013).
X. Chen, X. Ruan, K. Zhao, X. He, J. Zeng, Y. Li, L. Zheng, C.H. Park, and G. Li: Low sintering temperature and high piezoelectric properties of Li‐doped (Ba,Ca)(Ti,Zr)O3 lead‐free ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 632, 103 (2015).
X. Chen, Y. Li, J. Zeng, L. Zheng, C.H. Park, and G. Li: Phase transition and large electrostrain in lead‐free Li‐doped (Ba, Ca)(Ti, Zr)O3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99, 2170 (2016).
P. Patnaik: Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals (McGraw‐Hill, New York, 2003), pp. 497.
B. Tang, S.R. Zhang, Y. Yuan, L.B. Yang, and X.H. Zhou: Influence of tetragonality and secondary phase on the Curie temperature for barium titanate ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron 19, 1109 (2008).
M. Kuwabara, H. Matsuda, N. Kurata, and E. Matsuyama: Shift of the Curie point of barium titanate ceramics with sintering temperature. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 2590 (1997).
F. Baeten, B. Derks, W. Coppens, and E. van Kleef: Barium titanate characterization by differential scanning calorimetry. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 589 (2006).
S. Lee, Z.K. Liu, M.H. Kim, and C.A. Randall: Influence of nonstoichiometry on ferroelectric phase transition in BaTiO3. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 054119‐4 (2007).
B. Jaffe, W.R. Cook, Jr., and H. Jaffe: The Piezoelectric Effect in Ceramics. Piezoelectric Ceramics (Academic Press, London and New York, 1971), pp. 7–21.
S. Abhinay, R. Mazumder, A. Seal, and A. Sen: Tape casting and electrical characterization of 0.5Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3–0.5(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3 (BZT–0.5BCT) piezoelectric substrate. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 5 (2016).
B. Nan, S. Olhero, R. Pinho, P.M. Vilarinho, T.W. Button, and J.M.F. Ferreira: Direct ink writing of macroporous lead‐free piezoelectric Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc 102, 3191 (2018).
W. Heywang, K. Lubitz, and W. Wersing: Piezoelectricity: evolution and future of a technology. In Chapter 17 in Part III Characterisation Methods, M.J. Hoffmann, H. Kungl, R. Theissmann, and S. Wagner, eds. (Springer Science & Business Media, Germany, 2008); pp. 414.
J.C. Wurst and J.A. Nelson: Linear intercept technique for measuring grain‐size in 2‐phase polycrystalline ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 55, 109 (1972).
D. Berlincourt, T. Kinsley, T.M. Lambert, D. Schwartz, E.A. Gerber, and I.E. Fair: IRE Standards on piezoelectric crystals: Measurements of piezoelectric ceramics, 1961. Proc. IRE 49, 1161 (1961).
J. Fialka and P. Beneš: Comparison of methods for the piezoelectric coefficients measurement. Control Instrum. 62, 1047 (2013).
Acknowledgments
This research was carried out under the project CEITEC 2020 (LQ1601) with financial support from the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic under the National Sustainability Programme II. Part of the work was carried out with the support of the Erasmus+ Programme of the European Union and CEITEC Nano Research Infrastructure (MEYS CR, 2016–2019). The European Commission support for the production of this publication does not constitute an endorsement of the contents which reflects the views only of the authors, and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the information contained therein.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nan, B., Matoušek, A., Tofel, P. et al. Effect of lithium carbonate on the sintering, microstructure, and functional properties of sol–gel‐derived Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 piezoceramics. Journal of Materials Research 36, 1105–1113 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-020-00065-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-020-00065-6