Abstract
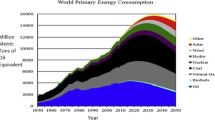
According to the US Department of Energy’s Energy Infomation Administration (EIA) (International Energy Outlook 2017), world energy consumption will increase 28% between 2015 and 2040, rising from 575 quadrillion Btu (∼606 quadrillion kJ) in 2015 to 736 quadrillion Btu (∼776 quadrillion kJ) in 2040. EIA predicts increases in consumption for all energy sources (excluding coal, which is estimated to remain flat)—fossil (petroleum and other liquids, natural gas), renewables (solar, wind, hydropower), and nuclear. Although renewables are the world’s fastest growing form of energy, fossil fuels are expected to continue to supply more than three-quarters of the energy used worldwide. Among the various fossil fuels, natural gas is the fastest growing, with a projected increase of 43% from 2015 to 2040. As the use of fossil fuels increases, the EIA projects world energy-related carbon dioxide emission to grow from ∼34 billion metric tons in 2015 to ∼40 billion metric tonnes in 2040 (an average 0.6% increase per year).


Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minh, N.Q., Shirley Meng, Y. Future energy, fuel cells, and solid-oxide fuel-cell technology. MRS Bulletin 44, 682–683 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2019.209
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2019.209