Abstract
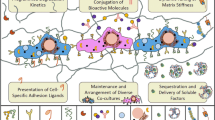
The following article is based on a presentation given by Samuel I. Stupp of Northwestern University as part of Symposium X—Frontiers of Materials Research on April 13, 2004, at the Materials Research Society Spring Meeting in San Francisco. Materials designed at the molecular and supramolecular scales to interact with cells, biomolecules, and pharmaceuticals will have a profound impact on technologies targeting the regeneration of body parts. Materials science is a great partner to stem cell biology, genomics, and proteomics in crafting the scaffolds that will effectively regenerate tissues lost to trauma, disease, or genetic defects. The repair of humans should be minimally invasive, and thus the best scaffolds would be liquids programmed to create materials inside our bodies. In this regard, self-assembling materials will play a key role in future technologies. This article illustrates how molecules are designed to assemble into cell scaffolds for human repair and provides examples relevant to brain damage, fractures of the skeleton, spinal cord injuries leading to paralysis, and diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.G. Anderson, J.A. Burdick, and R. Langer, Science 305 (2004) p. 1923.
E. Zamir and B. Geiger, J. Cell Sci. 114 (2001) p. 3577.
E. Cukierman, R. Pankov, D.R. Stevens, and K.M. Yamada, Science 294 (2001) p. 1708.
K.M. Yamada and B. Geiger, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9 (1997) p. 76.
R. Derynck and Y.E. Zhang, Nature 425 (2003) p. 577.
L.L. Hench and J.M. Polak, Science 295 (2002) p. 1014.
L.G. Griffith and G. Naughton, Science 295 (2002) p. 1009.
H. Shin, S. Jo, and A.G. Mikos, Biomaterials 24 (2003) p. 4353.
T. Boontheekul and D.J. Mooney, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 14 (2003) p. 559.
Y. Hirano and D.J. Mooney, Adv. Mater. 16 (2004) p. 17.
L.J. Chamberlain, I.V. Yannas, H.P. Hsu, G.R. Strichartz, and M. Spector, J. Neurosci. Res. 60 (2000) p. 666.
M.D. Pierschbacher and E. Ruoshlahti, Nature 309 (1984) p. 30.
U. Hersel, C. Dahmen, and H. Kessler, Biomaterials 24 (2003) p. 4385.
G.W. Fussell and S.L. Cooper, Biomaterials 25 (2004) p. 2971.
E. Smith, J. Bai, C. Oxenford, J. Yang, R. Somayaji, and H. Uludag, J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 41 (2003) p. 3989.
M.N. Yousaf, B.T. Houseman, and M. Mrksich, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98 (2001) p. 5992.
A.G. Mikos, Y. Bao, L.G. Cima, D.E. Ingber, J.P. Vacanti, and R. Langer, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 27 (1993) p. 183.
A.G. Mikos, M.D. Lyman, L.E. Freed, and R. Langer, Biomaterials 15 (1994) p. 55.
A.G. Mikos, A.J. Thorsen, L.A. Czerwonka, Y. Bao, R. Langer, D.N. Winslow, and J.P. Vacanti, Polymer 35 (1994) p. 1068.
D.J. Mooney, D.F. Baldwin, N.P. Suh, L.P. Vacanti, and R. Langer, Biomaterials 17 (1996) p. 1417.
J.D. Hartgerink, E. Beniash, and S.I. Stupp, Science 294 (2001) p. 1684.
M.O. Guler, S. Soukasene, J.F. Hulvat, and S.I. Stupp, Nano Lett. 5 (2005) p. 249.
H.A. Behanna, J. Donners, A.C. Gordon, and S.I. Stupp, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 (2005) p. 1193.
P. Berndt, G.B. Fields, and M. Tirrell, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117 (1995) p. 9515.
G.B. Fields, J.L. Lauer, Y. Dori, P. Forns, Y.C. Yu , and M. Tirrell, Biopolymers 47 (1998) p. 143.
S.G. Zhang, T. Holmes, C. Lockshin, and A. Rich, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90 (1993) p. 3334.
S.G. Zhang, Nat. Biotechnol. 21 (2003) p. 1171.
J.N. Israelachvili, Intermolecular and Surface Forces (Academic Press, London, 1992).
S. Tsonchev, G.C. Schatz, and M.A. Ratner, Nano Lett. 3 (2003) p. 623.
S. Tsonchev, G.C. Schatz, and M.A. Ratner, J. Phys. Chem. B 108 (2004) p. 8817.
G.A. Silva, C. Czeisler, K.L. Niece, E. Beniash, D.A. Harrington, J.A. Kessler, and S.I. Stupp, Science 303 (2004) p. 1352.
F.J. Solis, S.I. Stupp, and M. Olvera de la Cruz, J. Chem. Phys. 122 054905 (2005)
K.L. Niece, J.D. Hartgerink, J.J.J.M. Donnors, and S.I. Stupp, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125 (2003) p. 7146.
H. Okano, J. Neurosci. Res. 69 (2002) p. 698.
A. Storch and J. Schwarz, Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs 3 (2002) p. 774.
M.F. Mehler and J.A. Kessler, Arch. Neurol. 56 (1999) p. 780.
D.W. Pincus, R.R. Goodman, R.A.R. Fraser, M. Nedergaard, and S.A. Goldman, Neurosurgery 42 (1998) p. 858.
L. Kam, W. Shain, J.N. Turner, and R. Bizios, Biomaterials 22 (2001) p. 1049.
M. Matsuzawa, F.F. Weight, R.S. Potember, and P. Liesi, Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 14 (1996) p. 283.
S.K. Powell, J. Rao, E. Rogue, M. Nomizu, Y. Kuratomi, Y. Yamada, and H.K. Kleinman, J. Neurosci. Res. 61 (2000) p. 302.
T. Cornish, D.W. Branch, B.C. Wheeler, and J.T. Campanelli, Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 20 (2002) p. 140.
J.C. Chang, G.J. Brewer, and B.C. Wheeler, Biosens. Bioelectron. 16 (2001) p. 527.
B.C. Wheeler, J.M. Corey, G.J. Brewer, and D.W. Branch, J. Biomech. Eng., Trans. ASME 121 (1999) p. 73.
L. Lauer, A. Vogt, C.K. Yeung, W. Knoll, and A. Offenhausser, Biomaterials 23 (2002) p. 3123.
P. Thiebaud, L. Lauer, W. Knoll, and A. Offenhausser, Biosens. Bioelectron. 17 (2002) p. 87.
C.K. Yeung, L. Lauer, A. Offenhausser, and W. Knoll, Neurosci. Lett. 301 (2001) p. 147.
J.A. Kessler, private communication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stupp, S.I. Biomaterials for Regenerative Medicine. MRS Bulletin 30, 546–553 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs2005.148
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs2005.148