Abstract
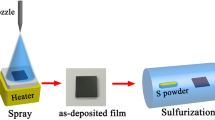
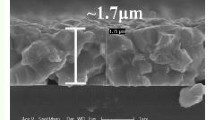
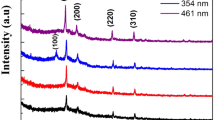
In this work, we present a solvothermal method to prepare bismuth (Bi)-doped CuGaS2 chalcopyrite nanocrystals ink and apply it to an all-solution-processed approach for the preparation of films with a thickness of approximately 730 nm and with enhanced optical properties and lower band gap energy than the undoped semiconductor films. The low-cost deposition method is comprised by spray deposition of the chal-cogenide nanocrystals ink onto the molybdenum substrates, producing microcrystalline films with grains larger than 400 nm originated from coalescence of Bi-doped nanocrystals. Bi-doped CuGaS2 microcrystalline films are a good candidate to be applied as an absorber layer in thin-film solar cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.M. Friedlmeier, P. Jackson, A. Bauer, D. Hariskos, O. Kiowski, R. Menner, R. Wuerz, and M. Powalla: High-efficiency Cu(ln,Ga)Se2 solar cells. Thin Solid Films 633, 13 (2016).
J. Van Deelen,and C. Frijters: CIGS cells with metallized front contact: longer cells and higher efficiency. Sol. Energy 143, 93 (2017).
Z. Lu, R. Jin, Y. Liu, L Guo, X. Liu, J. Liu, K. Cheng, and Z. Du: Optimization of chemical bath deposited cadmium sulfide buffer layer for high-efficient CIGS thin film solar cells. Mater. Lett. 204, 53 (2017).
L. Yu, R.S. Kokenyesi, D.A. Keszler, and A. Zunger: Inverse design of high absorption thin-film photovoltaic materials. Adv. Energy Mater. 3, 43 (2013).
J. Ramanujam, and U.P. Singh: Copper indium gallium selenide based solar cells - review. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 1306 (2017).
T.D. Lee, and A.U. Ebong: a review of thin film solar cell technologies and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 70, 1286 (2017).
M. Han, X. Zhang, Y. Zhang, and Z. Zeng: The group VA element noncompensated n-p codoping in CuGaS2 for intermediate band materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 144, 664 (2016).
W. Jing, Y. Wang, J. Zhu, W. Yao, and S. Song: Effects of Ti-doping on CuGaS2 thin films by co-sputtering and sulfurizing. Mater. Lett. 164, 513 (2016).
N. Armaroli, and V. Balzani: Solar electricity and solar fuels: status and perspectives in the context of the energy transition. Chem. A Eur. J. 22, 32 (2015).
X. Lv, S. Yang, M. Li, H. Li, J. Yi, M. Wang, G. Niu, and J. Zhong: Investigation of a novel intermediate band photovoltaic material with wide spectrum solar absorption based on Ti-substituted CuGaS2. Sol. Energy 103, 480 (2014).
P. Chen, M. Qin, H. Chen, C. Yang, Y. Wang, and F. Huang: Cr incorporation in CuGaS2 chalcopyrite: a new intermediate-band photovoltaic material with wide-spectrum solar absorption. Phys. Stat. Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 210, 1098 (2013).
L. Xiao, J. Zhu, T. Ding, Y. Wang, Y. Fan, and Q. Bo: Synthesis and characterization of Ce-incorporated CulnS2 chalcopyrites. Mater. Lett. 159, 392 (2015).
J. Koskelo, J. Hashemi, S. Huotari, and M. Hakala: First-principles analysis of the intermediate band in CuGa1_xFexS2. Phys. Rev. B 93, 165204 (2016).
M.M. Han, X.L. Zhang, and Z. Zeng: Sn doping induced intermediate band in CuGaS2. RSC Adv. 6, 110511 (2016).
