Abstract
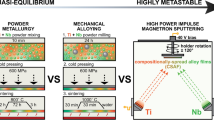
The Ti–35Nb–7Zr–5Ta (TNZT) alloy is a promising alloy because of its biocompatibility, high specific strength, and low Young’s modulus. This work aimed at investigating the viability to process the TNZT alloy by selective laser melting (SLM) and at optimizing the processing parameters to obtain densified bulk samples. The single-track approach was first used, and the optimized laser parameters were determined to produce bulk samples with a relative density of 99.0% when an energy input of 58.3 J/mm3 was used. The effect of porosity on mechanical properties was studied, and the as-built SLM samples presented slightly lower compressive strength than samples produced by Cu-mould suction casting, as a result of a columnar grain structure in the SLMed samples. Prototypes were manufactured, proving the feasibility of manufacturing parts of the TNZT alloy with complex geometry by SLM.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Herzog, V. Seyda, E. Wycisk, and C. Emmelmann: Additive manufacturing of metals. Acta Mater. 117, 371 (2016).
T. Debroy, H.L. Wei, J.S. Zuback, T. Mukherjee, J.W. Elmer, J.O. Milewski, A.M. Beese, A. Wilson-Heid, A. De, and W. Zhang: Additive manufacturing of metallic components—Process, structure, and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 92, 112 (2018).
S.A.M. Tofail, E.P. Koumoulos, A. Bandyopadhyay, S. Bose, L.O. Donoghue, and C. Charitidis: Additive manufacturing: Scientific and technological challenges, market uptake, and opportunities. Mater. Today 21, 22 (2018).
S.L. Sing, J. An, W.Y. Yeong, and F.E. Wiria: Laser and electron-beam powder-bed additive manufacturing of metallic implants: A review on processes, materials, and designs. J. Orthop. Res. 34, 369 (2016).
M. Niinomi, M. Nakai, and J. Hieda: Development of new metallic alloys for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 8, 3888 (2012).
M. Niinomi: Metals for Biomedical Devices, 1st ed. (CRC Press Woodhead Publishing Ltd., Cambridge, U.K., 2010); pp. 3–62.
H.Y. Kim, Y. Ikehara, J.I. Kim, H. Hosoda, and S. Miyazaki: Martensitic transformation, shape memory effect and superelasticty of Ti–Nb binary alloys. Acta Mater. 54, 2419 (2006).
L. Thijs, F. Verhaeghe, T. Craeghs, J.V. Humbeeck, and J-P. Kruth: A study of the microstructural evolution during selective laser melting of Ti–6Al–4V. Acta Mater. 58, 3303 (2010).
A. Kreitcberg, V. Brailovski, and S. Prokoshkin: New biocompatible near-beta Ti–Zr–Nb alloy processed by laser powder bed fusion: Process optimization. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 252, 821 (2018).
W. Chen, C. Chen, X. Zi, X. Cheng, X. Zhang, Y.C. Lin, and K. Zhou: Controlling the microstructure and mechanical properties of a metastable β titanium alloy by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 726, 240 (2018).
L.C. Zhang, D. Klemm, J. Eckert, Y.L. Hao, and T.B. Sercombe: Manufacture by selective laser melting and mechanical behavior of a biomedical Ti–24Nb–4Zr–8Sn alloy. Scr. Mater. 65, 21 (2011).
I. Gibson, D. Rosen, and B. Stucker: Additive manufacturing technologies: 3D printing, rapid prototyping, and direct digital manufacturing 2nd edition. Johnson Matthey Technol. Rev. 59, 193 (2015).
T.A.G. Donato, L.H. de Almeida, R.A. Nogueira, T.C. Niemeyer, C.R. Grandini, R. Caram, S.G. Schneider, and A.R. Santos: Cytotoxicity study of some Ti alloys used as biomaterial. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 29, 1365 (2009).
R. Banarjee, S. Nag, J. Stechschulte, and H.L. Fraser: Strengthening mechanisms in Ti–Nb–Zr–Ta and Ti–Mo–Zr–Fe orthopaedic alloys. Biomaterials 25, 3413 (2004).
Z. Liu and G. Welsch: Literature survey on diffusivities of oxygen, aluminum, and vanadium in alpha titanium, beta titanium, and in rutile. Metall. Trans. A 19, 1121 (1988).
V.R. Jablokov, N.G.D. Murray, H.J. Rack, and H.L. Freese: Influence of oxygen content on the mechanical properties of titanium–35niobium–7zirconium–5tantalum beta titanium alloy. J. ASTM Int. 2, 41 (2005).
Y.D. Zhang, D.P. Zhao, Y.J. Huang, M. Yan, J.H. Zhang, J.P. Luo, and J.F. Sun: Low-modulus biomedical Ti–30Nb–5Ta–3Zr additively manufactured by selective laser melting and its biocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 97, 275 (2019).
R. Boyer, G. Welsch, and E.W. Collings: Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys, 4th ed. (ASM International, Ohio, 1994); pp. 3–11.
