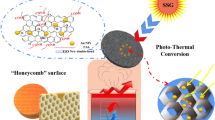
Abstract
Solar steam generation is an efficient and green technology for desalination and drinking water purification, however, impeded by high cost, low efficiency, and complicated process. Black titania is expected to exhibit excellent solar steam performance due to its outstanding light absorption properties, chemical stability, low cost, and innocuity. Herein, we design a high absorbing and efficient solar steam generation system based on a black titania/graphene oxide nanocomposite film affixed to airlaid paper wrapped over the surface of expandable polyethylene foam; the system possesses several important criteria required for the ideal solar steam generator: wide-spectrum absorption, adequate water supply, reduced heat loss for localized water heating, and porous structure for steam flow. Remarkably, we realized a solar thermal conversion efficiency of 69.1% under illumination of 1 kW/m2 without solar concentration, and the device delivered remarkable cycle stability.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.M. Mekonnen and A.Y. Hoekstra: Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2, e1500323 (2016).
M.A. Shannon, P.W. Bohn, M. Elimelech, J.G. Georgiadis, B.J. Mariñas, and A.M. Mayes: Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 452, 301–310 (2008).
J.M. La Riviere: Threats to the world’s water. Sci. Am. 261, 80–94 (1989).
M. Elimelech and W.A. Phillip: The future of seawater desalination: Energy, technology, and the environment. Science 333, 712–717 (2011).
G.W. Miller: Integrated concepts in water reuse: Managing global water needs. Desalination 187, 65–75 (2006).
V.G. Gude, N. Nirmalakhandan, and S. Deng: Desalination using solar energy: Towards sustainability. Energy 36, 78–85 (2011).
A. Lenert and E.N. Wang: Optimization of nanofluid volumetric receivers for solar thermal energy conversion. Sol. Energy 86, 253–265 (2012).
M.M. Naim and M.A.A. El Kawi: Non-conventional solar stills Part 1. Non-conventional solar stills with charcoal particles as absorber medium. Desalination 153, 55–64 (2003).
K.K. Murugavel and K. Srithar: Performance study on basin type double slope solar still with different wick materials and minimum mass of water. Renewable Energy 36, 612–620 (2011).
I. Al-Hayeka and O.O. Badran: The effect of using different designs of solar stills on water distillation. Desalination 169, 121–127 (2004).
O. Ansari, M. Asbik, A. Bah, A. Arbaoui, and A. Khmou: Desalination of the brackish water using a passive solar still with a heat energy storage system. Desalination 324, 10–20 (2013).
N.S. Lewis: Research opportunities to advance solar energy utilization. Science 351, aad1920 (2016).
G. Baffou and R. Quidant: Thermo-plasmonics: Using metallic nanostructures as nano-sources of heat. Laser Photonics Rev. 7, 171–187 (2013).
H. Jin, G. Lin, L. Bai, A. Zeiny, and D. Wen: Steam generation in a nanoparticle-based solar receiver. Nano Energy 28, 397–406 (2016).
O. Neumann, C. Feronti, A.D. Neumann, A. Dong, K. Schell, B. Lu, E. Kim, M. Quinn, S. Thompson, N. Grady, P. Nordlander, M. Oden, and N.J. Halas: Compact solar autoclave based on steam generation using broadband light-harvesting nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110, 11677–11681 (2013).
O. Neumann, A.S. Urban, J. Day, S. Lal, P. Nordlander, and N.J. Halas: Solar vapor generation enabled by nanoparticles. ACS Nano 7, 42–49 (2012).
H. Zhang, H-J. Chen, X. Du, and D. Wen: Photothermal conversion characteristics of gold nanoparticle dispersions. Sol. Energy 100, 141–147 (2014).
L. Zhou, Y. Tan, D. Ji, B. Zhu, P. Zhang, J. Xu, Q. Gan, Z. Yu, and J. Zhu: Self-assembly of highly efficient, broadband plasmonic absorbers for solar steam generation. Sci. Adv. 2, e1501227 (2016).
L. Zhou, Y. Tan, J. Wang, W. Xu, Y. Yuan, W. Cai, S. Zhu, and J. Zhu: 3D self-assembly of aluminium nanoparticles for plasmon-enhanced solar desalination. Nat. Photonics 10, 393–398 (2016).
H. Wang, L. Miao, and S. Tanemura: Morphology control of Ag polyhedron nanoparticles for cost-effective and fast solar steam generation. Solar RRL 1, 1600023 (2017).
G. Ni, N. Miljkovic, H. Ghasemi, X. Huang, S.V. Boriskina, C-T. Lin, J. Wang, Y. Xu, M.M. Rahman, and T. Zhang: Volumetric solar heating of nanofluids for direct vapor generation. Nano Energy 17, 290–301 (2015).
