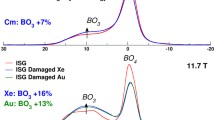
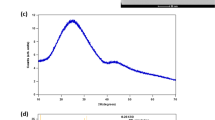
Abstract
Highly radioactive waste is incorporated into a glass matrix to convert it into a safe, passive form suitable for long-term storage and disposal. It is currently known that alpha decay can generate gaseous species, which can nucleate into bubbles, either through the production of helium or from ballistic collisions with the glass network that liberate oxygen. An effective method to probe this phenomenon utilizes ion beams to either directly implant helium or investigate the damage due to ballistic collisions. This paper provides an overview of the methodology, summarizes the results of current studies, and draws comparisons between them. We find that the irradiation scheme as well as the temperature and composition of the glass are important in determining whether bubble formation will occur. We also explore how analytical techniques can promote bubble formation and suggest avenues for further work.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
This reaction can also be written as 3He(d,α)p, which assumes that the electron from 1H is donated somewhere, for example, to the alpha particle, or that the 3He does not contain any electrons.
References
W.J. Weber, R.C. Ewing, C.A. Angell, G.W. Arnold, A.N. Cormack, J.M. Delaye, D.L. Griscom, L.W. Hobb, A. Navrotsky, D.L. Price, A.M. Stoneham, and M.C. Weinberg: Radiation effects in glasses used for immobilization of high-level waste and plutonium disposition. J. Mater. Res. 12, 1946 (1997).
A. Kerrache and J-M. Delaye: Interstitial sites for He incorporation in nuclear glasses and links to the structure: Results from numerical investigation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 326, 269 (2014).
J.F. Shackleford: Gas solubility and diffusion in oxide glasses—Implications for nuclear wasteforms. Procedia Mater. Sci. 9, 278 (2014).
S. Gin, A. Abdelouas, L.J. Criscenti, W.L. Ebert, K. Ferrand, T. Geisler, M.T. Harrison, Y. Inagaki, S. Mitsui, K.T. Mueller, J.C. Marra, C.G. Pantano, E.M. Pierce, J.V. Ryan, J.M. Chofield, C.I. Steefel, and J.D. Vienna: An international initiative on long-term behavior of high-level nuclear waste glass. Mater. Today 16, 243 (2013).
Nuclear Decommissioning Authority: Experimental Studies of the Chemical Durability of U.K. HLW and ILW Glass; RWM005105, AMEC/103498/03 (Amec: Didcot, UK, 2016).
T.A. Taylor, R.J. Short, N.R. Gribble, J. Roe, and C.J. Steele: Rhenium volatilisation as caesium perrhenate from simulated vitrified high level waste from a melter crucible. In GLOBAL 2013 Conference Proceedings, American Nuclear Society, Vol. 1663 (American Nuclear Society: La Grange Park, Illinois, 2013); p. 450.
S. Peuget, J-N. Cachia, C. Jégou, X. Deschanels, D. Roudil, V. Broudic, J-M. Delaye, and J-M. Bart: Irradiation stability of R7T7-type borosilicate glass. J. Nucl. Mater. 354, 1 (2006).
S. Peuget, T. Fares, E.A. Maugeri, R. Carabello, T. Charpentier, L. Martel, J. Somers, A. Janssen, T. Wiss, F. Rozenblum, M. Magnin, X. Deschanels, and C. Jégou: Effect of 10B(n, α)7Li irradiation on the structure of a sodium borosilicate glass. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 327, 22 (2014).
J.F. DeNatale and D.C. Howitt: A mechanism for radiation damage in silicate glasses. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 1, 489 (1984).
N. Ollier, G. Rizza, B. Boizot, and G. Petite: Effects of temperature and flux on oxygen bubble formation in Li borosilicate glass under electron beam irradiation. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 073511 (2006).
A.H. Mir, B. Boizot, T. Charpentier, M. Gennisson, M. Odorico, R. Podor, C. Jégou, S. Bouffard, and S. Peuget: Surface and bulk electron irradiation effects in simple and complex glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 453, 141 (2016).
J.F. DeNatale and D.G. Howitt: The gamma-irradiation of nuclear waste glasses. Radiat. Eff. 91, 89 (1985).
O.J. McGann, P.A. Bingham, R.J. Hand, A.S. Gandy, M. Kavčič, M. Žitnic, K. Bučar, R. Edge, and N.C. Hyatt: The effects of γ-radiation on model vitreous wasteforms intended for the disposal of intermediate and high level radioactive wastes in the United Kingdom. J. Nucl. Mater. 429, 353 (2012).
D. Manara, A. GranDjean, and D.R. Neuville: Advances in understanding the structure of borosilicate glasses: A Raman spectroscopy study. Am. Mineral. 94, 777 (2009).
