Abstract
We have developed a reproducible protocol for studying the effect of microwave radiation on the mechanical behavior ofBombyx mori cocoon silk. In the course of this work, we identified multiple improvements that can be made to ASTM F 1317-98, the standard according to which microwave oven power output is calibrated.
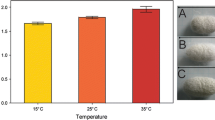
Exposure to microwaves does not significantly affect mechanical properties of silkworm silk, if samples are kept in a desiccator after degumming (or after degumming and microwaving) and prior to testing in a dry environment. This finding contrasts with previous work in which samples were not kept in a desiccator, and were tested in a relatively humid environment.
Because the effect of microwave radiation on the mechanical behavior of silk is sensitive to ambient moisture, meaningful comparison or pooling of test results acquired in different laboratories is contingent on standardization of both the sample storage environment and the environment in which samples are tested. Interpretation of the extensive existing literature on silk mechanical properties must take account of the reality that the sample storage and testing environments are not standardized and are usually not reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.A. Morrison, F.I. Bell, A. Beautrait, J. Ritchie, C. Smith, I.J. McEwen and C. Viney, Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 823, W8.4.1- W8.4.6 (2004).
R.D. Knight, Physics for Scientists and Engineers: a Strategic Approach (Pearson / Addison Wesley, San Francisco, 2004) p.527.
A.F. Mills, Basic Heat and Mass Transfer (2nd edition, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 1999) p.926.
S.A. Barringer, E.A. Davis, J. Gordon, K.G. Ayappa and H.T. Davis, AIChE Journal 40(9), 1433–1439 (1994).
S.A. Barringer, E.A. Davis, J. Gordon, K.G. Ayappa and H.T. Davis, Journal of Food Science 60(5), 1137–1142 (1995).
Inspired by and adapted from: www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/microwaves/mwintro.html (At the date this paper was written, the above URL was deemed to be useful supplementary material. Neither the authors nor the Materials Research Society warrants or assumes liability for the content or availability of URLs referenced in this paper.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reed, E.J., Viney, C. The Effect of Microwave Radiation on Tensile Properties of Silkworm (B. mori) Silk. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1301, 161–172 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2011.571
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2011.571