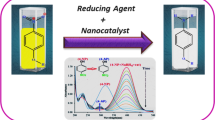
Abstract
Two different sized As(0) nanoparticles As1 (50 ± 7 nm) and As2 (70 ± 10 nm) are prepared by reducing arsenite with NaBH4 in the pH range 7–9, at controlled temperature (10 and 40 °C). Further, galvanic replacement reaction is used exploiting the reducing nature of As(0) to prepare two different sized hollow gold nanoparticles (HGNPs) AuNP1 (55 ± 7 nm) and AuNP2 (72 ± 7 nm). These HGNPs exhibit high catalytic activity towards 4-nitrophenol reduction under various conditions following first-order kinetics. AuNP1 shows ~6.6 time higher turnover frequency compared with that of AuNP2 due to its smaller size. Both catalysts are recycle able.








Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
C.Y. Tsai, S.P. Lu, J.W. Lin, and P.T. Lee: High sensitivity plasmonic index sensor using slablike gold nanoring arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 153108 (2011).
B.P. Timko, M. Arruebo, S.A. Shankarappa, J.B. McAlvin, O.S. Okonkwo, B. Mizrahi, C.F. Stefanescu, L. Gomez, J. Zhu, A. Zhu, J. Santamaria, R. Langer, and D.S. Kohane: Near-infrared-actuated devices for remotely controlled drug delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111, 1349 (2014).
W. Lu, M.P. Melancon, C. Xiong, Q. Huang, A. Elliott, S. Song, R. Zhang, L.G. Flores, J.G. Gelovani, L.V. Wang, G. Ku, R.J. Stafford, and C. Li: Effects of photoacoustic imaging and photothermal ablation therapy mediated by targeted hollow gold nanospheres in an orthotopic mouse xenograft model of glioma. Cancer Res. 71, 6116 (2011).
M.P. Melancon, W. Lu, Z. Yang, R. Zhang, Z. Cheng, A.M. Elliot, J. Stafford, T. Olson, J.Z. Zhang, and C. Li: In vitro and in vivo targeting of hollow gold nanoshells directed at epidermal growth factor receptor for photothermal ablation therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 7, 1730 (2008).
W. Lu, Q. Huang, G. Ku, X. Wen, M. Zhou, D. Guzatov, P. Brecht, R. Su, A. Oraevsky, L.V. Wang, and C. Li: Photoacoustic imaging of living mouse brain vasculature using hollow gold nanospheres. Biomaterials 31, 2617 (2010).
V. Sebastián, S.-K. Lee, C. Zhou, M.F. Kraus, J.G. Fujimoto, and K.F. Jensen: One-step continuous synthesis of biocompatible gold nanorods for optical coherence tomography. Chem. Commun. 48, 6654 (2012).
L. Tong, C.M. Cobley, J. Chen, Y. Xia, and J.X. Cheng: Bright three-photon luminescence from gold/silver alloyed nanostructures for bioimaging with negligible photothermal toxicity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 3485 (2010).
H.J. Fan, U. Gösele, and M. Zacharias: Formation of nanotubes and hollow nanoparticles based on Kirkendall and diffusion processes: a review. Small 3, 1660 (2007).
M.A. Mahmoud, B. Garlyyev, and M.A. El-Sayed: Determining the mechanism of solution metallic nanocatalysis with solid and hollow nanoparticles: homogeneous or heterogeneous. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 21886 (2013).
D. Seo and H. Song: Asymmetric hollow nanorod formation through a partial galvanic replacement reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 18210 (2009).
Y. Yin, C. Erdonmez, S. Aloni, and A.P. Alivisatos: Faceting of nanocrystals during chemical transformation: from solid silver spheres to hollow gold octahedra. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 12671 (2006).
R.J. Hickey, M. Seo, Q. Luo, and S.J. Park: Directional self-assembly of ligand-stabilized gold nanoparticles into hollow vesicles through dynamic ligand rearrangement. Langmuir 31, 4299 (2015).
G. Zhang, S. Sun, R. Li, and X. Sun: New insight into the conventional replacement reaction for the large-scale synthesis of various metal nanostructures and their formation mechanism. Chem. Eur. J. 16, 10630 (2010).
