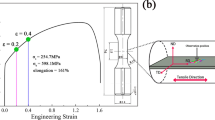
Abstract
The microstructure evolution of high nitrogen austenitic steel wires under various annealing times and drawing temperatures was carefully characterized. Special attention was paid to the widely distributed twins and the nanoprecipitates at twin boundaries (TBs) in high nitrogen stainless steels (HNSSs). The results of microhardness indicated that the traditional Hall–Petch (H–P) equation, which only took the role of grain boundaries into account, was unsuitable. A new H–P equation that connected grain size, twin density, precipitates at TBs, and microhardness in HNSS was established for the first time and showed to be in good agreement with the experimental results. By analyzing the strained regions near TBs, a model describing the precipitation of nano-M23C6 carbides on coherent twin boundaries and incoherent twin boundaries was proposed. In addition, the influence mechanism of the nano-M23C6 at TBs on microhardness was discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
U.K. Mudali and B. Raj: High Nitrogen Steels and Stainless Steels: Manufacturing, Properties and Applications (Alpha Science International, Pangbourne, England, 2004); p. 50.
M. Pujar, U.K. Mudali, and S.S. Singh: Electrochemical noise studies of the effect of nitrogen on pitting corrosion resistance of high nitrogen austenitic stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 53, 4178 (2011).
F. Shi, P. Tian, N. Jia, Z. Ye, Y. Qi, C. Liu, and X. Li: Improving intergranular corrosion resistance in a nickel-free and manganese-bearing high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel through grain boundary character distribution optimization. Corros. Sci. 107, 49 (2016).
S. Wang, K. Yang, Y. Shan, and L. Li: Study of cold deformation behaviors of a high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel and 316 L stainless steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 43, 171 (2007).
X. Gu, G.M. Michal, F. Ernst, H. Kahn, and A.H. Heuer: Numerical simulations of carbon and nitrogen composition-depth profiles in nitrocarburized austenitic stainless steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45, 4268 (2014).
H-Y. Ha, T-H. Lee, C-S. Oh, and S-J. Kim: Effects of combined addition of carbon and nitrogen on pitting corrosion behavior of Fe–18Cr–10Mn alloys. Scr. Mater. 61, 121 (2009).
L.L. Shaw, A.L. Ortiz, and J.C. Villegas: Hall–Petch relationship in a nanotwinned nickel alloy. Scr. Mater. 58, 951 (2008).
L. Lu, Y. Shen, X. Chen, L. Qian, and K. Lu: Ultrahigh strength and high electrical conductivity in copper. Science 304, 422 (2004).
Y.S. Sato, M. Urata, H. Kokawa, and K. Ikeda: Hall–Petch relationship in friction stir welds of equal channel angular-pressed aluminium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 354, 298 (2003).
R. Armstrong, I. Codd, R. Douthwaite, and N. Petch: The plastic deformation of polycrystalline aggregates. Philos. Mag. 7, 45 (1962).
R. Masumura, P. Hazzledine, and C. Pande: Yield stress of fine grained materials. Acta Mater. 46, 4527 (1998).
J. Hu, Y. Shi, X. Sauvage, G. Sha, and K. Lu: Grain boundary stability governs hardening and softening in extremely fine nanograined metals. Science 355, 1292 (2017).
W.J. Nam, C.M. Bae, and C.S. Lee: Effect of carbon content on the Hall–Petch parameter in cold drawn pearlitic steel wires. J. Mater. Sci. 37, 2243 (2002).
I. Kemp: Control of Mechanical Properties in High Strain Wire Drawing of Pearlitic Steel, in Materials Forum (Institute of Metals and Materials Australasia, Melbourne, Australia, 1990); p. 270.
Z. Yanushkevich, S. Dobatkin, A. Belyakov, and R. Kaibyshev: Hall–Petch relationship for austenitic stainless steels processed by large strain warm rolling. Acta Mater. 136, 39 (2017).
M. Odnobokova, M. Tikhonova, A. Belyakov, and R. Kaibyshev: Development of Σ3n CSL boundaries in austenitic stainless steels subjected to large strain deformation and annealing. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 4210 (2017).
D. Du, R. Fu, Y. Li, L. Jing, J. Wang, Y. Ren, and K. Yang: Modification of the Hall–Petch equation for friction-stir-processing microstructures of high-nitrogen steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 640, 190 (2015).
N. Hansen: Hall–Petch relation and boundary strengthening. Scr. Mater. 51, 801 (2004).
A.A. Salem, S.R. Kalidindi, and R.D. Doherty: Strain hardening regimes and microstructure evolution during large strain compression of high purity titanium. Scr. Mater. 46, 419 (2002).
A. Rohatgi, K.S. Vecchio, and G.T. Gray: The influence of stacking fault energy on the mechanical behavior of Cu and Cu–Al alloys: Deformation twinning, work hardening, and dynamic recovery. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32, 135 (2001).
Y.F. Shen, L. Lu, Q.H. Lu, Z.H. Jin, and K. Lu: Tensile properties of copper with nano-scale twins. Scr. Mater. 52, 989 (2005).
