Abstract
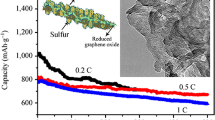
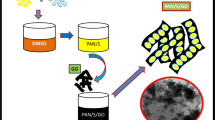
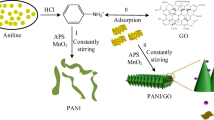
In this work, the authors report a facile method for the preparation of brush-structured nanocomposites of sulfur–polyaniline–graphene oxide (S–PANI–G) that were used for cathode materials of lithium–sulfur batteries (LSBs). The morphology and structure of composite were studied by x-ray photoelectron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and x-ray diffraction analysis. The nanocomposites exhibited good electrochemical performance involving good rate performance, high capacity, and promising cycling stability. The good performance of S–PANI–G results from the synergistic effect of sulfur, polyaniline, and graphene oxide. The composite and method reported here pave the way for the design and synthesis of novel cathode materials for LSBs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Evers and L.F. Nazar: New approaches for high energy density lithium–sulfur battery cathodes. Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 1135 (2012).
W. Chen, T. Lei, T. Qian, W. Lv, W. He, C. Wu, X. Liu, J. Liu, B. Chen, C. Yan, and J. Xiong: A new hydrophilic binder enabling strongly anchoring polysulfides for high-performance sulfur electrodes in lithium–sulfur battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1702889 (2018).
Q. Pang, C.Y. Kwok, D. Kundu, X. Liang, and L.F. Nazar: Lightweight metallic MgB2 mediates polysulfide redox and promises high-energy-density lithium–sulfur batteries. Joule 3, 136–148 (2019).
X. Ji, K.T. Lee, and L.F. Nazar: A highly ordered nanostructured carbon–sulphur cathode for lithium–sulphur batteries. Nat. Mater. 8, 500 (2009).
B.L. Ellis, K.T. Lee, and L.F. Nazar: Positive electrode materials for Li-ion and Li-batteries. Chem. Mater. 22, 691 (2010).
M. Rana, M. Li, X. Huang, B. Luo, I. Gentlec, and R. Knibbe: Recent advances in separators to mitigate technical challenges associated with re-chargeable lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 12, 6596–6615 (2019).
D. Gueon, J.T. Hwang, S.B. Yang, E. Cho, K. Sohn, D.K. Yang, and J.H. Moon: Spherical macroporous carbon nanotube particles with ultrahigh sulfur loading for lithium–sulfur battery cathodes. ACS Nano 12, 226–233 (2018).
H. Pan, K.S. Han, M.H. Engelhard, R. Cao, J. Chen, J.-G. Zhang, K.T. Mueller, Y. Shao, and J. Liu: Addressing passivation in lithium–sulfur battery under lean electrolyte condition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1707234 (2018).
J. Shim, K.A. Striebel, and E.J. Cairns: The lithium/sulfur rechargeable cell effects of electrode composition and solvent on cell performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 149, A1321 (2002).
J.A. Dean: Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry, 3rd ed. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1985).
L. Xiao, Y. Cao, J. Xiao, B. Schwenzer, M.H. Engelhard, L.V. Saraf, Z. Nie, G.J. Exarhos, and J. Liu: A soft approach to encapsulate sulfur: polyani-line nanotubes for lithium–sulfur batteries with long cycle life. Adv. Mater. 24, 1176 (2012).
S.H. Chung and A. Manthiram: Rational design of statically and dynamically stable lithium–sulfur batteries with high sulfur loading and low electrolyte/sulfur ratio. Adv. Mater. 30, 1705951 (2018).
Q. Pang, A. Shyamsunder, B. Narayanan, C.Y. Kwok, L.A. Curtiss, and L.F. Nazar: Tuning the electrolyte network structure to invoke quasi-solid state sulfur conversion and suppress lithium dendrite formation in Li–S batteries. Nat. Energy 3, 783 (2018).
H. Wang, Y. Yang, Y. Liang, J.T. Robinson, Y. Li, A. Jackson, Y. Cui, and H. Dai: Graphene-wrapped sulfur particles as a rechargeable lithium–sulfur battery cathode material with high capacity and cycling stability. Nano Lett. 11, 2644 (2011).
Y. Li, and N. Chopra: Progress in large-scale production of graphene. Part 2: vapor methods. JOM 67, 44 (2015).
Y. Li, and N. Chopra: Chemically modified and doped carbon nanotube-based nanocomposites with tunable thermal conductivity gradient. Carbon 77, 675 (2014).
F. Wu, J. Chen, R. Chen, S. Wu, L. Li, S. Chen, and T. Zhao: Sulfur/poly-thiophene with a core/shell structure: synthesis and electrochemical properties of the cathode for rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 6057 (2011).
X. Yu, J. Xie, Y. Li, H. Huang, C. Lai, and K. Wang: Stable-cycle and high-capacity conductive sulfur-containing cathode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 146, 335 (2005).
T. Chen, L. Ma, B. Cheng, R. Chen, Y. Hu, G. Zhu, Y. Wang, J. Liang, Z. Tie, J. Liu, and Z. Jin: Metallic and polar Co9S8 inlaid carbon hollow nano-polyhedra as efficient polysulfide mediator for lithium–sulfur batteries. Nano Energy 38, 239–248 (2017).
W.G. Chong, J.-Q. Huang, Z.-L. Xu, X. Qin, X. Wang, and J.-K. Kim: Lithium–sulfur battery cable made from ultralight, flexible graphene/car-bon nanotube/sulfur composite fibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 1604815 (2017).
