Abstract
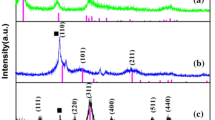
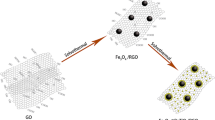
A low-temperature synthesis method for Mn3O4/graphene is described in this research. Adjusting the reaction time and temperature allows control over the phase and morphology of the synthesized manganese oxide, and therefore the microwave absorbing properties. X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and vector network analysis are used to characterize the phase, morphology, and electromagnetic properties. The results reveal that long reaction time can increase the particle size and high temperature can destroy the initial structure of graphene both of which have negative impact on the microwave absorbing properties. The Mn3O4–graphene composite synthesized in 140 °C for 4 h shows a maximum reflection loss (RL) reaching −20 dB at 14.4 GHz with absorber thickness of 2 mm, as well as an effective absorption bandwidth of more than 5 dB corresponding to RL below −10 dB.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Zhang, Y. Huang, T. Zhang, H. Chang, P. Xiao, H. Chen, Z. Huang, and Y. Chen: Broadband and tunable high‐performance microwave absorption of an ultralight and highly compressible graphene foam. Adv. Mater. 27, 2049 (2015).
Z. Yang, H. Lv, and R. Wu: Rational construction of graphene oxide with MOF-derived porous NiFe@C nanocubes for high-performance microwave attenuation. Nano Res. 9, 3671 (2016).
A. Baykal, Y. Köseoğlu, and M. Şenel: Low temperature synthesis and characterization of Mn3O4 nanoparticles. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 5, 169 (2007).
B. Wei, L. Wang, Q. Miao, Y. Yuan, P. Dong, R. Vajtai, and W. Fei: Fabrication of manganese oxide/three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide composites as the supercapacitors by a reverse microemulsion method. Carbon 85, 249 (2015).
D.K. Pappas, T. Boningari, P. Boolchand, and P.G. Smirniotis: Novel manganese oxide confined interweaved titania nanotubes for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx by NH3. J. Catal. 334, 1 (2016).
S. Wang, B. Gao, Y. Li, A. Mosa, A.R. Zimmerman, L.Q. Ma, W.G. Harris, and K.W. Migliaccio: Manganese oxide-modified biochars: Preparation, characterization, and sorption of arsenate and lead. Bioresour. Technol. 181, 13 (2015).
A. Elder, R. Gelein, V. Silva, T. Feikert, L. Opanashuk, J. Carter, R. Potter, A. Maynard, Y. Ito, and J. Finkelstein: Translocation of inhaled ultrafine manganese oxide particles to the central nervous system. Environ. Health Perspect. 114, 1172 (2006).
C-C. Hu and T-W. Tsou: Ideal capacitive behavior of hydrous manganese oxide prepared by anodic deposition. Electrochem. Commun. 4, 105 (2002).
P.R. Jothi, M. Pramanik, C. Li, S. Kannan, V. Malgras, R.R. Salunkhe, and Y. Yamauchi: Controlled synthesis of highly crystallized mesoporous Mn2O3 and Mn3O4 by using anionic surfactants. Chem.—Asian J. 11, 667 (2016).
V.C. Bose, K. Maniammal, G. Madhu, C. Veenas, A.A. Raj, and V. Biju: DC electrical conductivity of nanocrystalline Mn3O4 synthesized through a novel sol–gel route. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Vol. 73 (IOP Publishing, Bristol, England, 2015); p. 012084.
Y-F. Han, F. Chen, Z. Zhong, K. Ramesh, L. Chen, and E. Widjaja: Controlled synthesis, characterization, and catalytic properties of Mn2O3 and Mn3O4 nanoparticles supported on mesoporous silica SBA-15. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 24450 (2006).
P. Kharade, S. Chavan, S. Mane, P. Joshi, and D. Salunkhe: Synthesis and characterization of galvanostatically deposited Cr2O3, Mn3O4, Cr2O3/Mn3O4 layered composite thin film for supercapacitor application. J. Chin. Adv. Mater. Soc. 4, 1 (2016).
D. Yan, S. Cheng, R. Zhuo, J. Chen, J. Feng, H. Feng, H. Li, Z. Wu, J. Wang, and P. Yan: Nanoparticles and 3D sponge-like porous networks of manganese oxides and their microwave absorption properties. Nanotechnology 20, 105706 (2009).
