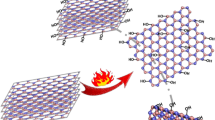
Abstract
Structural evolution induced and driven by a dual system and simultaneous passivation of phosphorene are reported. Different nano-objects of phosphorene or black phosphorus (BP) are obtained using a new method of exfoliation, in which solvent and an ionic polymer are combined to weaken the van der Waals forces and to scissor the nanosheets. Nanoribbons, nanorods, and nanoneedles are obtained under mechanical force and ambient conditions. Ionic polymer chains assist in curling the monolayer or few-layer nanosheet. Nafion is chosen to exfoliate the bulk BP and induce a morphological transition in BP nanosheets. The exfoliation of BP nanosheets results into thin and specific structures such as nanosheets/rods/needles. The nanosheets of phosphorene are covered and passivated simultaneously by the polymeric sheath that protects the nanosheets from degradation or oxidation and can be integrated with a device directly without any further coating.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, D. Jiang, M.I. Katsnelson, I.V. Grigorieva, S.V. Dubonos, and A.A. Forsov: Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 438, 197 (2005).
S. Wang, D. Scarabelli, L. Lu, Y.Y. Kuznetsova, L.N. Pfeiffer, K.W. West, G.C. Gardner, M.J. Manfra, V. Pelligrini, S.J. Wind, and A. Pinczuk: Observation of Dirac bands in artificial graphene in small period nanopatterned GaAs quantum well. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 29 (2018).
A. Radocea, T. Sun, T.H. Vo, A. Sinistkii, N.R. Aluru, and J.W. Lyding: Solution-synthesized chevron graphene nanoribbons exfoliated onto H:Si(100). Nano Lett. 17, 170 (2017).
M. Chhowalla, D. Jena, and H. Zhang: Two-dimensional semiconductors for transistors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 1, 16052 (2016).
A. Carvalho, M. Wang, X. Zhu, A.S. Rodin, H. Su, and A.H. Castro Neto: Phosphorene: From theory to applications (Nature Reviews Materials, 2016); p. 16061.
S. Soleimanikahnoj and I. Knezevic: Tunable electronic properties of multilayer phosphorene and its nanoribbons. J. Comput. Electron. 16, 568 (2017).
J. Kim, S.S. Baik, S.H. Ryu, Y. Sohn, S. Park, B.G. Park, J. Denlinger, Y. Yi, H.J. Choi, and K.S. Kim: Observation of tunable band gap and anisotropic Dirac semimetal state in black phosphorus. Science 349 (2015).
Q. Wei and X. Peng: Superior mechanical flexibility of phosphorene and few-layer black phosphorus. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 251915 (2014).
V. Sresht, A.A.H. Padua, and D. Blankschtein: Liquid-phase exfoliation of phosphorene: Design rules from molecular dynamics simulations. ACS Nano 9, 8255 (2015).
A.E. Castillo Del Rio, V. Pellegrini, H. Sun, J. Buha, D.A. Dinh, E. Lago, A. Ansaldo, A. Capasso, L. Manna, and F. Bonaccorso: Exfoliation of few-layer black phosphorus in low-boiling-point solvents and its applications in Li-ion batteries. Chem. Mater. 30, 506 (2018).
J. Kang, S.A. Wells, J.D. Wood, J.H. Lee, X. Liu, C.R. Ryder, J. Zhu, J.R. Guest, C.A. Husko, and M.C. Hersam: Stable aqueous dispersion of optically and electronically active phosphorene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 113, 11688 (2016).
M.C. Watts, F.S. Picco, L. Russel-Pavier, P.L. Cullen, T.S. Miller, S.P. Bartus, O.D. Payton, N.T. Skipper, V. Tileli, and C.A. Howard: Production of phosphorene nanoribbons. Nature 568, 216 (2019).
K.A. Mauritz, K.A. Moore, and R.B. Moore: State of understanding nafion. Chem. Rev. 104, 4535 (2004).
H.L. Tang and M. Pan: Synthesis and characterization of a self-assembled nafion/silica nanocomposite membrane for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 30 (2008).
H. Wang, H.W. Lee, Y. Deng, Z. Lu, P. Hsu, Y. Liu, D. Lin, and Y. Cui: Bifunctional non-noble metal oxide nanoparticle electrocatalysts through lithium-induced conversion for overall water splitting. Nat. Commun. 6, 7261 (2015).
A. Kumar: Simultaneous passivation and encapsulation of black phosphorus nanosheets (phosphorene) by optically active polypeptide micelles for biosensors. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2, 2397 (2019).
X. Niu, Y. Li, Y. Zhang, Q. Li, Q. Zhou, J. Zhao, and J. Wang: Photo-oxidative degradation and protection mechanism of black phosphorus: Insights from ultrafast dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 9, 5034 (2018).
J. Zhang, S. Shin, and W. Lu: Highly ambient-stable few-layer black phosphorene by pulsed laser exfoliation HEMM. Chem. Commun. 55, 2601 (2019).
T.K. Mukhopadhya and A. Datta: Ordering any dynamics for the formation of two-dimensional molecular crystals on black phosphorene. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 10210 (2017).
E.J. Roche, M. Pineri, and R. Duplessix: Phase separation in perfluorosulfonate ionomer membranes. J. Polym. Sci., Polym. Phys. Ed. 20, 107 (1982).