G. Calas, L. Cormier, L. Galoisy, and P. Jollivet: Structure–property relationships in multicomponent oxide glasses. C. R. Chim. 5, 831 (2002).
G. Calas, L. Galoisy, L. Cormier, G. Ferlat, and G. Lelong: The structural properties of cations in nuclear glasses. Procedia Mater. Sci. 7, 23 (2014).
J.F. Shackelford: Gas solubility and diffusion in oxide glasses—Implications for nuclear wasteforms. Procedia Mater. Sci. 7, 278–285 (2014).
J.E. Shelby: Helium diffusion and solubility in K2O–SiO2 glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 57, 260–263 (1974).
G. Gutierrez, S. Peuget, J.A. Hinks, G. Greaves, S.E. Donnelly, E. Oliviero, and C. Jégou: Helium bubble formation in nuclear glass by in situ TEM ion implantation. J. Nucl. Mater. 452, 565 (2014).
A.R. Hall, J.T. Dalton, B. Hudson, and J.A.C. Marples: Development and radiation stability of glasses for highly radioactive wastes. In Proceeding of the Symposium on Management of Radioactive Wastes from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle, Vol. 2 (International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 1976); p. 3.
D.G. Howitt, H.W. Chan, J.F. DeNatale, and J.P. Heuer: Mechanism for the radiolytically induced decomposition of soda–silicate glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 74, 1145 (1991).
B. Boizot, N. Ollier, F. Olivier, G. Petite, D. Ghalen, and E. Malchukova: Irradiation effects in simplified nuclear waste glass. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 240, 146 (2005).
J.F. DeNatale, D.G. Howitt, and G.W. Arnold: Radiation damage in silicate glass. Radiat. Eff. 98, 63 (1986).
R. Evron, Y. Cohen, O. Regev, and Y. Eyal: Ion Implantation Induced Microstructural Damage in a Nuclear Waste Glass (Nuclear Society of Israel: Haifa, Israel, 1994); pp. VIII–2–VIII–7.
A.H. Mir, S. Peuget, M. Toulemonde, C. Jégou, S. Miro, and S. Bouffard: Defect recovery and damage reduction in borosilicate glasses under double ion beam irradiation. Europhys. Lett. 112, 36002–1 (2015).
G. Karakurt, A. Abdelouas, J-P. Guin, M. Nivard, T. Sauvage, M. Paris, and J-F. Bardeau: Understanding of the mechanical and structural changes induced by alpha particles and heavy ions in the French simulated nuclear waste glass. J. Nucl. Mater. 475, 243 (2016).
L. Chen, D.F. Zhang, P. Lv, J.D. Zhang, Z. Du, W. Yuan, S. Nan, Z.H. Zhu, and T.S. Wang: Evolutions of molecular oxygen formation and sodium migration in Xe ion irradiated borosilicate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 448, 6 (2016).
C.L. Dube, M.C. Stennett, A.S. Gandy, and N.C. Hyatt: Simulation of alpha decay of actinides in iron phosphate glasses by ion irradiation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 371, 424 (2016).
M.T. Harrison: Vitrification of high level waste in the UK. Procedia Mater. Sci. 7, 10 (2014).
J.F. Ziegler, J.P. Biersack, and U. Littmark: The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter (Pergamon, New York, 1985).
H. Bethe and J. Ashkin: Experimental Nuclear Physics, E. Segré, ed. (J. Wiley, New York, 1953); p. 253.
J. Lindhard, M. Scharff, and H.E. Schiott: Range concepts and heavy ion ranges. Mat. Fys. Medd. K. Dan. Vidensk. Selsk. 33, 1 (1963).
P. Sigmund and A. Schinner: Progress in understanding heavy-ion stopping. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 382, 14 (2016).
W.G. Burns, A.E. Hughes, J.A.C. Marples, R.S. Neilson, and A.M. Stoneham: Effects of radiation on the leach rates of vitrified radioactive waste. J. Nucl. Mater. 107, 245 (1982).
L. Leay, W. Bower, G. Horne, P. Wady, A. Baidak, M. Pottinger, M. Nancekievill, A.D. Smith, S. Watson, P.R. Green, B. Lennox, J.A. Laverne, and S.M. Pimboltt: Development of irradiation capabilities to address the challenges of the nuclear industry. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 343, 62–69 (2015).
P.T. Wady, A. Draude, S.M. Shubeta, A.D. Smith, N. Mason, S.M. Pimblott, and E. Jimenez-Melero: Accelerated radiation damage test facility using a 5 MV tandem ion accelerator. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 806, 109 (2016).
