Abstract
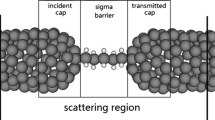
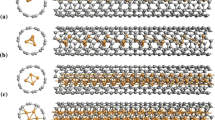
Applying a first-principles computational approach, we study the electronic and charge transport properties of the interfaces between metals and capped carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with various arrangements of topological defects. Observing the length scaling of resistance, we first show that capped CNTs exhibit only one CNT-body-determined low-slope scaling and the resulting very low long-length-limit resistance. The intrinsically low resistance (absence of Schottky-barrier-dominated high-slope scaling) of capped CNTs is next analyzed by the local density of states, which shows the formation of unusual propagating-type metal-induced gap states originating from the topological defect states that are well connected with CNT edge and body states.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.J. Tans, A.R.M. Verschueren, and C. Dekker: Room-temperature transistor based on a single carbon nanotube. Nature 393, 49 (1998).
R. Martel, T. Schmidt, H.R. Shea, T. Hertel, and P. Avouris: Single- and multi-wall carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 2447 (1998).
A. Javey, J. Guo, Q. Wang, M. Lundstrom, and H. Dai: Ballistic carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Nature 424, 654 (2003).
A.D. Franklin and Z. Chen: Length scaling of carbon nanotube transistors. Nature Nanotech. 5, 858 (2010).
J. Svensson and E.E.B. Campbell: Schottky barriers in carbon nanotubemetal contacts. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 111101 (2011).
S. Heinze, J. Tersoff, R. Martel, V. Derycke, J. Appenzeller, and P. Avouris: Carbon nanotubes as Schottky barrier transistors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 106801 (2002).
V. Vitale, A. Curioni, and W. Andreoni: Metal-carbon nanotube contacts: The link between Schottky barrier and chemical bonding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 5848 (2008).
Y. Zhang, N. Franklin, R. Chen, and H. Dai: Metal coating on suspended carbon nanotubes and its implication to metal-tube interaction. Chem. Phys. Lett. 331, 35 2000).
Y.-H. Kim and Y.M. Byun: Diameter dependence of charge transport across carbon nanotube-metal contacts from first principles. J. Kor. Phys. Soc. 55, 299 (2009).
Y.-H. Kim and H.S. Kim: Anomolous length scaling of carbon nanotubemetal contact resistance: An ab initio study. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 213113 (2012).
G. Brinkmann, P.W. Fowler, D.E. Manolopoulos, and A.H.R. Palser: A census of nanotube caps. Chem. Phys. Lett. 315, 335 (1999).
S. Reich, L. Li, and J. Robertson: Structure and formation energy of carbon nanotube caps. Phys. Rev. B 72, 165423 (2005).
M. Khazaei, K.A. Dean, A.A. Farajian, and Y. Kawazoe: Field emission signature of pentagons at carbon nanotube caps. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 6690 (2007).
J.J. Palacios, P. Tarakeshwar, and D.M. Kim: Metal contacts in carbon nanotube field effect transistors: Beyond the Schottky barrier paradigm. Phys. Rev. B 77, 113403 (2008).
C. Adessi, R. Avriller, X. Blase, A. Bournel, H.C. d’Honincthun, P. Dollfus, S. Fregonese, S. Galdin-Retailleau, A. Lopez-Bezanilla, C. Maneux, H.N. Nguyen, D. Querlioz, S. Roche, F. Triozon, and T. Zimmer: Multiscale simulation of carbon nanotube devices. C. R. Physique 10, 305 (2009).
D. Mann, A. Javey, J. Kong, Q. Wang, and H.J. Dai: Ballistic transport in metallic nanotubes with reliable Pd ohmic contacts. Nano Lett. 3, 1541 (2003).
Y. Nosho, Y. Ohno, S. Kishimoto, and T. Mizutani: Evidence of edge conduction at nanotube/metal contact in carbon nanotube devices. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, L474 (2007).
Y.-H. Kim, J. Tahir-Kheli, P.A. Schultz, and W.A. Goddard III: First-principles approach to the charge-transport characteristics of monolayer molecular-electronics devices: Application to hexanedithiolate devices. Phys. Rev. B 73, 235419 (2006).
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, and M. Ernzerhof: Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996).
SeqQuest Project (ver. 2.4), Sandia National Laboratories (http://dft.sandia.gov/Quest).
S. Datta: Quantum Transport: Atom to Transistor (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England, 2005).
J.G. Simmons: Generalized formula for the electric tunnel effect between similar electrodes separated by a thin insulating film. J. Appl. Phys. 34, 1793 (1963).
K. Nakada, M. Fujita, G. Dresselhaus, and M.S. Dresselhaus: Edge state in graphene ribbons: Nanometer size effect and edge shape dependence. Phys. Rev. B 54, 17954 (1996).
T. Kawai, Y. Miyamoto, O. Sugino, and Y. Koga: Graphitic ribbons without hydrogen-termination: Electronic structures and stabilities. Phys. Rev. B 62, R16349 (2000).
G.I. Lee, J.K. Kang, and Y.-H. Kim: Metal-Independent coherent electron tunneling through polymerized fullerene chains. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 7029 (2008).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF, Grant No. 2008-02807) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology. H.S. Kim, H.S. Kim, and Y.H. Kim were also supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF, Grant No. 2010-0006910). J.K. Kang and G.I. Lee were also supported by the WCU program (R-31-2008-000-10055-0) and the Korea Center for Artificial Photosynthesis (NRF-2009-C1AAA001-2009-0093879).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials
For supplementary material for this article, please visit http://dx.doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2012.14
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H.S., Kim, H.S., Lee, G.I. et al. Intrinsically low-resistance carbon nanotube-metal contacts mediated by topological defects. MRS Communications 2, 91–96 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2012.14
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2012.14