Abstract
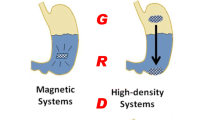
The optimal therapeutic efficiency of any treatment depends on patient adherence to the medication regimen. Medication adherence is the cornerstone of treatment outcomes that may consequently impact economic and healthcare costs. With the oral route being the preferred route of drug administration, slow or extended-release oral formulations can, therefore, be utilized. Here, a biocompatible oral delivery system that can be retained in the stomach for a week, while providing continuous release of the encased drug, is proposed. The fabrication of the delivery system was achieved using a simple mold casting technique. The hydrogel-based raft was able to float under simulated gastric conditions for seven days with pH switches to mimic the fasted and fed states of the stomach. The functionality of such a delivery system has been exemplified using two different model drugs—risperidone and metoprolol tartrate of varied solubilities and has been shown to effectively sustain the release of drugs under the tested conditions.
Impact statement
An oral delivery system is proposed to tackle the soaring problem of medication nonadherence predominantly for conditions that require long-term medication. The proposed delivery system is designed to float in the stomach, thereby prolonging gastric retention and sustaining drug release for more than a week. Subsequently, once drug release is completed, it can be dissolved away using an extrinsic trigger. Any chronic disease condition that requires multiple dosing per day or to be taken over a prolonged period would benefit from such a sustained-releasing drug delivery system. This reduces dosing frequency and consequently improves patient medication compliance. The proposed design allows for easy adaptation to different drugs making it customizable to the patient’s needs. The application of the delivery system may also be extended to the delivery and retention of miniature devices, such as glucose sensors that are to be retained for an extended period in the body, for the purpose of health monitoring or probing. In addition, this technology could have an impact beyond biomedical/pharmaceutical applications, where the need for extended release is a requirement. For instance, as a floating device for environmental purposes (i.e., slow release of pesticides into water bodies against mosquito breeding may be a possibility).
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
W.Y. Lam, P. Fresco, Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 217047 (2015)
F. Kleinsinger, Perm. J. 22(3), 18–033 (2018)
J. Kim, K. Combs, J. Downs, F. Tillman, U.S. Pharm. 43, 30 (2018)
I. Maidment, C. Huckerby, D. Shukla, Prescriber 31(11–12), 30 (2020)
A. Marengoni, S. Angleman, R. Melis, F. Mangialasche, A. Karp, A. Garmen, B. Meinow, L. Fratiglioni, Ageing Res. Rev. 10(4), 430 (2011)
C. Buttorff, T. Ruder, M. Bauman, Multiple Chronic Conditions in the United States (RAND Corporation, Santa Monica, 2017)
World Health Organization (WHO), Noncommunicable Disease (WHO, Geneva, 2021). Accessed 13 Apr 2021
M.H.H. Cheen, Y.Z. Tan, L.F. Oh, H.L. Wee, J. Thumboo, Int. J. Clin. Pract. 73(6), e13350 (2019)
U.K. Mandal, B. Chatterjee, F.G. Senjoti, Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 11(5), 575 (2016)
N.-N. Vrettos, C.J. Roberts, Z. Zhu, Pharmaceutics 13(10), 1591 (2021)
J. Tripathi, P. Thapa, R. Maharjan, S.H. Jeong, Pharmaceutics 11(4), 193 (2019)
D.H. Altreuter, A.R. Kirtane, T. Grant, C. Kruger, G. Traverso, A.M. Bellinger, Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 15(12), 1189 (2018)
M. Koziolek, M. Grimm, F. Schneider, P. Jedamzik, M. Sager, J.-P. Kühn, W. Siegmund, W. Weitschies, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 101, 75 (2016)
Y. Zhang, Y. Huang, Front. Chem. 8, 615665 (2021)
M. Patel, F. Shaikh, N. Surti, Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 83(2), 306 (2021)
A.K. Abbas, A.T. Alhamdany, Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 17(2), 159 (2020)
C. Zhao, L. Cai, M. Nie, L. Shang, Y. Wang, Y. Zhao, Adv. Sci. 8(7), 2004184 (2021)
X. Yan, S. Wang, K. Sun, Pharmaceutics 13(8), 1210 (2021)
R. Cargill, L.J. Caldwell, K. Engle, J.A. Fix, P.A. Porter, C.R. Gardner, Pharm. Res. 5(8), 533 (1988)
A.M. Bellinger, M. Jafari, T.M. Grant, S. Zhang, H.C. Slater, E.A. Wenger, S. Mo, Y.L. Lee, H. Mazdiyasni, L. Kogan, R. Barman, C. Cleveland, L. Booth, T. Bensel, D. Minahan, H.M. Hurowitz, T. Tai, J. Daily, B. Nikolic, L. Wood, P.A. Eckhoff, R. Langer, G. Traverso, Sci. Transl. Med. 8(365), 365ra157 (2016)
M. Peanparkdee, S. Iwamoto, R. Yamauchi, Rev. Agric. Sci. 4, 56 (2016)
L. Li, J. Zhao, Y. Sun, F. Yu, J. Ma, Chem. Eng. J. 372, 1091 (2019)
A. Belščak-Cvitanović, D. Komes, S. Karlović, S. Djaković, I. Spoljarić, G. Mršić, D. Ježek, Food Chem. 167, 378 (2015)
M.A. Khosravi Zanjani, B. Ghiassi Tarzi, A. Sharifan, N. Mohammadi, Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 13(3), 843 (2014)
A. Murayama, Y. Ichikawa, A. Kawabata, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 59(1), 5 (1995)
P. Matricardi, C.D. Meo, T. Coviello, F. Alhaique, Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 5(4), 417 (2008)
J. Wu, Z. Zhang, J.G. Gu, W. Zhou, X. Liang, G. Zhou, C.C. Han, S. Xu, Y. Liu, J. Control. Release 320, 337 (2020)
J.-S. Baek, C.C. Choo, C. Qian, N.S. Tan, Z. Shen, S.C.J. Loo, Small 12(27), 3712 (2016)
M.L. Bruschi, “Mathematical Models of Drug Release,” in Strategies to Modify the Drug Release from Pharmaceutical Systems, ed. by M.L. Bruschi (Woodhead Publishing, Sawston, 2015), pp. 63–86
H.O. Ammar, M.M. Ghorab, A.A. Mahmoud, S.H. Noshi, Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2(2), 43 (2016)
V. Korzhikov, I. Averianov, E. Litvinchuk, T.B. Tennikova, J. Microencapsul. 33(3), 199 (2016)
M.J. Prieto, N.E. del Rio Zabala, C.H. Marotta, H. Carreño Gutierrez, R. Arevalo Arevalo, N.S. Chiaramoni, S. del Valle Alonso, PLoS ONE 9(2), e90393 (2014)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from the Singapore Centre for Environmental Life Sciences Engineering (SCELSE) (MOE/RCE: M4330019.C70), Ministry of Education AcRF-Tier 1 Grant (RG19/18 & RT08/19 (S)), Singapore Food Agency (SFS_RND_SUFP_001_06), and the Singapore National Biofilm Consortium (SNBC/2021/SF2/P04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.D.K. and K.S. designed and carried out the experiments, analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. S.C.J.L. provided the overall direction for the work and edited the manuscript drafts.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kwang, G.D., Sampathkumar, K. & Loo, S.C.J. Ultralong floating hydrogel raft for prolonged gastric retention. MRS Bulletin 48, 342–350 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43577-022-00406-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43577-022-00406-2