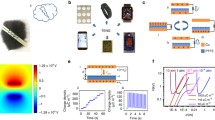
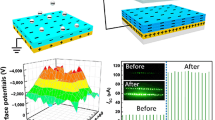
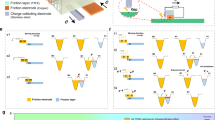
Abstract
Powering autonomous electronic devices is a key challenge toward the development of smart sensor networks. In this work, a state-of-the-art triboelectric nanogenerator is devised to enhance the output performance with an effective surface charge density of 70.2 µC/m2, which is 140 times higher than the initial results. Thin film Parylene-C material is deposited to increase charge accumulation by allowing the acceptance of more charges and enhance output performance by a factor of 10. By considering the merit of simple fabrication, we believe the effective charge inclusion layer will be an ideal energy source for low-power portable electronics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.R. Fan, Z.Q. Tian, and Z. Lin Wang: Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 1, 328–334 (2012).
F.R. Fan, W. Tang, and Z.L. Wang: Flexible Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Electronics. Adv. Mater.. 28, 4283–4305 (2016).
H. Zhang, Y. Yang, Y. Su, J. Chen, C. Hu, Z. Wu, Y. Liu, C.P. Wong, Y. Bando, and Z.L. Wang: Triboelectric nanogenerator as self-powered active sensors for detecting liquid/gaseous water/ethanol. Nano Energy 2, 693–701 (2013).
Z.L. Wang: Triboelectric nanogenerators as new energy technology and self-powered sensors–principles, problems and perspectives. R. Soc. Chem. 7, 9533–9557 (2014).
S. Wang, Y. Xie, S. Niu, L. Lin, and Z.L. Wang: Freestanding triboelectric-layer-based nanogenerators for harvesting energy from a moving object or human motion in contact and non-contact modes. Adv. Mater. 26, 2818–2824 (2014).
Y. Yang, H. Zhang, J. Chen, Q. Jing, Y.S. Zhou, X. Wen, and Z.L. Wang: Single-electrode-based sliding triboelectric nanogenerator for selfpowered displacement vector sensor system. ACS Nano 7, 7342–7351 (2013).
K-E. Byun, M.-H. Lee, Y. Cho, S-G. Nam, H-J. Shin, and S. Park: Potential role of motion for enhancing maximum output energy of triboelectric nanogenerator. APL Mater. 5, 074107 (2017).
M.L. Seol, S.H. Lee, J.W. Han, D. Kim, G.H. Cho, and Y.K. Choi: Impact of contact pressure on output voltage of triboelectric nanogenerator based on deformation of interfacial structures. Nano Energy 17, 63–71 (2015).
T. Huang, M. Lu, H. Yu, Q. Zhang, H. Wang, and M. Zhu: Enhanced power output of a triboelectric nanogenerator composed of electrospun nanofiber mats doped with graphene oxide. Sci. Rep. 5, 13942 (2015).
H. Van Ngoc and D.J. Kang: Flexible, transparent and exceptionally high power output nanogenerators based on ultrathin ZnO nanoflakes. Nanoscale 8, 5059–5066 (2016).
M.A.P. Mahmud, J. Lee, G. Kim, H. Lim, and K.B. Choi: Improving the surface charge density of a contact-separation-based triboelectric nanogenerator by modifying the surface morphology. Microelectron. Eng. 159, 102–107 (2016).
S. Niu, X. Wang, F. Yi, Y.S. Zhou, and Z.L. Wang: A universal selfcharging system driven by random biomechanical energy for sustainable operation of mobile electronics. Nat. Commun. 6, 8975 (2015).
Y. Yu and X. Wang: Chemical modification of polymer surfaces for advanced triboelectric nanogenerator development. Extreme Mech. Lett. 9, 514–530 (2016).
S-W.K. Wanchul Seung, H-J. Yoon, T. Yun Kim, H. Ryu, J. Kim, J-H. Lee, J. Hwan Lee, S. Kim, Y. Kwon Park, and Y. Jun Park: Boosting powergenerating performance of triboelectric nanogenerators via artificial control of ferroelectric polarization and dielectric properties. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1600988 (2017).