C. Leyens and M. Peters: Titanium and Titanium Alloys. Fundamentals and Applications (WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany, 2003); pp. 4–12.
J.H. Tan, W.L.E. Wong, and K.W. Dalgarno: An overview of powder granulometry on feedstock and part performance in the selective laser melting process. Addit. Manuf. 18, 228 (2017).
H.F. Fischmeister, A.D. Ozerskii, and L. Olsson: Solidification structure of gas atomized high-speed steel powders. Powder Metall. 25, 1 (1982).
I. Yadroitsev, P. Bertrand, and I. Smurov: Parametric analysis of the selective laser melting process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 8064 (2007).
I. Yadroitsev, A. Gusarov, I. Yadroitsava, and I. Smurov: Single track formation in selective laser melting of metal powders. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 210, 1624 (2010).
I. Yadroitsev and I. Smurov: Selective laser melting technology: From the single laser melted track stability to 3D parts of complex shape. Phys. Procedia 5, 551 (2010).
W.J. Sames, F.A. List, S. Pannala, R.R. Dehoff, and S.S. Babu: The metallurgy and processing science of metal additive manufacturing. Int. Mater. Rev. 61, 315 (2016).
C.Y. Yap, C.K. Chua, Z.L. Dong, Z.H. Liu, D.Q. Zhang, L.E. Loh, and S. L Sing: Review of selective laser melting: Materials and applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2, 1 (2015).
D. Bourell, J. Pierre, M. Leu, G. Levy, D. Rosen, A.M. Beese, and A. Clare: Materials for additive manufacturing. CIRP Ann. - Manuf. Technol. 66, 659 (2017).
B. Vrancken, L. Thijs, J-P. Kruth, and J. Van Humbeeck: Microstructure and mechanical properties of a novel β titanium metallic composite by selective laser melting. Acta Mater. 68, 150 (2014).
S.L. Sing, F.E. Wiria, and W.Y. Yeong: Selective laser melting of titanium alloy with 50 wt% tantalum: Effect of laser process parameters on part quality. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 77, 120 (2018).
R.L. Batalha, S. Pauly, U. Kühn, K. Kosiba, C. Bolfarini, C. Shyinti Kiminami, and P. Gargarella: Oligocrystalline microstructure in an additively manufactured biocompatible Ti–Nb–Zr–Ta alloy. Mater. Lett. 262, 127149 (2020).
H. Schwab, K.G. Prashanth, L. Löber, U. Kühn, and J. Eckert: Selective laser melting of Ti–45Nb alloy. Metals 5, 686 (2015).
W.E. Frazier: Metal additive manufacturing: A review. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23, 1917 (2014).
Y. Zheng, X. Xu, Z. Xu, J. Wang, and H. Cai: Metallic Biomaterials: New Directions and Technologies, 1st ed. (Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2017); pp. 1–13.
H.Y. Kim and S. Miyazaki: Several issues in the development of Ti–Nb-based shape memory alloys. Shape Memory Superelasticity 2, 380 (2016).
J-P. Kruth, B. Vandenbroucke, I.J. Van Vaerenbergh, and I. Naert: Rapid Manufacturing of Dental Prostheses by Means of Selective Laser Sintering/Melting, Vol. S4 (Proceedings of the AFPR, Netherlands, 2005).
B. Vandenbroucke and J.P. Kruth: Selective laser melting of biocompatible metals for rapid manufacturing of medical parts. Rapid Prototyp. J. 13, 196 (2007).
T. Gustmann, A. Neves, U. Kühn, P. Gargarella, C.S. Kiminami, C. Bolfarini, J. Eckert, and S. Pauly: Influence of processing parameters on the fabrication of a Cu–Al–Ni–Mn shape-memory alloy by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 11, 23 (2016).
P. Karimi, T. Raza, J. Anderson, and L.E. Svensson: Influence of laser exposure time and point distance on 75-µm-thick layer of selective laser melted alloy 718. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 94, 2199 (2018).
Acknowledgments
THe authors thank Dr. K. Kosiba, Dr. U. Kühn, Dr. H. Schwab, Dr. O. Ertugrul, Dr. O. Salman, and Dr. A. Funk for fruitful discussions and E. D’Almeida, B. Bartusch, C. Mix, H. Merker, and S. Donath for technical assistance. This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior, Brasil (CAPES)–Finance Code 001. This study was financed by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior, Brasil (CAPES), and German Research Foundation (DFG) through the BRAGECRIM collaboration project (CAPES BEX 7185/13-8 and DFG PA 2275/4-1), and by São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) under the Thematic Project No. 2013/05987-8 and Young Research Project No. 2017/27031-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Batalha, R.L., Batalha, W.C., Deng, L. et al. Processing a biocompatible Ti–35Nb–7Zr–5Ta alloy by selective laser melting. Journal of Materials Research 35, 1143–1153 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.90
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.90