H.M. Jakani, I.Z. Lopez, V.H. Mareau, and L. Gonon: Optimization of hydrophilic/hydrophobic phase separation in sPEEK membranes by hydrothermal treatments. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 16013 (2017).
Y. Li, F. Ma, and L. Wang: Phosphorene oxide as a promising cathode material for sealed non-aqueous Li-oxygen batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 7815 (2018).
T. Nilges: Expressway to partially oxidized phosphorene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115, 4311 (2018).
R. Quhe, Q. Li, Q. Zhang, Y. Wang, H. Zhang, J. Li, X. Zhang, D. Chen, K. Liu, Y. Ye, L. Dai, F. Pan, M. Lei, and J. Lu: Simulations of quantum transport in sub-5 nm monolayer phosphorene transistors. Phys. Rev. Appl. 10, 024022 (2018).
S. Fotoohi: Tunable rectification and negative differential resistance induced by asymmetric doping in phosphorene nanoribbon. Phys. Lett. A 383, 369 (2019).
H. Guo, N. Lu, J. Dai, X. Wu, and X.C. Zeng: Phosphorene nanoribbons, phosphorus nanotubes, and van der Waals multilayers. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 14051 (2014).
G. Seifert and E.R. Hernandez: Theoretical predictions of phosphorus nanotubes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 318, 355 (2000).
D. Pan, T.C. Wang, C. Wang, W. Guo, and Y. Yao: Self-assembled chiral phosphorus nanotubes from phosphorene: A molecular dynamics study. RSC Adv. 7, 24647 (2017).
P. Lazar, E. Otyepkova, M. Pykal, K. Cepe, and M. Otyepka: Role of the puckered anisotropic surface in the surface and adsorption properties of black phosphorus. Nanoscale 10, 8979 (2018).
Y. Deng, Z. Luo, N.J. Conrad, H. Liu, Y. Gong, S. Najmaei, P.M. Ajayan, J. Lou, X. Xu, and P.D. Ye: Black phosphorus-monolayer MoS2 van der Waals heterojunction p–n diode. ACS Nanos 8, 8292 (2014).
M.T. Edmond, A. Tadich, A. Carvalho, A. Ziletti, K.M. O’Donnell, S.P. Koenig, D.F. Coker, B. Ozyilmaz, A.H. Castro Neto, and M.S. Fuhrer: Creating a stable oxide at the surface of black phosphorus. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 14557 (2015).
W. Hu, L. Lin, R. Zhang, C. Yang, and J. Yang: Highly efficient photocatalytic water splitting over edge-modified phosphorene nanoribbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 15429 (2017).
K. Zhang, B. Jin, C. Park, Y. Cho, X. Song, X. Shi, S. Zhang, W. Kim, H. Zeng, and J.H. Park: Black phosphorene as a hole extraction layer boosting solar water splitting of oxygen evolution catalysts. Nat. Commun. 10, 2001 (2019).
L. Kou, T. Frauenheim, and C. Chen: Phosphorene as a superior gas sensor: Selective adsorption and distinct I–V response. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5, 2675 (2014).
K. Kalantar-zadeh and J. Zhen Ou: Biosensors based on two-dimensional MoS2. ACS Sens. 1, 5 (2016).
M. Zhang, Q. Wu, F. Zhang, L. Chen, X. Jin, Y. Hu, Z. Zheng, and H. Zhang: Black-phosphorous-based pulsed lasers: 2D black phosphorus saturable absorbers for ultrafast photonics. Adv. Opt. Mater. 7, 1970001 (2019).
Y. Zhou, M. Zhang, Z. Guo, L. Miao, S.T. Han, Z. Wang, X. Zhang, H. Zhang, and Z. Peng: Recent advances in black phosphorus-based photonics, electronics, sensors and energy devices. Mater. Horiz. 4, 997 (2017).
Z. Guo, S. Chen, Z. Wang, Z. Yang, Z. Liu, F. Xu, Y. Wang, J. Yi, Y. Liao, L. Chu, P. Yu, and X. Feng: Metal-ion-modified black phosphorus with enhanced stability and transistor performance. Adv. Mater. 29, 1703811 (2017).
J. Zheng, Z. Yang, S. Chen, Z. Liang, X. Chen, R. Cao, Z. Guo, K. Wang, Y. Zhang, J. Ji, M. Zhang, D. Fan, and H. Zhang: Black phosphorus based all-optical-signal-processing: Towards high performances and enhanced stability. ACS Photonics 4, 1466 (2017).
Acknowledgments
Author appreciates the generous support extended by the Linus Pauling Professor C.N.R. Rao, FRS. Assistance from the staff of Raman spectrometer, AFM, and TEM facilities group, ICMS, JNCASR, Bangalore, India, is also acknowledged. Authors thanks DST (India) and Sheikh Saqr Scholarship (UAE) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Material
43578_2020_35020141_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Controlled Nanostructures and Simultaneous Passivation of Black Phosphorus (Phosphorene) with Nafion, approximately 280 KB
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A. Controlled nanostructures and simultaneous passivation of black phosphorus (phosphorene) with Nafion. Journal of Materials Research 35, 141–152 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.395
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.395