Abstract
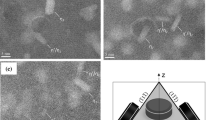
Aging treatment plays an important role in strengthening of 2198 Al–Li alloy. Through a serious of heat treatment processes, a large amount of precipitates emerge, mainly observed to be θ′(Al2Cu), Al3Zr, and T1(Al2CuLi), among which, T1 turns to be the most important precipitate that contributes to the strengthening of 2198 Al–Li alloy. While the temperature of the aging process is 175 °C, the density and size of T1 phase keep increasing through the process and reach peak in about 18 h. T1 phase tends to have a certain orientation relationship of \({\left({0001} \right)_{{{\rm{T}}_1}}}//{\left\{ {111} \right\}_{{\rm{AI}}}}\), \({\left\langle {1010} \right\rangle _{{{\rm{T}}_{\rm{1}}}}}//{\left\langle {110} \right\rangle _{{\rm{AI}}}}\) and may have different kinds of multilayered structures. In most of the multilayered structures, the distance between two adjacent copper-rich laths is less than that in classical single-layered phase. Thus, it can be inferred that the microstructure of T1 phase might change in the process of developing from single-layered structure to multilayered structure. In addition, the interactions between different phases become relatively frequent when the density of T1 phase reaches a threshold.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Araullo-Peters, B. Gault, F.D. Geuser, A. Deschamps, and J.M. Cairney: Microstructural evolution during ageing of Al–Cu–Li–x alloys. Acta Mater. 66, 199 (2014).
G. Huang and L. Wang: Development, application and prospect of aluminum–lithium alloys. Mater. Rev. 11, 21 (1997).
R.J. Rioja: The evolution of Al–Li base products for aerospace and space applications. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 43, 3325 (2012).
H. Wang, C. Shi, Z. Jia, and W. Zeng: Development and current status of aluminum–lithium alloy. Hot Work. Technol. 12, 146 (2012).
S.F. Zhang, W.D. Zeng, W.H. Yang, C.L. Shi, and H.J. Wang: Ageing response of a Al–Cu–Li 2198 alloy. Mater. Des. 63, 368 (2014).
T. Dursun and C. Soutis: Recent developments in advanced aircraft aluminium alloys. Mater. Des. 56, 862 (2014).
A. Heinz, A. Haszler, C. Keidel, S. Moldenhauer, R. Benedictus, and W.S. Miller: Recent development in aluminium alloys for aerospace applications. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 280, 102 (2000).
C. Giummarra, R.J. Rioja, G.H. Bray, P.E. Magnusen, and J.P. Moran: Al–Li alloys: Development of corrosion resistant, high toughness aluminium–lithium aerospace alloys. Proc. ICCA 1, 176 (2008).
B. Ahmed and S.J. Wu: Aluminum lithium alloys (Al–Li–Cu–X)-new generation material for aerospace applications. Appl. Mech. Mater. 440, 104 (2013).
O.C. Gamboni, J.A. Moreto, L.H.C. Bonazzi, C.O.F.T. Ruchert, and W.W. Bose Filho: Effect of salt-water fog on fatigue crack nucleation of Al and Al–Li alloys. Mater. Res. 17, 250 (2014).
C.S. Tsao, T.L. Lin, and M.S. Yu: An improved small-angle X-ray scattering analysis of δ′ precipitation in Al–Li alloy with hard-sphere interaction. Scr. Mater. 41, 81 (1999).
S.W. Chen and C.C. Huang: Solidification curves of Al Cu, Al Mg, and Al Cu Mg alloys. Acta Mater. 44, 1955 (1996).
L.Ü. Xin-Yu, E.J. Guo, P. Rometsch, and L.J. Wang: Effect of one-step and two-step homogenization treatments on distribution of Al3Zr dispersoids in commercial AA7150 aluminium alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22, 2645 (2012).
B. Decreus, A. Deschamps, and P. Donnadieu: Understanding the mechanical properties of 2198 Al–Li–Cu alloy in relation with the intra-granular and inter-granular precipitate microstructure. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 240, 012096 (2010).
C. Gao, Z. Zhu, J. Han, and H. Li: Correlation of microstructure and mechanical properties in friction stir welded 2198-T8 Al–Li alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 639, 489 (2015).
Y.Z. Shen, K.H. Oh, and D.N. Lee: Serrated flow behavior in 2090 Al–Li alloy. Key Eng. Mater. 345–346, 157 (2007).
T. Pardoen, Y. Marchal, and F. Delannay: Thickness dependence of cracking resistance in thin aluminium plates. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 47, 2093 (1999).
M.J. Kaufman, A.A. Morrone, and R.E. Lewis: Complications concerning TEM analysis of the δ-AlLi phase in aluminum–lithium alloys. Scr. Metall. Mater. 27, 1265 (1992).
A.A. Alekseev, E.A. Lukina, D.V. Zaytsev, and I.N. Fridlyander: Crystal analysis of nonequilibrium δnon-phase in Al–Li–Mg alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 519–521, 259 (2006).
B.P. Mao, X.D. Yan, and J. Shen: Precipitation behavior of T1 phase during thermo-mechanical treatment of 2197 Al–Li alloy. Chin. J. of Nonferrous Met. 25, 2366 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, K., Zhu, C., Zheng, J. et al. Precipitation of T1 phase in 2198 Al–Li alloy studied by atomic-resolution HAADF-STEM. Journal of Materials Research 34, 3535–3544 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.136
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.136