X. Zhang, A. Misra, H. Wang, M. Nastasi, J.D. Embury, T.E. Mitchell, R.G. Hoagland, and J.P. Hirth: Nanoscale-twinning-induced strengthening in austenitic stainless steel thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1096 (2004).
C. Pande, B. Rath, and M. Imam: Effect of annealing twins on Hall–Petch relation in polycrystalline materials. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 367, 171 (2004).
C.M. Hong, J. Shi, L.Y. Sheng, W.C. Cao, W.J. Hui, and H. Dong: Effects of hot-working parameters on microstructural evolution of high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Des. 32, 3711 (2011).
F.J. Humphreys: Quantitative metallography by electron backscattered diffraction. J. Microsc. 195, 170 (1999).
A.D. Schino and J.M. Kenny: Grain refinement strengthening of a micro-crystalline high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Lett. 57, 1830 (2003).
N.V. Malyar, J.S. Micha, G. Dehm, and C. Kirchlechner: Dislocation-twin boundary interaction in small scale Cu bi-crystals loaded in different crystallographic directions. Acta Mater. 129, 91 (2017).
X. Li, Y. Wei, L. Lu, K. Lu, and H. Gao: Dislocation nucleation governed softening and maximum strength in nano-twinned metals. Nature 464, 877 (2010).
J. Kacher, B.P. Eftink, B. Cui, and I.M. Robertson: Dislocation interactions with grain boundaries. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 18, 227 (2014).
K. Lu, L. Lu, and S. Suresh: Strengthening materials by engineering coherent internal boundaries at the nanoscale. Science 324, 349 (2009).
N.V. Malyar, J.S. Micha, G. Dehm, and C. Kirchlechner: Size effect in bi-crystalline micropillars with a penetrable high angle grain boundary. Acta Mater. 129, 312 (2017).
V. Gavriljuk, Y. Petrov, and B. Shanina: Effect of nitrogen on the electron structure and stacking fault energy in austenitic steels. Scripta Mater. 55, 537 (2006).
T. Yonezawa, K. Suzuki, S. Ooki, and A. Hashimoto: The effect of chemical composition and heat treatment conditions on stacking fault energy for Fe–Cr–Ni austenitic stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44, 5884 (2013).
M. Polcarová, J. Gemperlová, A. Jacques, J. Brádler, and A. George: Synchrotron radiation topographic study of slip transfer across grain boundaries in Fe–Si bicrystals. Opt. Eng. 39, 4440 (2006).
P.J. Imrich, C. Kirchlechner, and G. Dehm: Influence of inclined twin boundaries on the deformation behavior of Cu micropillars. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 642, 65 (2015).
Z.H. Jin, P. Gumbsch, K. Albe, E. Ma, K. Lu, H. Gleiter, and H. Hahn: Interactions between non-screw lattice dislocations and coherent twin boundaries in face-centered cubic metals. Acta Mater. 56, 1126 (2008).
V. Randle: Mechanism of twinning-induced grain boundary engineering in low stacking-fault energy materials. Acta Mater. 47, 4187 (1999).
T. Watanabe: The importance of grain boundary character distribution (GBCD) to recrystallization, grain growth and texture. Scripta Metall. Mater. 27, 1497 (1992).
P.J. Imrich, C. Kirchlechner, C. Motz, and G. Dehm: Differences in deformation behavior of bicrystalline Cu micropillars containing a twin boundary or a large-angle grain boundary. Acta Mater. 73, 240 (2014).
B. Weiss and R. Stickler: Phase instabilities during high temperature exposure of 316 austenitic stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 3, 851 (1972).
M.H. Lewis and B. Hattersley: Precipitation of M23C6 in austenitic steels. Acta Metall. 13, 1159 (1965).
K. Kaneko, T. Fukunaga, K. Yamada, N. Nakada, M. Kikuchi, Z. Saghi, J.S. Barnard, and P.A. Midgley: Formation of M23C6-type precipitates and chromium-depleted zones in austenite stainless steel. Scr. Mater. 65, 509 (2011).
B. Sasmal: Formation of lamellar M23C6 on and near twin boundaries in austenitic stainless steels. Bull. Mater. Sci. 6, 617 (1984).
S. Mahajan, C. Pande, M. Imam, and B. Rath: Formation of annealing twins in fcc crystals. Acta Mater. 45, 2633 (1997).
E.A. Trillo and L.E. Murr: A TEM investigation of M23C6 carbide precipitation behaviour on varying grain boundary misorientations in 304 stainless steels. J. Mater. Sci. 33, 1263 (1998).
N. Li, J. Wang, A. Misra, X. Zhang, J.Y. Huang, and J.P. Hirth: Twinning dislocation multiplication at a coherent twin boundary. Acta Mater. 59, 5989 (2011).
D. Hull and D.J. Bacon: Introduction to Dislocations, 4th ed. (Butterworth-Heinemann Publications, Oxford, Great Britain, 2001); p. 157.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support from Project of Science and Technology Plan of Hebei Province (No. 15211007D). The authors are also appreciative of the facilities and assistance provided by the Electron Microscope Unit at the HBIS research institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, S., Sun, Z., Xu, Z. et al. Effects of twins and precipitates at twin boundaries on Hall–Petch relation in high nitrogen stainless steel. Journal of Materials Research 33, 1764–1772 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.138
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.138