Abstract
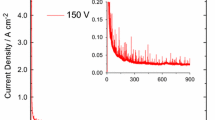
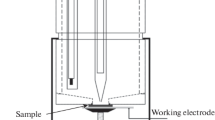
The formation of nanosized porous oxide layers on titanium (Ti) by asymmetric alternating current anodizing in sulfuric acid has been studied using electrochemical techniques. In order to prevent spark discharge at Ti electrode upon its anodization in 1.0 M H2S04 solution, the magnitude of the cathodic current is reduced using a special electrical circuit consisting of a variable resistor and two diodes. The unique surface treatment approach gives rise to the formation of nanosized porous layer in a very short period of time and without spark discharge. The surface of porous layers thus obtained has in vitro apatite-forming ability.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.M. Kim, F. Miyaji, T. Kokubo, and T. Nakamura: Effect of heat treatment on apatite-forming ability of Ti metal induced by alkali treatment. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 8, 341 (1997).
H.M. Kim, F. Miyaji, T. Kokubo, and T. Nakamura: Apatite-forming ability of alkali-treated Ti metal in body environment. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 105, 111 (1997).
H.M. Kim, F. Miyaji, T. Kokubo, S. Nishiguchi, and T. Nakamura: Graded surface structure of bioactive titanium prepared by chemical treatment. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 45, 100 (1999).
P. Ducheyne, W.V. Raemdonck, J.C. Heughebaert, and M. Heughebaert: Structural analysis of hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium. Biomaterials 7, 97 (1986).
K.A. Thomas, J.F. Kay, S.D. Cook, and M. Jarcho: The effect of surface macrotexture and hydroxylapatite coating on the mechanical strengths and histologic profiles of titanium implant materials. J. Biomed. Mater. fles. 21, 1395 (1987).
V.N. Bagratashvili, E.N. Antonov, E.N. Sobol, V.K. Popov, and S.M. Howdle: Macroparticle distribution and chemical composition of laser deposited apatite coatings. Appl. Phys. Lett. 66, 2451 (1995).
J. Lee and H. Aoki: Hydroxyapatite coating on Ti plate by a dipping method. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 5, 49 (1995).
P. Li, K. Groot, and T. Kokubo: Bioactive Ca10(P04)6(0H)2-Ti02 composite coating prepared by sol-gel process. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 7, 27 (1996).
P. Ducheyne, S. Radin, M. Heughebaert, and J.C. Heughebaert: Calcium phosphate ceramic coatings on porous titanium: effect of structure and compositionon electrophoretic deposition, vacuum sintering and in vitro dissolution. Biomaterials 11, 244 (1990).
M. Gottlander, C.B. Johansson, A. Wennerberg, T. Albrektsson, S. Radin, and P. Ducheyne: Bone tissue reactions to an electrophoretically applied calcium phosphate coating. Biomaterials 18, 551 (1997).
S. Tanaka, M. Aonuma, N. Hirose, and T. Tanaki: The preparation of porous Ti02 by immersing Ti in NaOH solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 149, D167 (2002).
S. Tanaka, T. Iwatani, N. Hirose, and T. Tanaki: Effect of hydrogen on the formation of porous Ti02 in alkaline solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 149, F186 (2002).
S. Tanaka, N. Hirose, and T. Tanaki: Effect of the temperature and concentration of NaOH on the formation of porous Ti02. J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, C789 (2005).
S. Tanaka, H. Tobinatsu, Y. Maruyama, T. Tanaki, and G. Jerkiewicz: Preparation and characterization of microporous layers on titanium. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 1, 2312 (2009).
T. Ohtsuka and N. Nomura: The dependence of the optical property of Ti anodic oxide film on its growth rate byellipsometry. Corros. Sci. 39, 1253 (1997).
K.H. Kim and N. Ramaswamy: Electrochemical surface modification of titanium in dentistry. Dent. Mater. J. 28, 20 (2009).
B. Yang, M. Uchida, H.M. Kim, X. Zhang, and T. Kokubo: Preparation of bioactive titanium metal via anodic oxidation treatment. Biomaterials 25, 1003 (2004).