W. Jeong, and G. Park: Structural and electrical properties of CuGaS thin films by electron beam evaporation. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 75, 93 (2003).
S.K. Kim, J.P. Park, M.K. Kim, K.M. Ok, and I.W. Shim: Preparation of CuGaS2 thin films by two-stage MOCVD method. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 92, 1311 (2008).
J.A. Hollingsworth, K.K. Banger, M.H.C. Jin, J.D. Harris, J.E. Cowen, E.W. Bohannan, J.A. Switzer, W.E. Buhro, and A.F. Hepp: Single source precursors for fabrication of I-III-VI2 thin-film solar cells via spray CVD. Thin Solid Films 431–432, 63 (2003).
S.-H. Chang, B.-C. Chiu, T.-L Gao, S.-L. Jheng, and H.-Y. Tuan: Selective synthesis of copper gallium sulfide (CuGaS2) nanostructures of different sizes, crystal phases, and morphologies. CrystEngComm 16, 3323 (2014).
B. Cordero, V. Gomez, A.E. Platero-Prats, M. Reves, J. Echeverrfa, E. Cremades, F. Barragan, and S. Alvarez: Covalent radii revisited. Dalt. Trans. No. 21, 2832 (2008).
N. Guijarro, M.S. Prevot, X. Yu, X.A. Jeanbourquin, P. Bornoz, W. Bouree, M. Johnson, F. Le Formal, and K. Sivula: A bottom-up approach toward all-solution-processed high-efficiency Cu(In,Ga)S2 photocathodes for solar water splitting. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1 (2016).
Y. Zhang, Q. Ye, J. Liu, H. Chen, X. He, C. Liao, J. Han, H. Wang, J. Mei, and W. Lau: Earth-abundant and low-cost CZTS solar cell on flexible molybdenum foil. RSCAdv. 4, 23666 (2014).
R. Moreno, E.A. Ramirez, and G. Gordillo Guzman: Study of optical and structural properties of CZTS thin films grown by co-evaporation and spray pyrolysis. J. Phys. Conf. Ser 687, 012041 (2016).
W.P.C. Lee, L.L. Tan, S. Sumathi, and S.P. Chai: Copper-doped flower-like molybdenum disulfide/bismuth sulfide photocatalysts for enhanced solar water splitting. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 43, 748 (2017).
M. Li, R. Zhao, Y. Su, J. Hu, Z. Yang, and Y. Zhang: Synthesis of CulnS2 nanowire arrays via solution transformation of Cu2S self-template for enhanced photoelectrochemical performance. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 203, 715 (2017).
K. Subbaramaiah, and V. S. Raja: Chemical spray deposition of CuGaS2 thin films. Proc. SPIE 1523, 555 (1992).
S. Ullah, H. Ullah, F. Bouhjar, M. Mollar, and B. Man: Synthesis of in-gap band CuGaS2: Cr absorbers and numerical assessment of their performance in solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 180, 322 (2017).
R. Strandberg, and I. Aguilera: Evaluation of vanadium substituted ln2S3 as a material for intermediate band solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 98, 88 (2012).
T. Ahsan, S. Kalainathan, N. Miyashita, T. Hoshii, Y. Okada, T. Ahsan, S. Kalainathan, N. Miyashita, T. Hoshii, and Y.O. Characterization: Characterization of Cr doped CuGaS2 thin films synthesized by chemical spray pyrolysis. Mech. Mater. Sci. Eng. MMSE J. Open Access 9, 380 (2017).
M. Han, X. Zhang, and Z. Zeng: The investigation of transition metal doped CuGaS2 for promising intermediate band materials. RSC Adv. 4, 62380 (2014).
I. Aksenov, Y. Kudo, and K. Sato: Optical absorption spectra in CuAIS2 doped with vanadium. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1359, L145 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrade, M.A.S., Mascara, L.H. Bismuth doping on CuGaS2 thin films: structural and optical properties. MRS Communications 8, 504–508 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.63
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.63