L. Wang, X. Jia, Y. Li, F. Yang, L. Zhang, L. Liu, X. Ren, and H. Yang: Synthesis and microwave absorption property of flexible magnetic film based on graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 14940 (2014).
H. Sun, R. Che, X. You, Y. Jiang, Z. Yang, J. Deng, L. Qiu, and H. Peng: Cross‐stacking aligned carbon‐nanotube films to tune microwave absorption frequencies and increase absorption intensities. Adv. Mater. 26, 8120 (2014).
C. Hu, Z. Mou, G. Lu, N. Chen, Z. Dong, M. Hu, and L. Qu: 3D graphene–Fe3O4 nanocomposites with high-performance microwave absorption. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 13038 (2013).
D. Wang, R. Kou, D. Choi, Z. Yang, Z. Nie, J. Li, L.V. Saraf, D. Hu, J. Zhang, and G.L. Graff: Ternary self-assembly of ordered metal oxide–graphene nanocomposites for electrochemical energy storage. ACS Nano 4, 1587 (2010).
X. Wang, S.M. Tabakman, and H. Dai: Atomic layer deposition of metal oxides on pristine and functionalized graphene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 8152 (2008).
X. Zhou, X. Huang, X. Qi, S. Wu, C. Xue, F.Y. Boey, Q. Yan, P. Chen, and H. Zhang: In situ synthesis of metal nanoparticles on single-layer graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 10842 (2009).
H-L. Xu, H. Bi, and R-B. Yang: Enhanced microwave absorption property of bowl-like Fe3O4 hollow spheres/reduced graphene oxide composites. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 07A522 (2012).
X. Ma, H. Tao, K. Yang, L. Feng, L. Cheng, X. Shi, Y. Li, L. Guo, and Z. Liu: A functionalized graphene oxide-iron oxide nanocomposite for magnetically targeted drug delivery, photothermal therapy, and magnetic resonance imaging. Nano Res. 5, 199 (2012).
H. Kim, S-W. Kim, Y-U. Park, H. Gwon, D-H. Seo, Y. Kim, and K. Kang: SnO2/graphene composite with high lithium storage capability for lithium rechargeable batteries. Nano Res. 3, 813 (2010).
H. Wang, C.M. Holt, Z. Li, X. Tan, B.S. Amirkhiz, Z. Xu, B.C. Olsen, T. Stephenson, and D. Mitlin: Graphene-nickel cobaltite nanocomposite asymmetrical supercapacitor with commercial level mass loading. Nano Res. 5, 605 (2012).
Q. Yang, L. Liu, D. Hui, and M. Chipara: Microstructure, electrical conductivity and microwave absorption properties of γ-FeNi decorated carbon nanotube composites. Composites, Part B 87, 256 (2016).
A.A. Amer, S. Reda, M. Mousa, and M.M. Mohamed: Mn3O4/graphene nanocomposites: Outstanding performances as highly efficient photocatalysts and microwave absorbers. RSC Adv. 7, 826 (2017).
Y. Long, J. Xie, H. Li, Z. Liu, and Y. Xie: Solvothermal synthesis, electromagnetic and electrochemical properties of jellylike cylinder graphene–Mn3O4 composite with highly coupled effect. J. Solid State Chem. 256, 256 (2017).
Y. Wang, H. Guan, C. Dong, X. Xiao, S. Du, and Y. Wang: Reduced graphene oxide (RGO)/Mn3O4 nanocomposites for dielectric loss properties and electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness at high frequency. Ceram. Int. 42, 936 (2016).
J-G. Wang, D. Jin, R. Zhou, X. Li, X-r. Liu, C. Shen, K. Xie, B. Li, F. Kang, and B. Wei: Highly flexible graphene/Mn3O4 nanocomposite membrane as advanced anodes for Li-ion batteries. ACS Nano 10, 6227 (2016).
G.C. Silva, F.S. Almeida, A.M. Ferreira, and V.S.T. Ciminelli: Preparation and application of a magnetic composite (Mn3O4/Fe3O4) for removal of as (III) from aqueous solutions. Mater. Res. 15, 403 (2012).
G. An, P. Yu, M. Xiao, Z. Liu, Z. Miao, K. Ding, and L. Mao: Low-temperature synthesis of Mn3O4 nanoparticles loaded on multi-walled carbon nanotubes and their application in electrochemical capacitors. Nanotechnology 19, 275709 (2008).