K. Bae, G. Kang, S.K. Cho, W. Park, K. Kim, and W.J. Padilla: Flexible thin-film black gold membranes with ultrabroadband plasmonic nanofocusing for efficient solar vapour generation. Nat. Commun. 6, 10103 (2015).
L. Zhang, B. Tang, J. Wu, R. Li, and P. Wang: Hydrophobic light-to-heat conversion membranes with self-healing ability for interfacial solar heating. Adv. Mater. 27, 4889–4894 (2015).
X. Hu, W. Xu, L. Zhou, Y. Tan, Y. Wang, S. Zhu, and J. Zhu: Tailoring graphene oxide-based aerogels for efficient solar steam generation under one sun. Adv. Mater. 29, 1604031 (2017).
H. Ghasemi, G. Ni, A.M. Marconnet, J. Loomis, S. Yerci, N. Miljkovic, and G. Chen: Solar steam generation by heat localization. Nat. Commun. 5, 4449 (2014).
X. Li, W. Xu, M. Tang, L. Zhou, B. Zhu, S. Zhu, and J. Zhu: Graphene oxide-based efficient and scalable solar desalination under one sun with a confined 2D water path. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 113, 13953–13958 (2016).
N. Xu, X. Hu, W. Xu, X. Li, L. Zhou, S. Zhu, and J. Zhu: Mushrooms as efficient solar steam-generation devices. Adv. Mater. 29, 1606762 (2017).
Y. Li, D. Lu, L. Zhou, M. Ye, X. Xiong, K. Yang, Y. Pan, M. Chen, P. Wu, T. Li, Y. Chen, Z. Wang, and Q. Xia: Bi-modified Pd-based/carbon-doped TiO2 hollow spheres catalytic for ethylene glycol electrooxidation in alkaline medium. J. Mater. Res. 31, 3712–3722 (2016).
Y. Liu, D. Su, Y. Zhang, L. Wang, G. Yang, F. Shen, S. Deng, X. Zhang, and S. Zhang: Anodized TiO2 nanotubes coated with Pt nanoparticles for enhanced photoelectrocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Res. 32, 757–765 (2017).
Z. Lyu, B. Liu, R. Wang, and L. Tian: Synergy of palladium species and hydrogenation for enhanced photocatalytic activity of {001} facets dominant TiO2 nanosheets. J. Mater. Res. 32, 2781–2789 (2017).
T. Xia, W. Zhang, J.B. Murowchick, G. Liu, and X. Chen: A facile method to improve the photocatalytic and lithium-ion rechargeable battery performance of TiO2 nanocrystals. Adv. Energy Mater. 3, 1516–1523 (2013).
T. Xia, C. Zhang, N.A. Oyler, and X. Chen: Hydrogenated TiO2 nanocrystals: A novel microwave absorbing material. Adv. Mater. 25, 6905–6910 (2013).
T. Xia, C. Zhang, N.A. Oyler, and X. Chen: Enhancing microwave absorption of TiO2 nanocrystals via hydrogenation. J. Mater. Res. 29, 2198–2210 (2014).
J. Wen, X. Li, W. Liu, Y. Fang, J. Xie, and Y. Xu: Photocatalysis fundamentals and surface modification of TiO2 nanomaterials. Chin. J. Catal. 36, 2049–2070 (2015).
Y. Xu, Y. Mo, J. Tian, P. Wang, H. Yu, and J. Yu: The synergistic effect of graphitic N and pyrrolic N for the enhanced photocatalytic performance of nitrogen-doped graphene/TiO2 nanocomposites. Appl. Catal., B 181, 810–817 (2016).
X. Chen, L. Liu, and F. Huang: Black titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 1861–1885 (2015).
Y. Liu, K. Mu, Y. Zhang, L. Wang, G. Yang, F. Shen, S. Deng, X. Zhang, and S. Zhang: Facile synthesis of a narrow-gap titanium dioxide anatase/rutile nanofiber film on titanium foil with high photocatalytic activity under sunlight. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 41, 10327–10334 (2016).
X. Liu, S. Gao, H. Xu, Z. Lou, W. Wang, B. Huang, and Y. Dai: Green synthetic approach for Ti3+ self-doped TiO2−x nanoparticles with efficient visible light photocatalytic activity. Nanoscale 5, 1870–1875 (2013).
Y. Zhou, C. Chen, N. Wang, Y. Li, and H. Ding: Stable Ti3+ self-doped anatase-rutile mixed TiO2 with enhanced visible light utilization and durability. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 6116–6124 (2016).
X. Chen, L. Liu, Y.Y. Peter, and S.S. Mao: Increasing solar absorption for photocatalysis with black hydrogenated titanium dioxide nanocrystals. Science 331, 746–750 (2011).
L. Liu and X. Chen: Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Self-structural modifications. Chem. Rev. 114, 9890–9918 (2014).
G. Zhu, J. Xu, W. Zhao, and F. Huang: Constructing black titania with unique nanocage structure for solar desalination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 31716–31721 (2016).