H. Arribart and D. Abriou: Ten years of atomic force microscopy in glass research. Ceram. Silik. 44, 121 (2000).
A.H. Mir, I. Monnet, M. Touelmonde, S. Bouffard, C. Jégou, and S. Peuget: Mono and sequential ion irradiation induced damage formation and damage recovery in oxide glasses: Stopping power dependence of the mechanical properties. J. Nucl. Mater. 469, 244 (2016).
A.Y. Terekhov, B.J. Heuser, M.A. Okuniewski, R.S. Averback, S. Seifert, and P.R. Jemian: Small-angle X-ray scattering measurements of helium-bubble formation in borosilicate glass. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 39, 647 (2006).
F. Chamssedine, T. Sauvage, S. Peuget, T. Fares, and G. Martin: Helium diffusion coefficient measurements in R7T7 nuclear glass by 3He(d,α)1H nuclear reaction analysis. J. Nucl. Mater. 400, 175 (2010).
T. Fares, S. Peuget, F. Chamssedine, T. Sauvage, O. Bouty, V. Broudic, X. Deschanels, E. Maugeri, R. Bès, and C. Jégou: Helium solubility in SON68 nuclear waste glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 3854 (2012).
R. Bès, T. Sauvage, S. Peuget, J. Haussy, F. Chamssedine, E. Oliviero, T. Fares, and L. Vincent: Helium mobility in SON68 borosilicate nuclear glass: A nuclear reaction analysis approach. J. Nucl. Mater. 443, 544 (2013).
S. Markelj, O.V. Ogorodnikova, P. Pelicon, T. Schwarz Selinger, P. Vavpetič, and I. Čadež: In situ nuclear reaction analysis of D retention in undamaged and self-damaged tungsten under atomic D exposure. Phys. Scr. T159, 014047 (2014).
S. Peuget, J-M. Delaye, and C. Jégou: Specific outcomes of the research on the radiation stability of the French nuclear glass towards alpha decay accumulation. J. Nucl. Mater. 444, 76 (2014).
M. Poon, R.G. Macaulany-Newcombe, J.W. Davis, and A.A. Haasz: Flux dependence of deuterium retention in single crystal tungsten. J. Nucl. Mater. 307–311 (Part 1), 723 (2002).
M. Callisti, M. Karlik, and T. Polcar: Bubbles formation in helium ion irradiated Cu/W multilayer nanocomposites: Effects on structure and mechanical properties. J. Nucl. Mater. 473, 18 (2016).
S. Fréchard, M. Walls, M. Koiak, J.P. Chevallier, J. Henry, and D. Gorse: Study by EELS of helium bubbles in a martensitic steel. J. Nucl. Mater. 393, 102 (2009).
K. Prikhodko and O. Emelyanova: Using EELS analysis in STEM to investigate the helium content in irradiated materials. In European Microscopy Congress 2016 Proceedings (Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, 2016); session IM08-410, number 5844.
M. Bowden, N.M. Dixon, J.D. Gardiner, and S.F. Carter: Raman microscope analysis of gaseous and solid inclusions in fluoride glass optical fibres. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 1, 34 (1990).
J-C. Wang, Q-B. Guo, X-F. Liu, Y. Dai, Z-Y. Wang, and J-R. Qiu: Bubble generation in germanate glass induced by femtosecond laser. Chin. Phys. Lett. 33, 036101 (2016).
N. Ollier, B. Champagnon, B. Boizot, Y. Guyot, G. Panczer, and B. Padlyak: Influence of external β-irradiation in oxide glasses. J. non-Crst. Solids 323, 200 (2003).
S. Cheng, G. Yang, Y. Zhao, M. Peng, J. Skibsted, and Y. Yue: Quantification of the boron speciation in alkali borosilicate glasses by electron energy loss spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 5, 17526 (2015).
A.H. Mir, I. Monnet, B. Boizot, C. Jegou, and S. Peuget: Electron and electron-ion sequential irradiation of borosilicate glasses: Impact of the pre-existing defects. J. Nucl. Mater. 4889, 91 (2017).
P.B. Rose, D.I. Woodward, M.I. Ojovan, N.C. Hyatt, and W.E. Lee: Crystallisation of a simulated borosilicate high-level waste glass produced on a full-scale vitrification line. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 357, 2989 (2011).
Acknowledgments
We thank Anamul Haq Mir for providing the image of bubbles in a U.K. Ca/Zn glass formulation as well as Bill Weber for some useful discussion. We also acknowledge the support of the University of Manchester’s Dalton Cumbrian Facility (DCF), a partner in the National Nuclear User Facility, the EP SRC U.K. National Ion Beam Centre and the Henry Royce Institute. We recognize Paul Wady and Samir Shubeta for their assistance during this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leay, L., Harrison, M.T. Bubble formation in nuclear glasses: A review. Journal of Materials Research 34, 905–920 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.29
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.29