A. Vázquez-Olmos, R. Redón, G. Rodríguez-Gattorno, M.E. Mata-Zamora, F. Morales-Leal, A.L. Fernández-Osorio, and J.M. Saniger: One-step synthesis of Mn3O4 nanoparticles: Structural and magnetic study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 291, 175 (2005).
H-P. Cong, X-C. Ren, P. Wang, and S-H. Yu: Macroscopic multifunctional graphene-based hydrogels and aerogels by a metal ion induced self-assembly process. ACS Nano 6, 2693 (2012).
S. Wakeland, R. Martinez, J.K. Grey, and C.C. Luhrs: Production of graphene from graphite oxide using urea as expansion–reduction agent. Carbon 48, 3463 (2010).
Z. Fan, J. Yan, T. Wei, L. Zhi, G. Ning, T. Li, and F. Wei: Asymmetric supercapacitors based on graphene/MnO2 and activated carbon nanofiber electrodes with high power and energy density. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 2366 (2011).
L. Li, Z. Hu, Y. Yang, P. Liang, A. Lu, H. Xu, Y. Hu, and H. Wu: Hydrothermal self‐assembly synthesis of Mn3O4/reduced graphene oxide hydrogel and its high electrochemical performance for supercapacitors. Chin. J. Chem. 31, 1290 (2013).
H-M. Lee, G.H. Jeong, D.W. Kang, S-W. Kim, and C-K. Kim: Direct and environmentally benign synthesis of manganese oxide/graphene composites from graphite for electrochemical capacitors. J. Power Sources 281, 44 (2015).
Y. Liu, T. Cui, T. Wu, Y. Li, and G. Tong: Excellent microwave-absorbing properties of elliptical Fe3O4 nanorings made by a rapid microwave-assisted hydrothermal approach. Nanotechnology 27, 165707 (2016).
Y. Duan, J. Liu, Y. Zhang, and T. Wang: First-principles calculations of graphene-based polyaniline nano-hybrids for insight of electromagnetic properties and electronic structures. RSC Adv. 6, 73915 (2016).
Y. Duan, H. Pang, Y. Zhang, J. Chen, and T. Wang: Morphology-controlled synthesis and microwave absorption properties of β-MnO2 microncube with rectangular pyramid. Mater. Charact. 112, 206 (2016).
H. Yang, T. Ye, Y. Lin, J. Zhu, and F. Wang: Microwave absorbing properties of the ferrite composites based on graphene. J. Alloys Compd. 683, 567 (2016).
R.S. Alam, M. Moradi, and H. Nikmanesh: Influence of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) volume percentage on the magnetic and microwave absorbing properties of BaMg0.5Co0.5TiFe10O19/MWCNTs nanocomposites. Mater. Res. Bull. 73, 261 (2016).
Y. Li, T. Wu, K. Jin, Y. Qian, N. Qian, K. Jiang, W. Wu, and G. Tong: Controllable synthesis and enhanced microwave absorbing properties of Fe3O4/NiFe2O4/Ni heterostructure porous rods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 387, 190 (2016).
Y. Chen, A. Zhang, L. Ding, Y. Liu, and H. Lu: A three-dimensional absorber hybrid with polar oxygen functional groups of MWNTs/graphene with enhanced microwave absorbing properties. Composites, Part B 108, 386 (2017).
Z. Liu, X. Zhou, Y. Zhang, Q. Liu, Q. Liu, B. Li, G. Zhu, D. Li, and X. Li: Fabrication of monodispersed, uniform rod-shaped FeCO3/CoCO3 microparticles using a facile solvothermal method and their excellent microwave absorbing properties. J. Alloys Compd. 665, 388 (2016).
H. Wang, L. Wan, J. Zhang, Y. Chen, W. Hu, L. Liu, C. Zhong, and Y. Deng: Enhanced microwave absorbing properties of surface-modified Co–Ni–P nanotubes. Mater. Lett. 169, 193 (2016).
J. Xiang, X. Zhang, Q. Ye, J. Li, and X. Shen: Synthesis and characterization of FeCo/C hybrid nanofibers with high performance of microwave absorption. Mater. Res. Bull. 60, 589 (2014).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The work is supported by Program for the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51577021) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (DUT17GF107). The authors also acknowledge support from Dr. Ishwar K. Puri and Dr. Rakesh P. Sahu in McMaster University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, H., Duan, Y., Liu, J. et al. Low-temperature synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of Mn3O4–graphene nanocomposite. Journal of Materials Research 33, 4062–4070 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.325
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.325