M. Ye, J. Jia, Z. Wu, C. Qian, R. Chen, P.G. O’Brien, W. Sun, Y. Dong, and G.A. Ozin: Synthesis of black TiOx nanoparticles by Mg reduction of TiO2 nanocrystals and their application for solar water evaporation. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1601811 (2017).
R. Ren, Z. Wen, S. Cui, Y. Hou, X. Guo, and J. Chen: Controllable synthesis and tunable photocatalytic properties of Ti3+-doped TiO2. Sci. Rep. 5, 10714 (2015).
S.K. Gupta, R. Desai, P.K. Jha, S. Sahoo, and D. Kirin: Titanium dioxide synthesized using titanium chloride: Size effect study using Raman spectroscopy and photoluminescence. J. Raman Spectrosc. 41, 350–355 (2009).
Z. Wang, C. Yang, T. Lin, H. Yin, P. Chen, D. Wan, F. Xu, F. Huang, J. Lin, X. Xie, and M. Jiang: H-doped black titania with very high solar absorption and excellent photocatalysis enhanced by localized surface plasmon resonance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 5444–5450 (2013).
I. Nakamura, N. Negishi, S. Kutsuna, T. Ihara, S. Sugihara, and K. Takeuchi: Role of oxygen vacancy in the plasma-treated TiO2 photocatalyst with visible light activity for NO removal. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 161, 205–212 (2000).
G. Wang, H. Wang, Y. Ling, Y. Tang, X. Yang, R.C. Fitzmorris, C. Wang, J.Z. Zhang, and Y. Li: Hydrogen-treated TiO2 nanowire arrays for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Nano Lett. 11, 3026–3033 (2011).
D. Chen, H. Feng, and J. Li: Graphene oxide: Preparation, functionalization, and electrochemical applications. Chem. Rev. 112, 6027–6053 (2012).
Y. Zhu, S. Murali, W. Cai, X. Li, J.W. Suk, J.R. Potts, and R.S. Ruoff: Graphene and graphene oxide: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv. Mater. 22, 3906–3924 (2010).
X. Li, J. Yu, S. Wageh, A.A. Al-Ghamdi, and J. Xie: Graphene in photocatalysis: A review. Small 12, 6640–6696 (2016).
X. Li, R. Shen, S. Ma, X. Chen, and J. Xie: Graphene-based heterojunction photocatalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 430, 53–107 (2018).
L. Yin, M. Zhao, H. Hu, J. Ye, and D. Wang: Synthesis of graphene/tourmaline/TiO2 composites with enhanced activity for photocatalytic degradation of 2-propanol. Chin. J. Catal. 38, 1307–1314 (2017).
D.W. Boukhvalov, M.I. Katsnelson, and Y-W. Son: Origin of anomalous water permeation through graphene oxide membrane. Nano Lett. 13, 3930–3935 (2013).
L. Yan, Y-N. Chang, L. Zhao, Z. Gu, X. Liu, G. Tian, L. Zhou, W. Ren, S. Jin, and W. Yin: The use of polyethylenimine-modified graphene oxide as a nanocarrier for transferring hydrophobic nanocrystals into water to produce water-dispersible hybrids for use in drug delivery. Carbon 57, 120–129 (2013).
Q. Hao, S. Hao, X. Niu, X. Li, D. Chen, and H. Ding: Enhanced photochemical oxidation ability of carbon nitride by π–π stacking interactions with graphene. Chin. J. Catal. 38, 278–286 (2017).
Y. Yang, Z. Ma, L. Xu, H. Wang, and N. Fu: Preparation of reduced graphene oxide/meso-TiO2/Au NPs ternary composites and their visible-light-induced photocatalytic degradation n of methylene blue. Appl. Surf. Sci. 369, 576–583 (2016).
C. Lai, M-M. Wang, G-M. Zeng, Y-G. Liu, D-L. Huang, C. Zhang, R-Z. Wang, P. Xu, M. Cheng, C. Huang, H-P. Wu, and L. Qin: Synthesis of surface molecular imprinted TiO2/graphene photocatalyst and its highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of target pollutant under visible light irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 390, 368–376 (2016).
G. Wang, Y. Fu, X. Ma, W. Pi, D. Liu, and X. Wang: Reusable reduced graphene oxide based double-layer system modified by polyethylenimine for solar steam generation. Carbon 114, 117–124 (2017).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work is financially supported by National Key R&D Program of China (Grant: 2016YFA0200200) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 51272071, 51203045, and 21401049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Material
43578_2018_33060674_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supporting Information: Black titania/GO nanocomposite films with excellent photothermal property for solar steam generation (approximately 92 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Hou, B., Wang, G. et al. Black titania/graphene oxide nanocomposite films with excellent photothermal property for solar steam generation. Journal of Materials Research 33, 674–684 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.25
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.25