Abstract
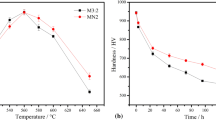
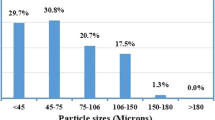
M3:2 high-speed steel (HSS) billets with or without Nb addition were prepared by spray deposition. The effects of Nb and post-thermal-mechanical processing (decomposition treatment and hot forging), as well as heat treatment, on the microstructure and properties of M3:2 HSS were investigated. The microstructure of the as-deposited M3:2 HSS consisted of equiaxed grains with a mean size of approximately 25 µm and discontinuous plate-like M2C and irregular MC carbides distributed along grain boundaries. 0.5% Nb addition can refine the M2C plates and spheroidize MC carbides. With 2% Nb addition, the refined grains with a mean size of approximately 12 µm and continuous net of M6C and a uniform distribution of NbC carbides were obtained. The decomposition of metastable M2C carbides can be accelerated with 0.5% Nb addition due to the refined size and lower thermodynamic stability of M2C plates. With the increased degree of decomposition of M2C carbide, the M6C and MC carbides became refined and more uniformly distributed after optimal thermal-mechanical processing and heat treatment, which leads to a significant increase in bend strength and toughness.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.V. Pirtovšek, G. Kugler, M. Godec, and M. Terčelj: Three important points that relate to improving the hot workability of ledeburitic tool steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 43, 3797 (2012).
J. Guo, L.Q. Ai, T.T. Wang, Y.L. Feng, D.C. Wan, and Q.X. Yang: Microstructure evolution and micro-mechanical behavior of secondary carbides at grain boundary in a Fe–Cr–W–Mo–V–C alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 715, 359 (2018).
V. Vitry, S. Nardone, J.P. Breyer, M. Sinnaeve, and F. Delaunois: Microstructure of two centrifugal cast high speed steels for hot strip mills applications. Mater. Des. 34, 372 (2012).
G.Y. Deng, Q. Zhu, K. Tieu, H.T. Zhu, M. Reid, A.A. Saleh, L.H. Su, T.D. Ta, J. Zhang, C. Lu, Q. Wu, and D.L. Sun: Evolution of microstructure, temperature and stress in a high speed steel work roll during hot rolling: Experiment and modeling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 240, 200 (2017).
M.M. Serna and J.L. Rossi: MC complex carbide in AISI M2 high-speed steel. Mater. Lett. 63, 691 (2009).
X.F. Zhou, F. Fang, F. Li, and J.Q. Jiang: Morphology and microstructure of M2C carbide formed at different cooling rates in AISI M2 high speed steel. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 1196 (2011).
D. Bombač, M. Terčelj, M. Fazarinc, and G. Kugler: On the increase of intrinsic workability and hot working temperature range of M42 ledeburitic super high steel in as-cast and wrought states. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 703, 438 (2017).
R.A. Mesquita and C.A. Barbosa: High-speed steels produced by conventional casting, spray forming and powder metallurgy. Mater. Sci. Forum 498, 244 (2005).
W.J. Shen, L.P. Yu, Z. Li, Y.H. He, Q.K. Zhang, H.B. Zhang, Y. Jiang, and N. Lin: In situ synthesis and strengthening of powder metallurgy high speed steel in addition of LaB6. Met. Mater. Int. 23, 1150 (2017).
C. Garcia, A. Romero, G. Herranz, Y. Blanco, and F. Martin: Effect of vanadium carbide on dry sliding wear behavior of powder metallurgy AISI M2 high speed steel processed by concentrated solar energy. Mater. Char. 121, 175 (2016).
D. Zhang, Z. Li, L. Xie, Y.F. Xiao, and F.C. Yin: Powder metallurgy of high speed steel produced by solid state sintering and heat treatment. Int. J. Mater. Res. 106, 870 (2015).
V. Trabadelo, S. Giménez, and I. Iturriza: Microstructural characterization of vacuum sintered T42 powder metallurgy high-speed steel after heat treatments. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 499, 360 (2009).
E.J. Lavernia and T.S. Srivatsan: The rapid solidification processing of materials: Science, principles, technology, advances, and applications. J. Mater. Sci. 45, 287 (2010).
G.Q. Zhang, H. Yuan, D.L. Jiao, Z. Li, Y. Zhang, and Z.W. Liu: Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of T15 high speed steel prepared by twin-atomiser spray forming and thermo-mechanical processing. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 558, 566 (2012).
E.R. Jesus, E.S. Jesus, and J.L. Rossi: Performance assessment of spray formed AISI M2 high-speed steel tools. Mater. Sci. Forum 530, 315 (2006).
P.S. Grant: Solidification in spray forming. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 38, 1520 (2007).
L. Lu, L.G. Hou, J.X. Zhang, H.B. Wang, H. Cui, J.F. Huang, Y.A. Zhang, and J.S. Zhang: Improved the microstructures and properties of M3:2 high-speed steel by spray forming and niobium alloying. Mater. Charact. 117, 1 (2016).
R.A. Mesquita and C.A. Barbosa: Spray forming high speed steel-properties and processing. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 383, 87 (2004).