G. Zheng, Q. Zhang, J.J. Cha, Y. Yang, W. Li, Z.W. Seh, and Y. Cui: Amphiphilic surface modification of hollow carbon nanofibers for improved cycle life of lithium sulfur batteries. Nano Lett. 13, 1265 (2013).
Y. Li, W. Shi, and N. Chopra: Functionalization of multilayer carbon shell-encapsulated gold nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensing and DNA immobilization. Carbon 100, 165 (2015).
K. Li, B. Wang, D. Su, J. Park, H. Ahn, and G. Wang: Enhance electrochemical performance of lithium–sulfur battery through a solution-based processing technique. J. Power Sources 202, 389 (2012).
Z. Chen, X.-L. Du, J.-B. He, F. Li, Y. Wang, Y.-L. Li, B. Li, and S. Xin: Porous coconut shell carbon offering high retention and deep lithiation of sulfur for lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 3385–33862 (2017).
C. Zhang, H.B. Wu, C. Yuan, Z. Guo, and X.W. Lou: Confining sulfur in double‐shelled hollow carbon spheres for lithium–sulfur batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 9592 (2012).
Z.W. Seh, W.Y. Li, J.J. Cha, G.Y. Zheng, Y. Yang, M.T. Mcdowell, P.C. Hsu, and Y. Cui: Sulphur–TiO2 yolk–shell nanoarchitecture with internal void space for long-cycle lithium–sulphur batteries. Nat. Commun. 4, 1331 (2012).
Y. Li, J. Dykes, T. Gilliam, and N. Chopra: A new heterostructured SERS substrate: free-standing silicon nanowires decorated with graphene-encapsulated gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 9, 5263 (2017).
Y. Li, and N. Chopra: Graphene encapsulated gold nanoparticle-quantum dot heterostructures and their electrochemical characterization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 344, 27 (2015).
S.S. Zhang: Role of LiNO3 in rechargeable lithium/sulfur battery. Electrochim. Acta 70, 344 (2012).
C. Barchasz, J.-C. Leprêtre, F. Alloin, and S. Patoux: New insights into the limiting parameters of the Li/S rechargeable cell. J. Power Source 199, 322 (2012).
X. Zheng-Long, J.-K. Kim, and K. Kang: Carbon nanomaterials for advanced lithium–sulfur batteries. Nano Today 19, 84–107 (2018).
P. Xiao, F. Bu, G. Yang, Y. Zhang, and Y. Xu: Integration of graphene, nano sulfur, and conducting polymer into compact, flexible lithium–sulfur battery cathodes with ultrahigh volumetric capacity and superior cycling stability for foldable devices. Adv. Mater. 29, 1703324 (2017).
D.C. Marcano, D.V. Kosynkin, J.M. Berlin, A. Sinitskii, Z. Sun, A. Slesarev, L.B. Alemany, W. Lu, and J.M. Tour: Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4, 4806 (2010).
L. Li, A.-R.O. Raji, H. Fei, Y. Yang, E.L.G. Samuel, and J.M. Tour: Nanocomposite of polyaniline nanorods grown on graphene nanoribbons for highly capacitive pseudocapacitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 5, 6622 (2013).
J. Xu, K. Wang, S.Z. Zu, B.H. Han, and Z. Wei: Hierarchical nanocompo-sites of polyaniline nanowire arrays on graphene oxide sheets with syner-gistic effect for energy storage. ACS Nano 4, 5019 (2010).
L. Hu, J. Tu, S. Jiao, J. Hou, H. Zhu, and D.J. Fray: In situ electrochemical polymerization of a nanorod-PANI–graphene composite in a reverse micelle electrolyte and its application in a supercapacitor. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 15652 (2012).
Y. Li, X. Zhao, P. Yu, and Q. Zhang: Oriented arrays of polyaniline nano-rods grown on graphite nanosheets for an electrochemical supercapacitor. Langmuir 29, 493 (2012).
T.A. Pascal, I. Villaluenga, K.H. Wujcik, D. Devaux, X. Jiang, D.R. Wang, N. Balsara, and D. Prendergast: Liquid sulfur impregnation of micropo-rous carbon accelerated by nanoscale interfacial effects. Nano Lett. 17, 2517–2523 (2017).
N. Li, M. Zheng, H. Lu, Z. Hu, C. Shen, X. Chang, G. Ji, J. Cao, and Y. Shi: High-rate lithium–sulfur batteries promoted by reduced graphene oxide coating. Chem. Commun. 48, 4106 (2012).
Y. Li, and N. Chopra: Structural evolution of cobalt oxide-tungsten oxide nanowire heterostructures for photocatalysis. J. Catal. 329, 514 (2015).
Y. Yang, G. Yu, J.J. Cha, H. Wu, M. Vosgueritchian, Y. Yao, Z. Bao, and Y. Cui: Improving the performance of lithium–sulfur batteries by conductive polymer coating. ACS Nano 5, 9187 (2011).
C. Zu, Y.-S. Su, Y. Fu, and A. Manthiram: Improved lithium–sulfur cells with a treated carbon paper interlayer. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 2291 (2013).
J. Balach, T. Jaumann, and L. Giebeler: Nanosized Li2S-based cathodes derived from MoS2 for high-energy density Li–S cells and Si–Li2S full cells in carbonate-based electrolyte. Energy Storage Mater. 8, 209–216 (2017).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was partly supported by the project funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2018M643698) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51802258).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.149.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Jing, R., You, C. et al. Brush-structured sulfur-polyaniline-graphene composite as cathodes for lithium-sulfur batteries. MRS Communications 9, 1355–1360 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.149
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.149