Abstract
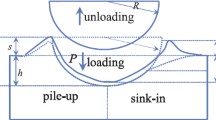
This paper aims to obtain an analytical expression for the ratio of unloading work of indentation (Wu) to total loading work of indentation (Wt) (work recovery ratio of indentation) in instrumented spherical indentation. The expanding cavity model and Lamé solution are used. Three typical stress–strain relations (elastic-perfectly plastic, linear hardening, and power-law hardening) are analyzed. The results of finite-element method coincide with the expressions. The expressions show that the work recovery ratio of indentation is just related to plastic parameters. Furthermore, elastic work (We) are obtained, and it is proved that We should be distinguished from Wu in spherical indentation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Hasanov: An inversion method for identification of elastoplastic properties for engineering materials from limited spherical indentation measurements. Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng. 15, 601 (2007).
M.Q. Le: Material characterization by instrumented spherical indentation. Mech. Mater. 46, 42 (2012).
N. Ogasawara, N. Chiba, and X. Chen: A simple framework of spherical indentation for measuring elastoplastic properties. Mech. Mater. 41, 1025 (2009).
C. Yu, Y.H. Feng, R. Yang, G.J. Peng, Z.K. Lu, and T.H. Zhang: An integrated method to determine elastic–plastic parameters by instrumented spherical indentation. J. Mater. Res. 29, 1095 (2014).
K.L. Johnson: The correlation of indentation experiments. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 18, 115 (1970).
R. Yang, T.H. Zhang, and Y.H. Feng: Theoretical analysis of the relationships between hardness, elastic modulus, and the work of indentation for work-hardening materials. J. Mater. Res. 25, 2072 (2010).
R. Hill: The Mathematical Theory of Plasticity (Oxford University Press, New York, 1998).
X.L. Gao and X.N. Jing: Two new expanding cavity models for indentation deformations of elastic strain-hardening materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43, 2193 (2006).
P. Jiang, T.H. Zhang, Y.H. Feng, R. Yang, and N.G. Liang: Determination of plastic properties by instrumented spherical indentation: expanding cavity model and similarity solution approach. J. Mater. Res. 24, 1045 (2009).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation advances in understanding and refinement. J. Mater. Res. 19, 3 (2004).
ISO 14577: 2002, Metallic materials—instrumented indentation test for hardness and materials parameters.
R. Yang, T.H. Zhang, P. Jiang, and Y.L. Bai: Experimental verification and theoretical analysis of the relationships between hardness, elastic modulus, and the work of indentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 231906 (2008).
Acknowledgments
Authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11025212, 11272318, 11172305, 11302231, 11372323, and 11402233).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, C., Yang, R., Feng, Y. et al. Relationships between the work recovery ratio of indentation and plastic parameters for instrumented spherical indentation. MRS Communications 5, 89–94 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2015.10
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2015.10