Abstract
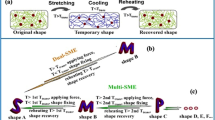
In this study, a novel shape memory polymer (SMP), eggshell membrane (ESM), with macroscopic mesh structures and microscopic crosslinked protein fibers, has shown water-stimulated shape recovery characteristics. Our results show that the collagen triple-helical molecular chains and disulfide-rich motifs in the ESM function as net-points retaining essential structures during deformation, while hydrogen bonds play a key role as switch units for shape recovery through water stimulation. We also demonstrate that programmable shape recovery characteristics of ESM can be obtained by modulating the number of net-points. This study may inspire the design of new programmable SMPs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Leng, X. Lan, Y. Liu, and S. Du: Shape-memory polymers and their composites: Stimulus methods and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 56, 1077–1135 (2011).
T. Xie: Tunable polymer multi-shape memory effect. Nature 464, 267–270 (2010).
D. Zhao, T. van Leeuwen, J. Cheng, and B.L. Feringa: Dynamic control of chirality and self-assembly of double-stranded helicates with light. Nat. Chem. 9, 250–256 (2017).
A.H. Gelebart, D.J. Mulder, G. Vantomme, A.P.H.J. Schenning, and D.J. Broer: A rewritable, reprogrammable, dual light-responsive polymer actuator. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 13436–13439 (2017).
M.Y. Razzaq, M. Behl, K. Kratz, and A. Lendlein: Multifunctional hybrid nanocomposites with magnetically controlled reversible shape-memory effect. Adv. Mater. 25, 5730–5733 (2013).
J. Wang, L. Sun, M. Zou, W. Gao, C. Liu, L. Shang, Z. Gu, and Y. Zhao: Bioinspired shape-memory graphene film with tunable wettability. Sci. Adv. 3, e1700004 (2017).
Y. Xiao, S. Zhou, L. Wang, and T. Gong: Electro-active shape memory properties of poly(ε-caprolactone)/functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposite. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2, 3506–3514 (2010).
H. Deng, Y. Dong, J.W. Su, C. Zhang, Y. Xie, C. Zhang, M.R. Maschmann, Y. Lin, and J. Lin: Bioinspired programmable polymer gel controlled by swellable guest medium. ACS. Appl. Mater. Inter. 9, 30900–30908 (2017).
A.V. Salvekar, W. Huang, R. Xiao, Y.S. Wong, S.S. Venkatraman, K.H. Tay, and Z. Shen: Water-responsive shape recovery induced buckling in biodegradable photo-cross-linked poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogel. Acc. Chem. Res. 50, 141–150 (2017).
M. Ma, L. Guo, D.G. Anderson, and R. Langer: Bio-inspired polymer composite actuator and generator driven by water gradients. Science 339, 186–189 (2013).
Z. Fang, Y. Kuang, P. Zhou, S. Ming, P. Zhu, Y. Liu, H. Ning, and G. Chen: Programmable shape recovery process of water-responsive shape-memory poly(vinyl alcohol) by wettability contrast strategy. ACS. Appl. Mater. Inter. 9, 5495–5502 (2017).
X. Xiao and J. Hu: Animal hairs as water-stimulated shape memory materials: mechanism and structural networks in molecular assemblies. Sci. Rep. 6, 26393 (2016).
Z. Liu, D. Jiao, and Z. Zhang: Remarkable shape memory effect of a natural biopolymer in aqueous environment. Biomaterials 65, 13–21 (2015).
N.N. Ashton and R.J. Stewart: Self-recovering caddisfly silk: energy dissipating, Ca2+-dependent, double dynamic network fibers. Soft Matter 11, 1667–1676 (2015).
O. Emile, A.L. Floch, and F. Vollrath: Shape memory in spider draglines. Nature 440, 621–621 (2006).
M. Baláž: Eggshell membrane biomaterial as a platform for applications in materials science. Acta Biomater. 10, 3827–3843 (2014).
Q. Li, Y. Bai, T. Jin, S. Wang, W. Cui, I. Stanciulescu, R. Yang, H. Nie, L. Wang, and X. Zhang: Bioinspired engineering of poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels and natural protein fibers for layered heart valve constructs. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 9, 16524–16535 (2017).
X. Wang, Q. Li, Y. Yuan, B. Mei, R. Huang, Y. Tian, J. Sun, C. Cao, G. Lu, and G. Liang: New method for effectively and quantitatively labeling cysteine residues on chicken eggshell membrane. Org. Biomol. Chem. 10, 8082–8086 (2012).
T. Nakano, N. Ikawa, and L. Ozimek: Chemical composition of chicken eggshell and shell membranes. Poult. Sci. 82, 510–514 (2003).
K. Simkiss and C. Tyler: A histochemical study of the organic matrix of hen egg-shells. Q. J. Microsc. Sci. 98, 19–28 (1957).
N. Li, L. Niu, Y. Qi, C.K.Y. Yiu, H. Ryou, D.D. Arola, J. Chen, D.H. Pashley, and F.R. Tay: Subtleties of biomineralisation revealed by manipulation of the eggshell membrane. Biomaterials 32, 8743–8752 (2011).
V.K. Kodali, S.A. Gannon, S. Paramasivam, S. Raje, T. Polenova, and C. Thorpe: A novel disulfide-rich protein motif from avian eggshell membranes. PLoS ONE 6, e18187 (2011).
H. Su, J. Han, N. Wang, Q. Dong, D. Zhang, and C. Zhang: In situ synthesis of lead sulfide nanoclusters on eggshell membrane fibers by an ambient bio-inspired technique. Smart Mater. Struct. 17, 015045 (2008).
C. Li, H. Liao, X. Zhang, X. Yu, and M. Tong: Preparation of cationic modified collagen extracted from leather wastes and their application in dye flocculation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 134, 45363 (2017).
H. Du and J. Zhang: Solvent induced shape recovery of shape memory polymer based on chemically cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol). Soft Matter 6, 3370–3376 (2010).
T. Yang, M. Chen, X. Hu, Z. Wang, J. Wang, and P.K. Dasgupta: Thiolated eggshell membranes sorb and speciate inorganic selenium. Analyst 136, 83–89 (2011).
P.Y. Chen, J. Mckittrick, and M.A. Meyers: Biological materials: Functional adaptations and bioinspired designs. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57, 1492–1704 (2012).
D.A. Carrino, J.E. Dennis, T.M. Wu, J.L. Arias, M.S. Fernandez, J.P. Rodriguez, D.J. Fink, A.H. Heuer, and A.L. Caplan: The avian eggshell extracellular matrix as a model for biomineralization. Connect. Tissue Res. 35, 325–329 (1996).
F.G. Torres, O.P. Troncoso, F. Piaggio, and A. Hijar: Structure-property relationships of a biopolymer network: the eggshell membrane. Acta Biomater. 6, 3687–3693 (2010).
C.A. Miles and A.J. Bailey: Thermally labile domains in the collagen molecule. Micron 32, 325–332 (2001).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31670981, 31300788) and the Hundred-Talent Program from the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The authors thank Wei Cui and Yuling Ma at the Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences for assistance with sample preparation and microstructure characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary material
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at {rs|https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.100|url|}
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Liu, C., Li, Q. et al. Natural eggshell membranes exhibiting programmable shape recovery characteristics. MRS Communications 8, 903–910 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.100
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.100