Abstract
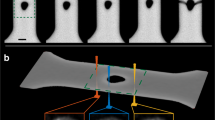
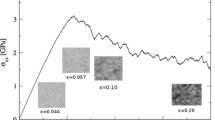
We observed the formation of dominant shear bands in model ZrCuAl metallic glass (MG) nanowires (18-nm-long) in molecular dynamics simulations, which implies size-independent incipient plasticity in MG materials. The MG nanowires were prepared using the simulated casting technique to ensure proper relaxation of sample surfaces. Under uniaxial compression, shear bands initiate at the surfaces and lead to reduced icosahedral short-range order. The shear band formation is sensitive to sample thermal history, which calls for careful consideration of sample preparation effects in both experimental and numerical studies of size effect in MG samples.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Schuh, T. Hufnagel, and U. Ramamurty: Mechanical behavior of amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 55, 4067–4109 (2007).
A.L. Greer: Metallic glasses…on the threshold. Mater. Today 12, 14–22 (2009).
C.A. Volkert, A. Donohue, and F. Spaepen: Effect of sample size on deformation in amorphous metals. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 083539 (2008).
K. Nakayama, Y. Yokoyama, T. Ono, M. Chen, K. Akiyama, T. Sakurai, and A. Inoue: Controlled formation and mechanical characterization of metallic glassy nanowires. Adv. Mater. 22, 872 (2010).
D. Jang and J.R. Greer: Transition from a strong-yet-brittle to a stronger-and-ductile state by size reduction of metallic glasses. Nat. Mater. 9, 215–219 (2010).
H. Guo, P.F. Yan, Y.B. Wang, J. Tan, Z.F. Zhang, M.L. Sui, and E. Ma: Tensile ductility and necking of metallic glass. Nat. Mater. 6, 735–739 (2007).
A.R. Yavari, K. Georgarakis, W.J. Botta, A. Inoue, and G. Vaughan: Homogenization of plastic deformation in metallic glass foils less than one micrometer thick. Phys. Rev. B 82, 172202 (2010).
A. Bharathula, S.W. Lee, W.J. Wright, and K.M. Flores: Compression testing of metallic glass at small length scales: effects on deformation mode and stability. Acta Mater. 58, 5789–5796 (2010).
D. Jang, C.T. Gross, and J.R. Greer: Effects of size on the strength and deformation mechanism in Zr-based metallic glasses. Int. J. Plast. 27, 858–867 (2011).
C.Q. Chen, Y.T. Pei, O. Kuzmin, Z.F. Zhang, E. Ma, and J. Hosson: Intrinsic size effects in the mechanical response of taper-free nanopillars of metallic glass. Phys. Rev. B 83, 180201 (2011).
X.L. Wu, Y.Z. Guo, Q. Wei, and W.H. Wang: Prevalence of shear banding in compression of Zr41Ti14Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 pillars as small as 150 nm in diameter. Acta Mater. 57, 3562–3571 (2009).
A. Dubach, R. Raghavan, J.F. Löffler, J. Michler, and U. Ramamurty: Micropillar compression studies on a bulk metallic glass in different structural states. Scripta Mater. 60, 567–570 (2009).
B.E. Schuster, Q. Wei, T.C. Hufnagel, and K.T. Ramesh: Size-independent strength and deformation mode in compression of a Pd-based metallic glass. Acta Mater. 56, 5091–5100 (2008).
Y. Shi and M. Falk: Atomic-scale simulations of strain localization in three-dimensional model amorphous solids. Phys. Rev. B 73, 214201 (2006).
Y.Q. Cheng, A.J. Cao, and E. Ma: Correlation between the elastic modulus and the intrinsic plastic behavior of metallic glasses: the roles of atomic configuration and alloy composition. Acta Mater. 57, 3253–3267 (2009).
Q.K. Li and M. Li: Molecular dynamics simulation of intrinsic and extrinsic mechanical properties of amorphous metals. Intermetallics 14, 1005–1010 (2006).
Y.Q. Cheng, A.J. Cao, H.W. Sheng, and E. Ma: Local order influences initiation of plastic flow in metallic glass: effects of alloy composition and sample cooling history. Acta Mater. 56, 5263–5275 (2008).
Y. Shi: Size-independent shear band formation in amorphous nanowires made from simulated casting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 121909 (2010).
Y. Cheng, E. Ma, and H. Sheng: Atomic level structure in multicomponent bulk metallic glass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 245501 (2009).
Y. Shi and M. Falk: Does metallic glass have a backbone? The role of percolating short range order in strength and failure. Scr. Mater. 54, 381–386 (2006).
Y. Yokoyama, T. Yamasaki, P.K. Liaw, and A. Inoue: Study of the structural relaxation-induced embrittlement of hypoeutectic Zr-Cu-Al ternary bulk glassy alloys. Acta Mater. 56, 6097–6108 (2008).
X.J. Gu, S.J. Poon, G.J. Shiflet, and J.J. Lewandowski: Ductile-to-brittle transition in a Ti-based bulk metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 60, 1027–1030 (2009).
G. Kumar, D. Rector, R.D. Conner, and J. Schroers: Embrittlement of Zr-based bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 57, 3572–3583 (2009).
H. Zhang, S. Maiti, and G. Subhash: Evolution of shear bands in bulk metallic glasses under dynamic loading. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 56, 2171–2187 (2008).
C.J. Lee, Y.H. Lai, J.C. Huang, X.H. Du, L. Wang, and T.G. Nieh: Strength variation and cast defect distribution in metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 63, 105–108 (2010).
Acknowledgment
We thank Michael Falk, Craig Maloney, Liping Huang, Despina Louca and Peter K. Liaw for stimulating discussions. Y.F.S. acknowledges financial support from NSF under Grant No. CMMI-1031408 and H.W.S. from NSF under Grant No. DMR-0907325. The molecular dynamics simulations were carried out in LAMMPS using the computational facilities of the Computational Center for Nanotechnology Innovations (CCNI) at RPI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials
For supplementary material for this article, please visit http://dx.doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2011.26
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Q., Sheng, H.W. & Shi, Y. Dominant shear bands observed in amorphous ZrCuAl nanowires under simulated compression. MRS Communications 2, 13–16 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2011.26
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2011.26