S. Wang, Y. Xie, S. Niu, L. Lin, C. Liu, Y. Zhou, and Z.L. Wang: Maximum surface charge density for triboelectric nanogenerators achieved by ionized-air injection: methodology and theoretical understanding. Adv. Mater. 26, 6720–6728 (2014).
W. Jie, W. Changsheng, D. Yejing, Z. Zhihao, W. Aurelia, Z. Tiejun, and Z. Lin Wang: Achieving ultrahigh triboelectric charge density for efficient energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 8, 1–7 (2017).
Y. Feng, Y. Zheng, G. Zhang, D. Wang, F. Zhou, and W. Liu: A new protocol toward high output TENG with polyimide as charge storage layer. Nano Energy 38, 467–476 (2017).
C. Villeneuve-Faure, K. Makasheva, L. Boudou, and G. Teyssedre: charge injection in thin dielectric layers by atomic force microscopy: influence of geometry and material work function of the AFM tip on the injection process. Nanotechnology 27, 245702 (2016).
H.Y. Li, L. Su, S.Y. Kuang, C.F. Pan, G. Zhu, and Z.L. Wang: Significant Enhancement of Triboelectric Charge Density by Fluorinated Surface Modification in Nanoscale for Converting Mechanical Energy. Adv. Funct. Mater.. 25, 5691–5697 (2015).
H.W. Lo and Y.C. Tai: Parylene-based electret power generators. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 18, 104006 (2008).
A. Kahouli, A. Sylvestre, L. Ortega, F. Jomni, B. Yangui, M. Maillard, B. Berge, J.C. Robert, and J. Legrand: Structural and dielectric study of parylene C thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 152901 (2009).
P. Song, S. Kuang, N. Panwar, G. Yang, T. Danny, S. Tjin, W. Ng, M. Majid, G. Zhu, K. Yong, and Z.L. Wang: A self-powered implantable drug-delivery system using biokinetic energy. Adv. Mater. 29, 1605668 (2017).
O. Access, A. Heid, A. Stett, and V. Bucher: examination of dielectric strength of thin Parylene C films under various conditions. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2, 39–41 (2016).
S. Genter and O. Paul: Parylene-C as an electret material for micro energy harvesting. Proc. Power MEMS. pp. 317–320.
Y. Wada, Y. Hamate, S. Nagasawa, and H. Kuwano: Aging characteristics of electret used in a vibration-based electrostatic induction energy harvester. 2011 16th Int. Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference, pp. 2626–2629 (2011).
J. Ma, Y. Jie, J. Bian, T. Li, X. Cao, and N. Wang: From triboelectric nanogenerator to self-powered smart floor: a minimalist design. Nano Energy 39, 192–199 (2017).
Z.H. Lin, G. Cheng, S. Lee, K.C. Pradel, and Z.L. Wang: Harvesting water drop energy by a sequential contact-electrification and electrostatic-induction process. Adv. Mater. 26, 4690–4696 (2014).
F.R. Fan, L. Lin, G. Zhu, W. Wu, R. Zhang, and Z.L. Wang: Transparent triboelectric nanogenerators and self-powered pressure sensors based on micropatterned plastic films. Nano Lett. 12, 3109–3114 (2012).
H-H. Hsieh, F-C. Hsu, and Y-F. Chen: Energetically Autonomous, Wearable, and Multifunctional Sensor. ACS Sensors 3, 113–120 (2018).
Acknowledgment
This research was supported under the AMPEERS-2 project by the theme “Networks and energy storage”. The authors thank Thierry CAMILLIONI for the Instron setup and Jessica MAZUIR for advice in preparation of cross section sample for imaging by SEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary material
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.64
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravichandran, A.N., Ramuz, M. & Blayac, S. Increasing surface charge density by effective charge accumulation layer inclusion for high-performance triboelectric nanogenerators. MRS Communications 9, 682–689 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.64
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.64