C.K. Kim, J.I. Park, S. Lee, Y.C. Kim, N.J. Kim, and J.S. Yang: Effects of alloying elements on microstructure, hardness, and fracture toughness of centrifugally cast high-speed steel rolls. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36, 87 (2005).
F.S. Pan, P.D. Ding, S.Z. Zhou, M. Kang, and D.V. Edmonds: Effects of silicon additions on the mechanical properties and microstructure of high speed steels. Acta Mater. 45, 4703 (1997).
A.S. Chaus: Modifying cast tungsten-molybdenum high-speed steels with niobium, zirconium, and titanium. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 47, 53 (2005).
J.W. Park, H.C. Lee, and S. Lee: Composition, microstructure, hardness, and wear properties of high-speed steel rolls. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30, 399 (1999).
L.A. Dobrzański and A. Zarychta: The structure and properties of W–Mo–V high-speed steels with increased contents of Si and Nb after heat treatment. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 77, 180 (1998).
R.A. Mesquita and H.J. Kestenbach: Influence of silicon on secondary hardening of 5 wt% Cr steels. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 556, 970 (2012).
M. Filipovic, Z. Kamberovic, M. Korac, and M. Gavrilovski: Microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe–Cr–C–Nb white cast irons. Mater. Des. 47, 41 (2013).
M.A. Hamidzadeh, M. Meratian, and M.M. Zahrani: A study on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI D2 tool steel modified by niobium. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 556, 758 (2012).
X.H. Zhi, J.D. Xing, H.G. Fu, and B. Xiao: Effect of niobium on the as-cast microstructure of hypereutectic high chromium cast iron. Mater. Lett. 62, 857 (2008).
G.C. Coelho, J.A. Golczewski, and H.F. Fischmeister: Thermodynamic calculations for Nb-containing high-speed steels and white-cast-iron alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 34, 1749 (2003).
F.S. Pan, W.Q. Wang, A.T. Tang, L.Z. Wu, T.T. Liu, and R.J. Cheng: Phase transformation refinement of coarse primary carbides in M2 high speed steel. Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater. 21, 180 (2011).
H. Fredriksson, M. Hillert, and M. Nica: The decomposition of the M2C carbide in high speed steel. Scand. J. Metall. 8, 116 (1970).
E.S. Lee, W.J. Park, K.H. Baik, and S. Ahn: Different carbide types and their effect on bend properties of a spray-formed high speed steel. Scr. Mater. 39, 1133 (1998).
E.S. Lee, W.J. Park, J.Y. Jung, and S. Ahn: Solidification microstructure and M2C carbide decomposition in a spray-formed high-speed steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 29, 1395 (1998).
Y.K. Luan, N.N. Song, Y.L. Bai, X.H. Kang, and D.Z. Li: Effect of solidification rate on the morphology and distribution of eutectic carbides in centrifugal casting high-speed steel rolls. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 210, 536 (2010).
J. Mclaughlin, R.W. Kraft, and J.I. Goldstein: Characterization of the solidification structures within the dendritic core of M2 high speed steel. Metall. Trans. A 8, 1787 (1977).
R.H. Barkalow, R.W. Kraft, and J.I. Goldstein: Solidification of M2 high speed steel. Metall. Trans. 3, 919 (1972).
H.F. Fischmeister, R. Riedl, and S. Karagöz: Solidification of high-speed tool steels. Metall. Trans. A 20, 2133 (1989).
G. Zepon, N. Ellendt, V. Uhlenwinkel, and C. Bolfarini: Solidification sequence of spray-formed steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47, 842 (2016).
S. Karagöz and H.F. Fischmeister: Niobium-alloyed high speed steel by powder metallurgy. Metall. Trans. A 19, 1395 (1988).
H.B. Wang, L.G. Hou, J.X. Zhang, L. Lu, H. Cui, J.F. Huang, and J.S. Zhang: Microstructures and high temperature properties of spray formed Nb-containing M3 high speed steel. Mater. Werkst. 45, 689 (2014).
H.B. Wang, L.G. Hou, J.X. Zhang, L. Lu, Y.P. Yu, H. Cui, and J.S. Zhang: Microstructures and properties of spray formed Nb-containing M3 high speed steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 50, 1421 (2014).
H. Henein, V. Uhlenwinkel, U. Fritsching: Metal Spray and Spray Deposition, 1st ed. (Springer International Publishing, Cham, Switzerland, 2017); p. 320.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the State Key Development Program for Basic Research of China (Grant No. 2011CB606303), Open Foundation of State Key Laboratory for Advanced Metals and Materials, University of Science and Technology Beijing (Grant No. 2018-Z01), Program of the University Students’ Innovation and Pioneering (Grant No. XZG-16-08-15), and Ph.D. Research Startup Project of Jiangxi University of Science and Technology (Grant No. 3401223322). The authors thank Dr. Lin Lu, Dr. Jinxiang Zhang, Dr. Zhigang Wang, Mr. Xiyu He, Ms. Panpan Jiang, Ms. Xinger Wen, and Ms. Lili Zhao for their help with material preparation and academic discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Hou, L., Ou, P. et al. Enhanced microstructures and properties of spray-formed M3:2 high-speed steels by niobium addition and thermal-mechanical treatment. Journal of Materials Research 34, 1043–1053 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.460
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.460