Abstract
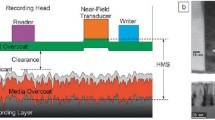
Heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) is the next-generation technology that is required to deliver areal densities in excess of 2 terabit/in2 for high-capacity, low-cost hard drives.The recording process relies on spatially and temporally localized heating of the media surface to lower its coercivity during the magnetic writing process. This scheme drives substantial changes to the recording head write element architecture, combining the conventional electromagnet structure with integrated optical light delivery layers, focusing optics, and plasmonic nanostructures to generate subwavelength optical spots. Power losses associated with the strong optical fields required for heating the media can cause local temperatures in excess of 400°C at the recording head surface. Coupled with high pressures, an oxidative/corrosive air-bearing environment, and a sub-3 nm head-media spacing, this introduces new challenges for the functional materials in recording heads required to balance performance and long-term reliability demands. Here, we briefly review specific challenges associated with HAMR heads, highlighting the major requirements, failure modes, and needed innovations for the near-field transducer and optical-waveguide subsystems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.A. Challener, C. Peng, A.V. Itagi, D. Karns, W. Peng, Y. Peng, X.M. Yang, X. Zhu, N.J. Gokemeijer, Y.T. Hsia, G. Ju, R.E. Rottmayer, M.A. Seigler, E.C. Gage, Nat. Photonics 3, 220 (2009).
J. Gosciniak, M. Mooney, M. Gubbins, B. Corbett, Nanophotonics 4 (7), 503 (2015).
U. Boettcher, H. Li, R.A. de Callafon, F.E. Talke, IEEE Trans. Magn. 47 (7), 1823 (2011).
D.G. Baranov, D.A. Zuev, S.I. Lepeshov, O.V. Kotov, A.E. Krasnok, A.B. Evlyukhin, B.N. Chichkov, Optica 4, 814 (2017).
S. Bruynooghe, N. Schmidt, M. Sundermann, H.W. Becker, S. Spinzig, Opt. Inter. Coatings 2010, paper ThA9, https://www.osapublishing.org/conference.cfm?meetingid=38&yr=2010.
M.D. Arnold, M.G. Blaber, Opt. Express 17, 3835 (2009).
S. Link, M.A. El-Sayed, J. Phys. Chem. B 103 (40), 8410 (1999).
S.L. Westcott, J.B. Jackson, C. Radloff, N.J. Halas, Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 66, 155431 (2002).
H.R. Eragamreddy, U. Guler, K. Chaudhuri, A. Dutta, A.V. Kildishev, V.M. Shalaev, A. Boltasseva, in Conf. Lasers Electro-Optics (Optical Society of America, 2017), p. FTu4H.7.
C. Sönnichsen, T. Franzl, T. Wilk, G. von Plessen, J. Feldmann, O. Wilson, P. Mulvaney, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 077402 (2002).
B. Foerster, A. Joplin, K. Kaefer, S. Celiksoy, S. Link, C. Sönnichsen, ACS Nano 11 (3), 2886 (2017).
M. Kuttge, H.J. Lezec, H.A. Atwater, A. Polman, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 113110 (2008).
E.D. Palik, Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids (Academic Press, San Diego, 1998).
P.B. Johnson, R.W. Christy, Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 6, 4370 (1972).
J.H. Weaver, H.P.R. Frederikse, Optical Properties of Selected Elements, 82nd ed. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2001).
A. Wu, Y. Kubota, T. Klemmer, T. Rausch, C. Peng, Y. Peng, D. Karns, X. Zhu, Y. Ding, E. Chang, Y. Zhao, H. Zhou, K. Gao, J.-U. Thiele, M. Seigler, G. Ju, E. Gage, IEEE Trans. Magn. 49 (2), 779 (2013).
A. Kossoy, D. Simakov, S. Olafsson, K. Leosson, Thin Solid Films 536, 50 (2013).
J. Dalla Torre, G.H. Gilmer, D.L. Windt, R. Kalyanaraman, F.H. Baumann, P.L. O’Sullivan, J. Sapjeta, T. Dias de la Rubia, M. Djafari Rouhani, J. Appl. Phys. 94, 263 (2003).
T. Karabacak, G.-C. Wang, T.-M. Lu, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 22, 1778 (2004).
D. Gupta, Science 11, 7 (2003).
S. Kilgore, C. Gaw, H. Henry, D. Hill, D. Schroder, “Electromigration of Electroplated Gold Interconnects,” Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 863, P.R. Besser, A.J. McKerrow, F. Iacopi, C.P. Wong, J.J. Vlassak, Eds. (Materials Research Society, Warrendale, PA, 2005), p. B8.30.
Q. Huang, C. Lilley, R. Divan, M. Bode, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 7 (6), 688 (2008).
A. Taylor, A. Siddiquee, J. Chon, ACS Nano 8, 12071 (2014).
H. Im, S.-H. Oh, Small 10, 680 (2014).
F.A. Nichols, W.W. Mullins, J. Appl. Phys. 36, 1826 (1965).
S. Karim, M.E. Toimil-Molares, A.G. Balogh, W. Ensinger, T.W. Cornelius, E.U. Khan, R. Neumann, Nanotechnology 17, 5954 (2006).
S. Karim, M.E. Toimil-Molares, W. Ensinger, A.G. Balogh, T.W. Cornelius, E.U. Khan, R. Neumann, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, 3767 (2007).
K. Hirata, R. Hosoi, K. Kawamori, T. Roppongi, “Plasmon Generator and Thermally-Assisted Magnetic Recording Head Having the Same,” US Patent 8,964,514 (August 7, 2012).
R. Ji, B. Xu, Z. Cen, J.F. Ying, Y.T. Toh, J. Appl. Phys. 117, 17A918 (2015).
H. Aouani, J. Wenger, D. Gerard, H. Rigneault, E. Devaux, T.W. Ebbesen, F. Mahdavi, T. Xu, S. Blair, ACS Nano 3, 2043 (2009).
T. Habteyes, S. Dhuey, E. Wood, D. Gargas, S. Cabrini, P.J. Schuck, A.P. Alivisatos, S.R. Leone, ACS Nano 6, 5702 (2012).
M. Jeong, J. Freedman, H. Liang, C.-M. Chow, V. Sokalski, J.A. Bain, J. Malen, Phys. Rev. Appl. 5, 014009 (2016).
M.G. Blaber, M.D. Arnold, M.J. Ford, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 22 (14), 143201 (2011).
P.R. West, S. Ishii, G.V. Naik, N.K. Emani, V.M. Shalaev, A. Boltasseva, Laser Photon. Rev. 4, 795 (2010).
G.V. Naik, V.M. Shalaev, A. Boltasseva, Adv. Mater. 25, 3264 (2013).
G.V. Naik, J. Kim, A. Boltasseva, Opt. Mater. Express 1, 1090 (2011).
U. Guler, A. Boltasseva, V. Shalaev, Science 344, 263 (2014).
T. Rausch, A.S. Chu, P.-L. Lu, S. Puranam, D. Nagulapally, T. Lammers, J.W. Dykes, E.C. Gage, IEEE Trans. Magn. 51 (4), 3000405 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kautzky, M.C., Blaber, M.G. Materials for heat-assisted magnetic recording heads. MRS Bulletin 43, 100–105 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2018.1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2018.1