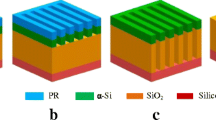
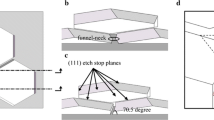
Abstract
Operations on biological living cells and molecular devices have driven research towards implementation of high-aspect-ratio nano-needles. However, current nano-needle fabrication is complicated to control the sizes and angles. In this work, we develop a simple method to fabricate repeatable and integrated circuit (IC)-compatible sharp silicon nano-needles based on boron etch-stop in tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide (TMAH) solutions, and the needle angles can be accurately controlled. An analytical model is proposed to efficiently predict the needle sizes and explain the etching evolution of silicon nano-needles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Obataya, C. Nakamura, S. Han, N. Nakamura, and J. Miyake, Nano Lett. 5, 27 (2005).
K. Yum, N. Wang, and M. F. Yu, Nanoscale 2, 363 (2009).
S. W. Han, C. Nakamura, I. Obataya, N. Nakamura, and J. Miyake, Biosensors & Bioelectronics 20, 2120 (2005).
M. Jouzi, M. B. Kerby, A. Tripathi, and J. Xu, Langmuir 24, 10786 (2008).
S. W. Han, C. Nakamura, N. Kotobuki, I. Obataya, H. Ohgushi, T. Nagamune, and J. Miyake, Nanomedicine: NBM 4, 215(2008).
A. Goryu, A. Ikedo, M. Ishida, and T. Kawano, Nanotechnology 21, 125302(2010).
C. H. Hsu, H. C. Lo, C. F. Chen, C. T. Wu, J. S. Hwang, D. Das, J. Tsai, L. C. Chen, and K. H. Chen, Nano Lett. 4, 471(2004).
P. M. Rao and X. L. Zheng, Nano Lett. 9, 3001(2009).
O. Tabata, R. Asahi, H. Funabashi, K. Shimaoka, and S. Sugiyama, Sens. Actuators A 34, 51(1992).
K. Sato, M. Shikida, T. Yamashiro, K. Asaumi, Y. Iriye, and M. Yamamoto, Sens. Actuators A 73, 131(1999).
E. Steinsland, M. Nese, A. Hanneborg, R. W. Bernstein, H. Sandmo, and G. Kittilsland, Sens. Actuators A 54, 728(1996).
S. Tatic-Lucic, W. Y. Zhang, and N. Navneet, Sens. Actuators A 123–24, 640(2005).
M. C. Acero, J. Esteve, C. Burrer, and A. Gotz, Sens. Actuators A 46, 22(1995).
Rikard A. Wind, Melissa A. Hines, Surface Science 460, 21(2000).
E. van Veenendaal, K. Sato, M. Shikida, A. J. Nijdam, and J. van Suchtelen, Sens. Actuators A 93, 232(2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, S., Xu, Y., Yang, J. et al. Sharp Silicon Nano-Needles Based on Boron Etch-Stop in TMAH Solutions. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1301, 225–228 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2011.71
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2011.71