Y.H. Shih, C.T. Lin, C.M. Liu, C.C. Chen, C.S. Chen, and K.L. Ou: Effect of nano-titanium hydride on formation of multi-nanoporous Ti02 film on Ti. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 3678 (2007).
S. Tanaka, Y. Fukushima, I. Nakamura, T. Tanaki, and G. Jerkiewicz: Preparation and characterization of microporous layers on titanium by anodization in sulfuric acid with and without hydrogen charging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 3340 (2013).
S. Hrapovic, B.L. Luan, M.D. Amours, G. Vatankhah, and G. Jerkiewicz: Morphology, chemical composition, and electrochemical characteristics of colored titanium passive layers. Langmuir 17, 3051 (2001).
G. Jerkiewicz, B. Zhao, S. Hrapovic, and B.L. Luan: Discovery of reversible switching of coloration of passive layers on titanium. Chem. Matter. 20, 1877 (2008).
B. Zhao and G. Jerkiewicz: Electrochemically formed passive layers on titanium—Preparation and biocompatibility assessment in Hank’s balanced salt solution. Canadian J. Chem. 84, 1132 (2006).
J. Drunen, B. Zhao, and G. Jerkiewicz: Corrosion behavior of surface-modified titanium in a simulated body fluid. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 5931 (2011).
B.E. Conway and G. Jerkiewicz: Factors in the electrolytic sorption of H into metals and its relation to cathodic hydrogen evolution kinetics. Zeitschrift Physik. Chemie 183, 281 (1994).
G. Jerkiewicz and A. Zolfaghari: Comparison of hydrogen electroadsorption from the electrolyte with hydrogen adsorption from the gas phase. J. Electrochem. Soc. 143, 1240 (1996).
G. Jerkiewicz: Hydrogen sorption at/in electrodes. Prog. Surf. Sci. 57, 137 (1998).
S.Y. Qian, B.E. Conway, and G. Jerkiewicz: Comparative effects of adsorbed S-species on H sorption into Pd from UPD and OPD H: a kinetic analysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 25, 539 (2000).
T. Kokubo and H. Takadama: How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 27, 2907 (2006).
N.Y. Iwata, G.H. Lee, S. Tsunakawa, Y. Tokuoka, and N. Kawashima: Preparation of diopside with apatite-forming ability by sol-gel process using metal alkoxide and metal salts. Colloid. Surf. B: Biointerfaces 33, 1 (2004).
N.Y. Iwata, G.H. Lee, Y. Tokuoka, and N. Kawashima: Sintering behavior and apatite formation of diopside prepared by coprecipitation process. Colloid. Surf. B: Biointerfaces 34, 239 (2004).
F. Xiao, K. Tsuru, S. Hayakawa, and A. Osaka: In vitro apatite deposition on titania film derived from chemical treatment of Ti substrates with an oxysulfate solution containing hydrogen peroxide at low temperature. Thin Solid Films 441, 271 (2003).
T. Kasuga, H. Kondo, and M. Nogami: Apatite formation on Ti02 in simulated body fluid. J. Crystal Growth 235, 235 (2002).
T. Kokubo, H.M. Kim, and M. Kawashita: Novel bioactive materials with different mechanical properties. Biomaterials 24, 2161 (2003).
Q. Ma, M. Li, Z. Hu, Q. Chen, and W. Hu: Enhancement of the bioactivity of titanium oxide nanotubes by precalcification. Mater. Lett. 62, 3035 (2008).
K. Shimogori: Hydrogen absorption by titanium. Boshoku Gijutsu 30, 349 (1981).
T. Fukuzuka, K. Shimogori, H. Satoh, and H. Tomari: The effect of dissolved oxygen on prevention of hydrogen absorption of titanium in dilute HCI solutions. Boshoku Gijutsu 28, 379 (1979).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank to Daniel Morrall (Kyoto University) for his valuable comments on this manuscript. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP24550241. A part of this work was financed by the Light Metal Educational Foundation, Inc., Japan. In addition, this work was partially funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwata, N.Y., Tanaka, Si., Fukushima, Y. et al. Preparation of nanosized porous oxide layers on titanium by asymmetric AC electrolysis in sulfuric acid. MRS Communications 9, 194–202 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.237
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.237