Abstract
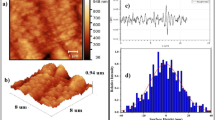
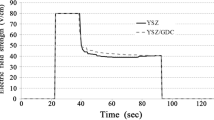
Quantum simulations of oxygen incorporation at a Σ5 grain boundary in yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), a common solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) electrolyte, show that the incorporation energy is reduced compared with YSZ with no grain boundaries. The simulation results are supported by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements conducted on a single crystalline YSZ substrate with nanogranular interlayered YSZ. EIS results showed that single crystalline YSZ membranes with nanogranular surface (i.e., high grain boundary densities) exhibit small electrode impedances than the reference single crystalline YSZ. The 20-nm-thick nanogranular YSZ interlayer was fabricated by atomic layer deposition and the performance for SOFCs with nanograined interlayer was increased by factor of 2 at operating temperatures between 350 and 450 °C.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Knoner, K. Reimann, R. Rower, U. Sodervall, and H.E. Schaeffer: Enhanced oxygen diffusivity in interfaces of nanocrystalline ZrO2⋅Y2O3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 3860 (2003).
I. Kosacki, C.M. Rouleau, P.F. Becher, J. Bentley, and D.H. Lowndesb: Surface/interface-related conductivity in nanometer thick YSZ films. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 7, A459 (2004).
H. Huang, T.M. Gür, Y. Saito, and F.B. Prinz: High ionic conductivity in ultrathin nanocrystalline gadolinia-doped ceria films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 143107 (2006).
J.H. Shim, C.C. Chao, H. Huang, and F.B. Prinz: Atomic layer deposition of yttria-stabilized zirconia for solid oxide fuel cells. Chem. Mater. 19, 3850 (2007).
J.H. Shim, J.S. Park, T.P. Holme, K. Crabb, W. Lee, Y.B. Kim, X. Tian, T.M. Gür, and F.B. Prinz: Enhanced oxygen exchange and incorporation at surface grain boundaries on an oxide ion conductor. Acta Mater. 60, 1 (2012).
G. Kresse and J. Furthmüller: Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169 (1996).
G. Kresse and J. Joubert: From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. J. Phys. Rev. B 59, 1758 (1999).
J. Perdew and A. Zunger: Density-functional approximation for the correlation energy of the inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. B 23, 5048 (1982).
H.J. Monkhorst and J.D. Pack: Special pointes for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 13, 5188 (1976).
W. Lee, H.J. Jung, M. Lee, Y. Kim, J.S. Park, R. Sinclair, and F.B. Prinz: Oxygen surface exchange at grain boundaries of oxide ion conductors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 965 (2012).
W.C. Conner and J.L. Falconer: Spillover in heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 95, 759 (1995).
H. Huang, M. Nakamura, P. Su, R. Fasching, Y. Saito, and F.B. Prinz: High-performance ultrathin solid oxide fuel cells for low-temperature operation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 154, B20 (2007).
S. Souza, S.J. Visco, and L.C. De Jonghe: Thin-film solid oxide fuel cell with high performance at low-temperature. Solid State Ionics 98, 57 (1997).
T.P. Holme, R. Pornprasertsuk, and F. Prinz: Interpretation of low temperature solid oxide fuel cell electrochemical impedance spectra. J. Electrochem. Soc. 157, B64 (2010).
Y. Kim, T. Holme, T.M. Gür, and F.B. Prinz: Surface-modified lowtemperature solid oxide fuel cell. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 4684 (2011).
Y. Kim, J.S. Park, T.M. Gür, and F.B. Prinz: Oxygen activation over engineered surface grains on YDC/YSZ interlayered composite electrolyte for LT-SOFC. J. Power Sources 196, 19550 (2011).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Turgut M. Gür for helpful discussion, and the members of Nanoscale Prototyping Laboratory at Stanford University for their support and suggestions. This research used resources of the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center, which is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.S., Holme, T.P., Shim, J.H. et al. Improved oxygen surface exchange kinetics at grain boundaries in nanocrystalline yttria-stabilized zirconia. MRS Communications 2, 107–111 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2012.18
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2012.18