E.A. You, R.W. Ahn, H.L. Min, M.R. Raja, T.V. O’Halloran, and T.W. Odom: Size control of arsenic trioxide nanocrystals grown in nanowells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 10863 (2009).
A. Pal, S. Saha, S.K. Maji, M. Kundu, and A. Kundu: Wet-chemical synthesis of spherical arsenic nanoparticles by a simple reduction method and its characterization. Adv. Mater. Lett. 3, 177 (2012).
A. Pal, S. Saha, S.K. Maji, R. Sahoo, M. Kundu, and A. Kundu: Galvanic replacement of As(0) nanoparticles by Au(III) for nanogold fabrication and SERS application. New J. Chem. 38, 1675 (2014).
R. Sahoo, S. Dutta, M. Pradhan, C. Ray, A. Roy, T. Pal, and A. Pal: Arsenate stabilized Cu2O nanoparticle catalyst for one-electron transfer reversible reaction. Dalt. Trans. 43, 6677 (2014).
S. Saha, A. Pal, S. Kundu, S. Basu, and T. Pal: Photochemical green synthesis of calcium-alginate-stabilized Ag and Au nanoparticles and their catalytic application to 4-nitrophenol reduction. Langmuir 26, 2885 (2010).
P. Mahamallik and A. Pal: A soft-template mediated approach for Au(0) formation on a heterosilica surface and synergism in the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. RSC Adv. 5, 78006 (2015).
T. Aditya, A. Pal, and T. Pal: Nitroarene reduction: a trusted model reaction to test nanoparticle catalysts. Chem. Commun. 51, 9410 (2015).
T. Ma, W. Yang, S. Liu, H. Zhang, and F. Liang: A comparison reduction of 4-nitrophenol by gold nanospheres and gold nanostars. Catalysts 7, 38 (2017).
J. Zeng, Q. Zhang, J. Chen, and Y. Xia: A comparison study of the catalytic properties of Au-based nanocages, nanoboxes, and nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 10, 30 (2010).
R. He, Y.C. Wang, X. Wang, Z. Wang, G. Liu, W. Zhou, L. Wen, Q. Li, X. Wang, X. Chen, J. Zeng, and J.G. Hou: Facile synthesis of pentacle gold-copper alloy nanocrystals and their plasmonic and catalytic properties. Nat. Commun. 5, 1 (2014).
Y.S. Seo, E.-Y. Ahn, J. Park, T.Y. Kim, J.E. Hong, K. Kim, Y. Park, and Y. Park: Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol with gold nanoparticles synthesized by caffeic acid. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12, 7 (2017).
S.S. Dash and B.G. Bag: Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using renewable Punica granatum juice and study of its catalytic activity. Appl. Nanosci. 4, 55 (2014).
X. Wu, C. Lu, Z. Zhou, G. Yuan, R. Xiong, and X. Zhang: Green synthesis and formation mechanism of cellulose nanocrystal-supported gold nanoparticles with enhanced catalytic performance. Environ. Sci. Nano. 1, 71 (2014).
M. Mukhopadhyay and P. Dauthal: Prunus domestica fruit extract mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles and its catalytic activity for 4–nitrophenol reduction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 51, 13014 (2012).
S.K. Das, C. Dickinson, F. Lafir, D.F. Brougham, and E. Marsili: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles biosynthesized with Rhizopus oryzae protein extract. Green Chem. 14, 1322 (2012).
Z. Gao, R. Su, R. Huang, W. Qi, and Z. He: Glucomannan-mediated facile synthesis of gold nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9, 1 (2014).
J. Lee, J.C. Park, and H. Song: A nanoreactor framework of a Au@SiO2 yolk/shell structure for catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol. Adv. Mater. 20, 1523 (2008).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank IIT Kharagpur for the instrumental facilities and financial support. We would also thank Prof. N. Sarkar of Chemistry Department, IIT Kharagpur for providing the DLS facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.214
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalyan, I., Pal, T. & Pal, A. Time and temperature dependent formation of hollow gold nanoparticles via galvanic replacement reaction of As(0) and its catalytic application. MRS Communications 9, 270–279 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.214
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.214